NSP NETWORK SERVICES PLATFORM NETWORK RESOURCE CONTROLLER - FLOW (NRC-F) NETWORK RESOURCE CONTROLLER - PACKET (NRC-P) NETWORK RESOURCE CONTROLLER - TRANSPORT (NRC-T) NETWORK RESOURCE CONTROLLER - CROSS DOMAIN (NRC-X) NETWORK SERVICES DIRECTOR RELEASE 17 1
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (2.04 MB, 140 trang )
NSP
Network Services Platform
Network Resource Controller - Flow (NRC-F)
Network Resource Controller - Packet (NRC-P)
Network Resource Controller - Transport (NRC-T)
Network Resource Controller - Cross domain (NRC-X)
Network Services Director
Release 17.12
User Guide
3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA
Issue 1
December 2017
Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential
Use pursuant to applicable agreements
NSD | NRC
Legal notice
Nokia is a registered trademark of Nokia Corporation. Other products and company names mentioned herein may be trademarks or
tradenames of their respective owners.
The information presented is subject to change without notice. No responsibility is assumed for inaccuracies contained herein.
© 2017 Nokia.
Contains proprietary/trade secret information which is the property of Nokia and must not be made available to, or copied or used by
anyone outside Nokia without its written authorization.
Not to be used or disclosed except in accordance with applicable agreements.
Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential Release 17.12
Use pursuant to applicable agreements December 2017
2 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA Issue 1
NSD | NRC
Contents
About this document............................................................................................................................................7
Part I: Getting started ...........................................................................................................................................9
1 What's new?..................................................................................................................................................11
1.1 What's new in NSP Release 17 ........................................................................................................11
2 NSD and NRC modules................................................................................................................................17
2.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................17
2.2 NRC-F ...............................................................................................................................................21
2.3 NRC-P...............................................................................................................................................25
2.4 NRC-T ...............................................................................................................................................32
2.5 NRC-X...............................................................................................................................................38
2.6 NSD...................................................................................................................................................40
3 Applications overview .................................................................................................................................45
3.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................45
3.2 Service Fulfillment.............................................................................................................................45
3.3 To create physical links between ports..............................................................................................47
3.4 Policy Management...........................................................................................................................48
3.5 Task Scheduler..................................................................................................................................48
3.6 Autonomous System Optimizer.........................................................................................................48
3.7 To steer flows to next hops for autonomous systems .......................................................................49
3.8 To steer flows to next hops for VIP customers ..................................................................................49
3.9 Latency Steering Optimizer...............................................................................................................51
3.10 To add an NE point............................................................................................................................52
3.11 To add or modify a destination site....................................................................................................52
3.12 To modify an internal connection.......................................................................................................54
3.13 To add or modify an external connection ..........................................................................................54
3.14 To configure Latency optimization settings .......................................................................................55
3.15 Traffic Steering Controller .................................................................................................................57
3.16 To add a flow .....................................................................................................................................57
3.17 IP/MPLS Optimization .......................................................................................................................58
3.18 To find a path.....................................................................................................................................58
3.19 To create PCE-initiated LSPs............................................................................................................59
3.20 To place a link set into maintenance mode .......................................................................................60
3.21 Cross Domain Coordination ..............................................................................................................62
Release 17.12 Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential
December 2017 Use pursuant to applicable agreements
Issue 1 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA 3
NSD | NRC
3.22 To configure the network map ...........................................................................................................62
3.23 To import existing cross domain links................................................................................................63
3.24 To automatically discover cross domain links ...................................................................................63
3.25 To manually create cross domain links .............................................................................................64
3.26 To upload or withdraw optical SRLG and/or latency .........................................................................65
3.27 To place link sets into maintenance mode ........................................................................................66
4 Tenants and roles.........................................................................................................................................67
4.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................67
4.2 To view services associated with a tenant ........................................................................................69
4.3 To manage tenants associated with a port........................................................................................69
Part II: Services and Templates.........................................................................................................................71
5 Services ........................................................................................................................................................73
Service description ......................................................................................................................................73
5.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................73
5.2 Object life cycle .................................................................................................................................73
5.3 Service CAC......................................................................................................................................74
5.4 E-Line services..................................................................................................................................75
5.5 C-Line services .................................................................................................................................80
5.6 E-LAN services .................................................................................................................................81
