Tài liệu WCDMA technology and FOMA installation plan pdf
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (246.33 KB, 20 trang )
W-CDMA technology
and FOMA installation plan
3
rd
September, 2002
Network planning Dept.
NTT DoCoMo
2
Today’s Items
Principle of CDMA
- Frequency allocation
- Principle of DS-CDMA
- Transmit power control
Basic W-CDMA Transmission Technologies
- Two-layer spreading code assignment
- Inter-BS asynchronous mode
Characteristics of W-CDMA
- Statistical Multiplexing effect
- MS stand-by time
- Coherent RAKE reception (RAKE time diversity)
3G Roll Out Plan
- FOMA service content
- 3G Roll out plan
3
In case of 3 cell repetition
Frequency Allocation
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
1
f
2
f
2
f
3
f
1
f
1
f
3
f
2
f
1
f
3
f
1
f
3
f
2
f
2
f
1
f
3
f
3
f
2
f
3
f
2
FDMA / TDMA CDMA
Same frequency in all area.
Take care of frequency allocation.
4
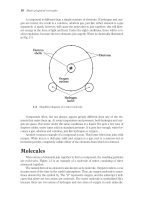
Principal Diagram
Frequency
Synthesizer
Channel
Coding
Data
Modulation
Spreading
Code
~
Spreading
~
Filter
Data
Demodulation
Channel
Decoding
Spreading
Code
Frequency
Synthesizer
Despreading
W
B(5MHz)
B(5MHz)
W
W
SF (spreading factor)=
Symbol rate of transmitted data
Chip rate of spread data
5
Principal Diagram
(Waveform of spreading codes in DS-CDMA)
1
-1
1 1 1
1
-1
1
-1
1
-1
1
-1
1 -1
-1
1
-1
1 1
-1-1-1-1
1 1
0
-2
0 0 0
2 2
-2
1
-1
1
-1
1
-1
1
-1
1
-1
1 1 1
Integrate
& dump
User 1
User 2
Transmitted data
sequence
Spreading code
Spreading code
Composite signal
Spreading code
Recovered transmitted data
sequence for user 1
receiver User 1
Integration over the symbol length to recover
6
despreading
despreading
Power control
Transmit Power Control
MS
MS
MS
MS
Near – far problem
Node B
Node B
TPC
is essential
Minimize
the Tx power
Increase
the system capacity
7
SIR measurement
TPC bit
Target SIR
SIR
Up Link
Transmit power control
Closed loop transmit power control in the Uplink
Tslot
Transmit Power Control
Down Link
1dB step
8
Today’s Items
Principle of CDMA
- Frequency allocation
- Principle of DS-CDMA
- Transmit power control
Basic W-CDMA Transmission Technologies
- Two-layer spreading code assignment
- Inter-BS asynchronous mode
Characteristics of W-CDMA
- Statistical Multiplexing effect
- MS stand-by time
- Coherent RAKE reception (RAKE time diversity)
3G Roll Out Plan
- FOMA service content
- 3G Roll out plan
9
Two-layer Spreading Code Assignment
Scrambling Code
10m sec length
(38,400 chip)
Channelization Code
4 chip
|
512 chip
X
transmission data is spread by scrambling codes and channelization codes.
Extremely large number of scrambling code can be used.
Elimination of interference components
arising form multiple CH
Increase
the system capacity
10
How to use (1/2)
Down Link
Scrambling Code
Channelization
Code
Up Link
MS
(A)
Scrambling Code
MS
(B)
Node-B
Node-B
Channelization
Code
11
How to use (2/2)
Down Link Up Link
Scrambling Code -To identify cells.
-Code shall be assigned to
each cell.
-Number of Code ; 512
-Assignment work by
System Designer is required.
-To identify Users.
-Code shall be assigned to
each user.
-Number of Code ; 2
24
-Assignment work by
System Designer is not
required.
Channelization Code -To identify the channels to
be used in a cell.
-Code shall be assigned to
each user.
-To identify the channels
to be used in a user.
-Code shall be assigned to
each channel.
Summary
12
Inter-BS Asynchronous mode (1/2)
Code Assignment in Downlink
-comparison between Asynchronous and Synchronous at inter-cell
Cell-A
Cell-B
Cell-C
S
c
r
a
m
b
l
i
n
g
C
o
d
e
C
h
a
n
n
e
l
i
z
a
t
i
o
n
C
o
d
e
A set of Orthogonal Multi-SF Code
Inter-cell Asynchronous
Cell-A
Cell-B
Cell-C
Time Shift
Time Shift
S
c
r
a
m
b
l
i
n
g
C
o
d
e
C
h
a
n
n
e
l
i
z
a
t
i
o
n
C
o
d
e
GPS
GPS
GPS
GPS
Outer Timing
Source
Inter-cell Synchronous
13
Benefit of Asynchronous
-
No need Outer Timing Source.
-
Flexibly implement in-door service in code planning.
-
Available to assign the same channelization
code in each cell.
- In Downlink, easy to assign scrambling code
because of many code available as 512.
Inter-BS Asynchronous mode (2/2)
14
Today’s Items
Principle of CDMA
- Frequency allocation
- Principle of DS-CDMA
- Transmit power control
Basic W-CDMA Transmission Technologies
- Two-layer spreading code assignment
- Inter-BS asynchronous mode
Characteristics of W-CDMA
- Statistical Multiplexing effect
- MS stand-by time
- Coherent RAKE reception (RAKE time diversity)
3G Roll Out Plan
- FOMA service content
- 3G Roll out plan
15
Statistical Multiplexing effect N/c
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
0
50
100
150
200
10%
1%
Outage=0.1%
Voice Activity=0.4
Capacity C
User #1
User #2
User #3
User #4
User #5
User #6
User #7
Active C user OK!
(C+1)user
Statistical Multiplexing Effect
16
Rx.OFF
Rx. OFF
ON
PCH PCH
Low bit-rate
common
control
channel
MS Stand-by Time
High bit-rate
common
control
channel
ON
ON
PCH
PCH
ON
Wideband accelerates the bit rate in the control channel,
And make it possible to reduce the rate of intermittent reception.
17
Node B
Coherent RAKE Reception (RAKE time diversity)
Coherent Rake
combining
Delay time
Narrow-band received signal
MS
Multi-pass
Wide-band received signal
Power
Estimation
filter
Channel
decoder
Recovered
data
Rake combiner
Radio transmitted environment
in urban area
Wide-band High resolution
High efficiency
of Rake combiner
18
7.68Mcps
1
µ
s
Delay profile
19
Node B1
Selection
combining
Site Diversity
Quality=5
Quality=10
MS
Node B2 Node B1 Node B2
MS
Replica
generating
Up Link Down Link
RNC RNC
20
Site Diversity ( Field trial )
Added Akasaka-site
Delete Aoyama-site
0
20
40
60
80
RSSI (MS) [dBμ]
Akasaka-site
Aoyama-site
0
5
10
15
20
E
b
/I
0
(BTS) [dB]
time
time