Lecture supply chain management chapter 3 sourcing and procurement
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (8.72 MB, 46 trang )
1/14/20
CHAPTER 3: SOURCING AND PROCUREMENT
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
LOGO
Contents
1
vIntroduction (Definitions, function)
2
vSourcing
3
vSourcing process Steps
4
vOutsourcing
5
vCase Studies
LOGO
1
1/14/20
Course book and support materials
LOGO
vAlan Harrison and et. (2014), Logistics
management and strategy competing through the
supply chain (fifth edition), Pearson, (course book)
chapter 9-pp.353-387
vArnold J.R. Tony et al. (2008), Introduction to
materials management (sixth edition), Pearson,
chapter 7, pp.191-215
vMichael Hugos (2003), Essentials of Supply Chain
Management, John Wiley and Sons Inc. chapter 2:
pp.43-76
Learning Objectives
LOGO
vGain the concept of sourcing, purchasing
and procurement
vApply the principles of the drivers of
procurement value
vUse the procurement core-processes
vApproach the management of the supply
base
2
1/14/20
Terminologies
LOGO
1. Purchasing
2. Procurement
3. Sourcing
4. Vendor
5. Supplier relationship management (SRM)
Procurement vs. purchasing
LOGO
vProcurement:
vSourcing:
vPurchasing:
vSource: Douglas M. Lambert et al (2001):
Strategic logistics management. McGraw-Hill
3
1/14/20
LOGO
1. Definition
vPurchasing: is the function of procuring
materials,
supplies,
and
services,
maintaining purchase order priorities,
managing supplier relationships, and
ensuring high levels of performance to
achieve quality, delivery and cost
objectives
Categories of purchasing
No
1
Categories
Resale
2
Conversion
3
MRO support
LOGO
Industries
Distributors
Retailers
Wholesalers
Manufacturers
Channel
Postponement
All Organization
4
1/14/20
Detailed Purchasing Responsibilities
LOGO
vProvide an uninterrupted flow of materials
and services
vPurchasing products competitively
vKeeping inventory investment to a minimum
vProviding consistent, quality purchased
materials and services
vDeveloping the supplier base
vDeveloping people resources and
information tools for productivity optimization
Purchasing objectives
LOGO
Some basic functions:
Determining purchasing specifications: right
quality, right quantity, and right delivery (time and
place).
- Selecting supplier (right source)
- Negotiating terms and conditions of purchase (right
price)
- Issuing and administration of purchase orders.
5
1/14/20
Definition of sourcing
LOGO
vThe body of integrated activities that
focuses on the purchase of materials,
supplies, and services needed to reach
the firm’s strategic goals. In a narrow
sense, sourcing describes the process of
buying, in a broader context, sourcing
involves determining the need, selecting
the supplier, arriving at the appropriate
price, terms, and conditions, drafting the
contract, and growing mutually beneficial
supplier relationships
Definition of procurement
LOGO
vProcurement is the process of getting the
goods and/or services your company
needs to fulfill its business model. Some of
the tasks involved in procurement include
developing standards of quality, financing
purchases, negotiating price, buying
goods, inventory control and disposal of
waste products like packaging.
6
1/14/20
Function of Procurement
LOGO
vFive main activity
categories:
§ Purchasing
§ Consumption
management
§ Vendor Selection
§ Contract Negotiation
§ Contract
Management
LOGO
7
1/14/20
LOGO
2. Sourcing
LOGO
Sourcing strategy in Supply chain
The role and the importance of sourcing
Viewpoints and development process of SM
Sourcing Strategy
Basic factors to determine sourcing strategy
Outsourcing in Supply chain
Definition, advantages and risks
Basic factors to make outsource decision
Partner choice process
Logistics service outsource
8
1/14/20
Strategic Sourcing
LOGO
vA comprehensive approach for locating
and sourcing key material suppliers, which
often includes the business process of
analyzing total spend for material spend
categories. There is a focus on the
development of long-term relationships
with trading partners who can help the
purchaser meet profitability and customer
satisfaction goals.