5.7 L3 VPN services................................................................................................................................82
5.8 LAG service.......................................................................................................................................84
5.9 OCh service ......................................................................................................................................84
5.10 ODU service......................................................................................................................................85
5.11 Other services ...................................................................................................................................85
Service provisioning....................................................................................................................................87
5.12 To enable service CAC......................................................................................................................87
5.13 To provision E-LAN services .............................................................................................................87
5.14 To provision E-Line services .............................................................................................................91
5.15 To provision C-Line services .............................................................................................................94
5.16 To provision L3 VPN services ...........................................................................................................97
5.17 To provision LAG services...............................................................................................................100
5.18 To provision ODU services..............................................................................................................103
5.19 To provision OCh services ..............................................................................................................105
Service management .................................................................................................................................109
5.20 Service management description....................................................................................................109
5.21 To view and edit a service ...............................................................................................................109
Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential Release 17.12
Use pursuant to applicable agreements December 2017
4 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA Issue 1
NSD | NRC
5.22 To view all services and edit a service ............................................................................................110
5.23 To manage service tunnel bandwidth ..............................................................................................111
6 Templates and policies ..............................................................................................................................113
6.1 Introduction......................................................................................................................................113
6.2 Service templates............................................................................................................................113
6.3 Service policies ...............................................................................................................................114
6.4 IP/MPLS policies .............................................................................................................................115
6.5 To create an E-Line service template ..............................................................................................116
6.6 To create an E-LAN service template..............................................................................................118
6.7 To create a C-Line service template................................................................................................119
6.8 To create an OCh service template.................................................................................................120
6.9 To create an ODU service template ................................................................................................121
6.10 To create a LAG service template ...................................................................................................122
6.11 To create an L3 VPN service template............................................................................................123
6.12 To create an Endpoint QoS template ..............................................................................................124
6.13 To modify the RD/RT Range policy .................................................................................................125
6.14 To modify the Tunnel Creation template..........................................................................................127
6.15 To create a Tunnel Selection policy.................................................................................................128
6.16 To create a Steering Parameter ......................................................................................................130
6.17 To create a Router ID Mapping policy .............................................................................................130
6.18 To create a Path Profile policy.........................................................................................................131
7 Bandwidth modification ............................................................................................................................133
7.1 Bandwidth modification scheduling .................................................................................................133
7.2 To schedule bandwidth modification tasks ......................................................................................133
Glossary ............................................................................................................................................................135
Release 17.12 Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential
December 2017 Use pursuant to applicable agreements
Issue 1 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA 5
NSD | NRC
List of tables
Table 2-1 Supported optical configurations....................................................................................................34
Table 2-2 Card compatibility with OTN/OCS applications..............................................................................36
Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential Release 17.12
Use pursuant to applicable agreements December 2017
6 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA Issue 1
NSD | NRC
About this document
Purpose
The NSP NSD and NRC User Guide serves as an introduction to the NSD and NRC modules of the
NSP, and provides detailed information regarding their operation.
Document support
Customer documentation and product support URLs:
• Customer Documentation Welcome Page
• Technical support
How to comment
Documentation feedback
• Documentation Feedback
Release 17.12 Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential
December 2017 Use pursuant to applicable agreements
Issue 1 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA 7
NSD | NRC
Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential Release 17.12
Use pursuant to applicable agreements December 2017
8 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA Issue 1
NSD | NRC
Part I: Getting started
Overview
Purpose
This volume serves as an introduction to the NSD and NRC modules of the NSP, and explains their
function within the broader solution.
Contents
Chapter 1, What's new? 11
Chapter 2, NSD and NRC modules 17
Chapter 3, Applications overview 45
Chapter 4, Tenants and roles 67
Release 17.12 Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential
December 2017 Use pursuant to applicable agreements
Issue 1 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA 9
NSD | NRC
Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential Release 17.12
Use pursuant to applicable agreements December 2017
10 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA Issue 1
NSD | NRC What's new?
1 What's new?
1.1 What's new in NSP Release 17
1.1.1 Introduction
This chapter highlights new features for NSP Release 17 and provides pointers into the
documentation for more information. The NSP NSD and NRC Release Description provides
Committed feature lists for all of Release 17.
1.1.2 Maintenance releases
Some maintenance releases may not be listed in this section, either because no new features are
introduced or because the introduced features do not require documentation.
1.1.3 What's new in NSP Release 17.12
The following table lists the features added in NSP Release 17.12 and described in the NSD and
NRC customer documentation.
Key Summary See
NSD features
NSPF-114889 Service save — support for 3.2.2 “Service configuration without
service creation without deployment” (p. 46)
NSPF-126706 deployment (beta quality) —
Support of service creation on
NRC-F features brownfield SDPs and LSPs of 3.9 “Latency Steering Optimizer” (p. 51)
NSPF-112618 any transport type (beta quality)
NRC-P features 3.20 “To place a link set into
NSPF-113210 Latency Steering Optimizer maintenance mode” (p. 60)
(phase 1)
2.4.5 “Supported optical configurations”
IP link maintenance mode (p. 34)
2.4.6 “OTN/OCS applications
NRC-T features 11DPM12 and 11DPM8/ compatibility” (p. 35)
NSPF-113791 11DPM4M
Release 17.12 Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential
December 2017 Use pursuant to applicable agreements
Issue 1 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA 11
What's new in NSP Release 17 NSD | NRC
Key Summary See
NSPF-113864 Service Provisioning API: 2.4.8 “Physical layer disjoint path with
Physical Layer Disjoint Path SRLG constraints” (p. 37)
(SRLG Constraints)- L0/L1 MRN
NSPF-123215 Co-related optics services in a 2.4.9 “SDN-controlled L0 reversion for
group-auto reversion control collocated OCh services” (p. 38)
NSPF-125864 Cross-navigation between the NSP Optical User Guide
optical and the IP/MPLS layers
(Bottom-Up)
NSPF-126383 PSS24x and PSS8x support 2.4.5 “Supported optical configurations”
(p. 34)
2.4.6 “OTN/OCS applications
compatibility” (p. 35)
NRC-X features
NOTE: The NRC-X module and the corresponding Cross Domain Coordination application are
beta quality in Release 17.12.
NSPF-114724 Multi-layer, 2D topology map 3.22 “To configure the network map”
(p. 62)
NSPF-122922 IP/optical correlation 3.21 “Cross Domain Coordination”
enhancements (p. 62)
NSPF-122924 Coordinated maintenance 3.27 “To place link sets into
actions maintenance mode” (p. 66)
NSPF-124359 Bottom-up, multi-layer topology 3.22 “To configure the network map”
navigation (p. 62)
NSPF-126865 Landing page for Cross Domain Cross Domain Coordination application
Coordination application
1.1.4 What's new in NSP Release 17.9
The following table lists the features added in NSP Release 17.9 and described in the NSD and
NRC customer documentation.
Key Summary See
5.6.2 “EVPN-based E-LAN service” (p. 81)
NSD features EVPN-based E-LAN Service 5.11.1 “E-Access services” (p. 85)
Provisioning (EVPN-MPLS)
NSPF- Half-service creation for
114762 SDP-based services
(E-Access)
NSPF-
114779
Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential Release 17.12
Use pursuant to applicable agreements December 2017
12 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA Issue 1
NSD | NRC What's new in NSP Release 17
Key Summary See
Chapter 4, “Tenants and roles”
NSPF- NSD tenant enhancements —
114782 Customer ID and template 6.15 “To create a Tunnel Selection policy”
assignment (p. 128)
5.11.2 “Services on SDPs with multiple
NSPF- Full support of PCC-initiated loopback IP addresses” (p. 86)
114811 LSPs from NSD NSP NSD and NRC Release Description
NSPF- Selecting SDP with multiple “Cards supporting optical E-Line services”
114844 loopback IP addresses (p. 77)
NSPF- Verification of NSD features 5.4.5 “EVPN-based E-Line service” (p. 79)
114847 when VSR-NRC populates the
IGP topology 2.2.3 “OpenFlow controller rules” (p. 24)
NSPF- Support of E-Line service on Autonomous System Optimizer application
114852 1830 PSS nodes with
endpoints on L2 cards NSP Developer portal
103SCEC and 11OCEC
“Integrated multi-domain path computation”
NSPF- EVPN-based E-Line service (p. 31)
114874 provisioning (EVPN-VPWS) 2.3.9 “Northbound interface for topology
retrieval” (p. 32)
NRC-F features 2.3.5 “Anycast and loopback for LSPs”
(p. 29)
NSPF- Support for OpenFlow
112628 Controller SR capabilities 2.4.6 “OTN/OCS applications compatibility”
(p. 35)
NSPF- AS-based optimization NSP Developer portal
112644 topology enhancements
NRC-P features
NSPF- LSP path NBI REST API
113198
NSPF- Support path computation for
113199 multiple, integrated domains
NSPF- Topology NBI modifications
113202
NSPF- Support Anycast and loopback
113203 for LSPs
NRC-T features
NSPF- OCS PSS 36 and PSS 64
118569 configuration support
NSPF- SRLG and latency on physical
121419 links
Release 17.12 Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential
December 2017 Use pursuant to applicable agreements
Issue 1 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA 13
What's new in NSP Release 17 NSD | NRC
Key Summary See
NRC-X features
NOTE: The NRC-X module and the corresponding Cross Domain Coordination application are
beta quality in Release 17.9.