Strategic sourcing Objectives
LOGO
vEstablish close, collaborative relationships with
key suppliers
vEnsure reliable quality and delivery of materials
vReduce supply risks
vEstablish a smaller, more flexible, more
responsive supplier base
vClosely integrate supplier input to product
development and innovation
vReduce external spending
vReduce transaction costs
9
1/14/20
Why sourcing is very important? LOGO
Suitable cost cutting centre
Ensuring smooth and continuous production
line and business
Intra-corporate interaction center
“Door” role
Supp
- liers
Sourcing
R&D, Design
Manufacture
Finance
Quality
management
Custo
-mers
Why sourcing is very important? LOGO
Industries
Percent of material
cost in cost of good
sold
Average
Petrochemical industry
Transport
Car manufacture
Wood industry
Food processing
Paper industry
Electronic equipment
PC, Electronic device
10
1/14/20
LOGO
DEVELOPMENT PROCESS OF SOURCING MANAGEMENT
• Meet
the
highest
requirement
of
customers
with
the
lowest cost
• Relationship Building
• Lowest Total Cost
• Lowest Unit cost
LOGO
DEVELOPMENT PROCESS OF SOURCING MANAGEMENT
Purchasing (Operational)
Meet the requirement of Production and business
department
Finding the lowest price source
Order and giving detailed product requirements
Implement contracts and solve problems
Statistics and follow the data
Deploy and control
Easy to change suppliers
Support from IT
11
1/14/20
LOGO
DEVELOPMENT PROCESS OF SOURCING MANAGEMENT
Procurement (Tactical)
• Conduct in-depth researches
• Material searching and
having substitute plan
• Finding the lowest total cost:
• Procurement, inventory,
transport cost.
• Choosing, negotiating with suppliers
• Ensuring the continuous, regular sources
• Building the relationship with suppliers
LOGO
DEVELOPMENT PROCESS OF SOURCING MANAGEMENT
Supply Chain Management
(Strategic)
• Building close and positive relationships
with suppliers
• Finding the opportunities and threats in the
sourcing market
• Participate actively in the strategic
planning process
• Finding ways to enhance value from
supply relationships:
• Suppliers join in design,
manufacturing process.
• Reduce the complication in
sourcing
• Sharing information and
opportunities
12
1/14/20
LOGO
Sourcing strategy
Depend on the number of suppliers
Multiple suppliers strategy
Create competitive pressure on
among suppliers
Few suppliers strategy
Some
strategies in
sourcing
Long-term partners relationship development
to meet the requirements of end users
Customers – Suppliers Alliance strategy (Keiretsu)
Suppliers become an integrated part of the
enterprise’s alliance
Vertical Integration
Have the ownership of supply source,
Strict control
Sourcing strategy
LOGO
Multiple suppliers
strategy
- Many sources for a product
- Competitive environment, low
price, good service, low risk
- Focus on price, short-term benefit
- Opposition relations, less open
- Variety of product
- Delivery at the warehouse
- Single transaction
13
1/14/20
Sourcing strategy
LOGO
Few suppliers
strategy
- Some sources for a product
- Collaboration, long term and
stable relationship.
- Economies of scale
- Selective supply contracts
- Just in time (regular delivery)
- Small lot for each deliver
- Controlling the material at the
supplier’s sites
Sourcing strategy
LOGO
Customers –
Suppliers Alliance
strategy (Keiretsu)
- Exclusive supply contract
- Same objectives and must be
identified clearly.
- System integration
- Dependent and adaptive
- Investment and benefit sharing
- Discuss and interact regularly
Supplier plays a important role in the success of the
company, takes part in from the first stage (design the
products)
14
1/14/20
LOGO
Sourcing strategy
Number of
Suppliers and the
relationship level
Transactional
relationship
Operational
relationship
Multiple suppliers
ü Short-term relationship
ü Focus on cost, price
ü Extended arm
Tactical
relationship
Selective suppliers
Strategic
Alliances
Few Suppliers
One Supplier
ü Long-term relationship
ü Sticking, benefits for
both sides
ü Planning together
ü Senior managers
attended
ü Open communication
LOGO
15
1/14/20
LOGO
Sourcing strategy
Selecting
suppliers
Request for
quotation
Detail
evaluating
Site
visit
Potential
suppliers
list
Supply
contract
RELATIONSHIP DEVELOPMENT WITH SUPPLIERS
LOGO
In order to manufacture famous brand all over the world,
you need have an idea, unique design, qualitative
specifications. However, above all you must have good
suppliers
-
Right quality
Right quantity
Right time
Good attitude
Product design and
customer service
cooperation.