NSPF- Inter-layer links discovery 2.5.3 “Inter-layer links discovery” (p. 39)
114716
NSPF- New Cross Domain Cross Domain Coordination application
114720 Coordination application
NSPF- Optically disjoint IP routing 2.5.4 “Optically disjoint IP routing” (p. 40)
114721
NSPF- IP routing based on optical 2.5.5 “IP routing based on optical latency”
114726 latency (p. 40)
NSPF- NRC-X base platform 2.5 “NRC-X” (p. 38)
114731
NSPF- NRC-X license NSP NSD and NRC Release Description
122839
1.1.5 What's new in NSP Release 17.6
The following table lists the features added in NSP Release 17.6 and described in the NSD and
NRC customer documentation.
Key Summary See
NSD features Provide L3 VPN services on 5.7.3 “L3 VPN services on 9500 MPR NEs”
9500 MPR NEs (p. 83)
NSPF- L2 E-Line services over 5.4.4 “Optical E-line service over Ethernet rings
114819 ERP protection with L2 with ERP” (p. 78)
cards on 1830 PSS NEs
NSPF-
114877
1.1.6 What's new in NSP Release 17.3
The table below lists the features added in NSP Release 17 and described in NSD and NRC
customer documentation.
Key Summary See
NRC-F features 3.8 “To steer flows to next hops for VIP
customers” (p. 49)
NSP-1275 VIP-based flow steering
NRC-P features
Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential Release 17.12
Use pursuant to applicable agreements December 2017
14 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA Issue 1
NSD | NRC What's new in NSP Release 17
Key Summary See
“PCE-initiated LSPs” (p. 29)
NSP-1112 Support for PCE-initiated 3.19 “To create PCE-initiated LSPs” (p. 59)
LSPs 2.3.8 “Multi-domain path computation” (p. 31)
NSP-1116 Support for multiple 6.4.1 “Router ID Mapping templates” (p. 115)
NSP-2049 integrated domains path
computation IP/MPLS Optimization application
Multi-instance topology 5.19 “To provision OCh services” (p. 105)
support for OSPF and ISIS
5.19 “To provision OCh services” (p. 105)
NSP-4230 Override profile routing for 5.19 “To provision OCh services” (p. 105)
delegated LSPs 5.18 “To provision ODU services” (p. 103)
5.18 “To provision ODU services” (p. 103)
NRC-T features
NSP NSD and NRC Release Description
NSP-707 1830 PSS 9.1 support: Flex
NSP-2327 Grid-related changes NSP NSD and NRC Release Description
Explicit routing 5.15 “To provision C-Line services” (p. 94)
6.7 “To create a C-Line service template”
NSP-3002 D5X500 support (p. 119)
5.4.2 “Multi-domain E-Line services” (p. 76)
NSP-3264 Support for Y-cable
NSP-4203 protected configurations 5.21 “To view and edit a service” (p. 109)
NSP-4704 Support for 200G line mode
of 260SCX2 6.11 “To create an L3 VPN service template”
NSD features OPSB with (p. 123)
NSP-1249 11QPEN4/11QPA4/OTU4 “PCC-initiated LSPs” (p. 115)
mode 260SCX2 6.15 “To create a Tunnel Selection policy”
(p. 128)
CPIPE support for NSD
NSP-2170 ELINE spans multi-domain
NSP-2243 with VLAN hand-off and
NSP-2646 MS-PW
NSP-2725
Cross-launch from NSD to
Service Supervision Web
App
Support of IP link latency
during service provisioning
Support of PCC-initiated
LSPs
Release 17.12 Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential
December 2017 Use pursuant to applicable agreements
Issue 1 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA 15
What's new in NSP Release 17 NSD | NRC
Key Summary See
NSP-2739 NSD and NRC Release Description
Enhance the NSD scale for
NSP-3268 resync and discovery by 5.23 “To manage service tunnel bandwidth”
making it multi-threaded (p. 111)
Enhancements to
brownfield LSP and SDP
Support
Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential Release 17.12
Use pursuant to applicable agreements December 2017
16 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA Issue 1
NSD | NRC NSD and NRC modules
2 NSD and NRC modules
2.1 Overview
2.1.1 Introduction
The NSD and NRC modules of the NSP form a carrier software-defined networking (SDN) platform
that unifies service automation with network optimization, allowing network operators to deliver on-
demand network services cost-effectively and with scalability. Using these modules, operator can
define, provision, and activate network services across networks that span multiple layers (Layer 0
to Layer 3), services, and infrastructures (physical and virtual), as well as equipment from multiple
vendors. The NSD and NRC modules are scalable, and based on standard protocols with multiple
APIs.