Increase value and facilitate for
the manufacturing process
16
1/14/20
RELATIONSHIP DEVELOPMENT WITH SUPPLIERS
Competitive
market
Suppliers
structure
Sourcing
Strategy
Suppliers – customers
relationship
Long-terms relationship
Supplier involvement
Team work between two
parties
IT
•
•
•
Logistics
integration
LOGO
Suppliers
success
Company
success
Interactive and sustainable relationship
RELATIONSHIP DEVELOPMENT WITH SUPPLIERS
LOGO
17
1/14/20
Factors to determine sourcing strategy
Which type of
sourcing strategies
and which
relationship are
suitable
LOGO
Depend on many
factors
Type of material need to buy
Risk level of buying decision
Power and attitude of suppliers
Procurement division capability
Ability to maintain a stable supply
without increasing risk
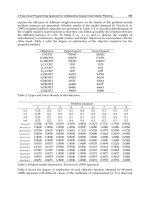
KRALJIC Matrix
Factors to determine sourcing strategy
•
Classify the materials
need to buy
•
•
•
The important role of
determination
Raw material cost/total
cost
Value added contribution
Profit contribution
•
•
•
•
LOGO
Exclusive level
Complicated level
Speed of technology
development
Penetration barriers
18
1/14/20
Factors to determine sourcing strategy
High
Profit impact
Classify the
materials which
needed
Low
Leverage Items
Strategic Items
Low risk, high value
Normal material
Competitive source
Logistics service
ü
ü
ü
ü
LOGO
ü
ü
ü
ü
High risk, high value
Availability
Essential materials
Equipment, machine
Non-critical Items
Bottleneck Items
ü Low risk, high value
ü Availability and easy
to substitute
ü Indirect materials
ü Stationery
ü
ü
ü
ü
High risk, low value
Technical materials
Rare
Difficult to substitute
Supply risk
Factors to determine sourcing strategy
Earthquake
Tsunami
Nuclear incident
Profit impact
High
Stalling the global Low
automotive industry
Leverage Items
LOGO
Strategic Items
ü Tire
ü Trunk
ü Chassis
ü Assembly line
ü Engine
ü Braking system
Non-critical Items
ü Mirror
ü Battery
ü Screws
Bottleneck Items
ü Air bagel
ü Electronic chip
ü The battery
High
Low
Supply risk
19
1/14/20
Factors to determine sourcing strategy
ü Seed
ü Foods
ü Veterinary
Medicine
Profit impact
High
Low
Leverage Items
Strategic Items
ü Using multiple
suppliers
ü Exploit the call option
ü Identify the scale and
optimized price
ü Senior decision
ü Building alliances
ü Global supplier
Bottleneck Items
Non-critical Items
ü Local Suppliers
ü Surf the price
ü Simple and
automatic process
ü Risk prevention plan
ü Supplier’s reliability
ü Cooperation
relationship
ü Accepting high price if
needed
Low
Supply risk
Factors to determine sourcing strategy
Multiple Suppliers
-
Many sources for a product
Competitive environment, low
price, good service, low risk
Price focus, short-term benefit
Opposite relationship, less open.
Variety products
Delivered at warehouse
LOGO
High
LOGO
Few Suppliers
-
One or few sources for a product
Cooperation relationship, stable, long –
terms
Take the advantage of economies of scale.
Selective sourcing contract
Regular delivery
Small shipment for one delivery
Delivered at the place which uses material
- The characteristics of sourcing market
- The capability of suppliers
- Procurement and sourcing opinions of
enterprises
20