The NSD and NRC modules act as bridge between the IT and network worlds. Upstream, they
provide standard APIs, object models, and abstractions to IT OSS applications. Downstream, they
manage network complexity by translating simple service requests into commands that program
physical and virtual network elements. This is done automatically, across both IP and optical
boundaries, and across multiple network vendors.
The following NSP and NRC modules are available for deployment as part of NSP in this release:
• Network Resource Controller — Flow — flow-based traffic steering
• Network Resource Controller — Packet (NRC-P) — MPLS path computation
• Network Resource Controller — Transport (NRC-T) — Optical path computation
• Network Resource Controller — Cross Domain (NRC-X) — Multi-layer correlation and multi-
domain coordination
• Network Services Director (NSD) — multi-vendor service fulfillment
Note: The NRC-X module and the corresponding Cross Domain Coordination application are
beta quality in this release.
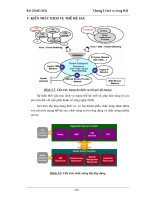
The following figure shows a typical NSP deployment on virtual machines, with all NSD and NRC
modules included:
Release 17.12 Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential
December 2017 Use pursuant to applicable agreements
Issue 1 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA 17
Overview NSD | NRC
Service automation
With the Network Services Director (NSD), OSS and IT applications are able to quickly
communicate their service requests using simplified, abstract APIs and object models. Operators
can also use policies to abstract their service placement intentions. For instance, a policy can be
used to map a service request to the network path with the lowest latency, a specific amount of
available bandwidth, and the least amount of congestion. If such a path is not available, the policy
can dictate mapping to a secondary path and switch to a suitable path when the desired conditions
have been met. If no suitable path is available, the policy can communicate this, or request a new
path to be computed by passing the associated parameters to the network optimization modules. To
complete service provisioning, the NSP handles the complex task of provisioning the operator's
multi-domain, multi-vendor network using SDN standards such as NetConf/Yang, OpenFlow,
PCE-P, and other protocols. In the case of legacy equipment, traditional mechanisms such as CLI
are used. This functionality is available from the Service Fulfillment application.
For more information, see 2.6 “NSD” (p. 40) and 2.4 “NRC-T” (p. 32).
Network optimization
The Network Resource Controller (NRC) modules centralize path computation and network
optimization in order to leverage a whole network view and make the best possible decision for
each request. For IP, this is done with a packet PCE. For Optical, this is done with a transport PCE.
Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential Release 17.12
Use pursuant to applicable agreements December 2017
18 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA Issue 1
NSD | NRC Overview
For hybrid IP/Optical network, this is done with hierarchical PCEs. The latter for the simultaneous
provisioning of services across IP and Optical networks. Centralized path computation elements are
opened up to application and policy control, and to specialized algorithms. For instance, path
computation can be enhanced to take link congestion into account. You can also make better use of
your network assets and keep SLAs high by using KPIs and metrics to trigger optimization policies.
You can also do all this in a multi-tenant way where each tenant – or in essence, each business unit
- has their own abstracted view of the network and their own policies for maintaining service quality
and assurance.
For more information, see:
• 2.2 “NRC-F” (p. 21)
• 2.3 “NRC-P” (p. 25)
• 2.5 “NRC-X” (p. 38)
External applications notifications
The NSD and NRC modules provide a base platform for asynchronous event notifications to
external applications, such as orchestrators. These notifications are transported using HTTP Server
Side Events (SSE) according to the IETF RESTCONF protocol specification. Notifications are
defined in the YANG modeling language and encoded in JSON format. This base platform is used
by the modules to realize different types of notifications.
Clients of the modules' northbound interface (NBI) receive notifications whenever the state of a
managed object changes. This simplifies synchronization with the modules, as periodic polling of
the REST API is avoided. Notifications are provided for the operational and administrative status of
services and endpoints.
Note: By default, a maximum of 10 users can be subscribed to these notifications. This
amount can be modified from the configuration file in the directory where the NSD and NRC
installer was extracted. See the NSP NSD and NRC Installation and Upgrade Guide for more
information.
2.1.2 Applications
The NSD and NRC modules also provide functionality using browser-based applications. Each of
these applications use the standard NSD and NRC REST security mechanisms for authentication
and authorization, so every request sent to the server contains the provided session key. All
applications are HTML5–based, and supported on the latest version of Google Chrome. Use the
following URL to access the NSP dashboard, from which you can launch all supported applications:
https://server
Where server is the hostname or IP address of your installed NSD and NRC server.
For more information about the individual applications, see Chapter 3, “Applications overview”.
Release 17.12 Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential
December 2017 Use pursuant to applicable agreements
Issue 1 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA 19
Overview NSD | NRC
2.1.3 NSD and NRC REST APIs
The NSD and NRC modules provide northbound RESTful APIs that expose a simplified view of the
network. This view is constructed from the internal model, which is stored in the Topology
Database. The APIs support queries, service creation requests, and many additional functions.
To view and interact with the APIs online, go to one of the following URLs:
• https://server:8543/sdn/doc
• https://server:8543/task-scheduler/doc
Where server is the hostname or IP address of your installed NSD and NRC server.
2.1.4 Additional components
The NSD and NRC modules rely on the following additional components to provide end-to-end
functionality:
• Topology Database — The Topology Database contains a representation of the network in the
form of a highly abstract, multi-layer graph. The graph is stored in a Neo4j database.
• Network Mediation — The Network Mediation component is responsible for populating the
Topology Database with the network information and for deployment of network configuration. It
is comprised of the generic plugin framework, as well as the mediation plugins that operate
inside these. Plugins may interact with the network through Element Manager Systems (EMS)
such as the NFM-P, and/or standard communication protocols such as PCEP, BGP-LS, or
OpenFlow. The NSD and NRC modules support the deployment of network tunnels, services,
and, potentially, tunnels.
• Service Connection Manager — The Service Connection Manager is responsible for finding
appropriate tunnels for services.
• Algorithm Framework — The Algorithm Framework is the component that provides a run time
environment for the invocation and execution of both routing and optimization algorithms.
• Network Deployment — The NSD and NRC modules support the deployment of network tunnels,
services, and, potentially, tunnels. This means that some plugins and mediation framework may
support the “push to the network” function that involves the mapping and conversion of the
Topology Database entities to the network objects.
• Security — Security is the component that handles sign-in, encryption, logging of operator
actions, and network events.
• Relational Database — A PostgreSQL database that contains all non-topological information
requiring persistence. This includes policies, templates, etc.
• Global Cache — The Global Cache enables the NSD and NRC modules to track resources
being used by the network, including the resources of services that originate from the NFM-P. In
order for the NSD to discover such services, they must have their “NSD-managed” flag enabled
within the NFM-P. Once this is done, the usage of VLAN IDs, L3 VPN Route Distinguishers (RD),
and L3 VPN Route Targets (RT) can be tracked across NFM-P/NSD managed networks. When
the NSD requests one of these resources, the Global Cache verifies their availability before
assignment. Only freed resources are considered available for usage. All services created using
the NSD will be validated for resource usage, and therefore will not infringe upon the resources
of existing services.
Nokia – Proprietary and Confidential Release 17.12
Use pursuant to applicable agreements December 2017
20 3HE-12072-AAAD-TQZZA Issue 1





![development with the force.com platform [electronic resource] building business applications in the cloud](https://media.store123doc.com/images/document/14/y/zs/medium_Qs04cLaWf8.jpg)
![microsoft silverlight 5 data and services cookbook [electronic resource] over 100 practical recipes for creating rich, data-driven, business applications in silverlight 5](https://media.store123doc.com/images/document/14/y/ev/medium_neP7R4h80c.jpg)