WebSphere Studio Application Developer Version 5 Programming Guide part 30 pdf
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (235.14 KB, 10 trang )
264 WebSphere Studio Application Developer Version 5 Programming Guide
The
jspsql.jar file contains the tags and
dbbeans.jar contains the actual
classes used to access the database.
Creating a JSP
We now create a TestTagLib.jsp file to use tag libraries. See “Working with
JSPs” on page 210 for details about creating a new JSP.
Open TestTagLib.jsp in Page Designer. You can use the JSP editor to insert the
database tags into your page when you are in the Design view. To be able to use
the custom tags from the database tag library, you first have to do two things:
Import the tag library into your Web application as described above.
Create the taglib directive in the JSP.
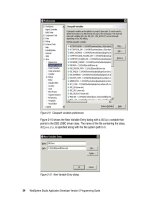
To insert the taglib directive, bring up the context menu on the page in the Design
view and select
Page Properties
. In the dialog shown select
JSP Tags
and
JSP
Directive - taglib
from the
Tag Type
drop-down menu (Figure 8-16).
Figure 8-16 Insert JSP taglib directive
Click
Add
to select the tag library to add, and the dialog shown in Figure 8-17 is
displayed.
Chapter 8. Developing Web applications with database access 265
Figure 8-17 Selecting a tag library
Click
Import
to locate the jspsql.jar file to import. The Import a Tag Library
dialog opens (Figure 8-18). Click
Browse
to locate the JAR file:
<wsadhome>\wstools\eclipse\plugins\com.ibm.etools.dbjars_5.0.1\jars\jspsql.jar
Figure 8-18 Importing a tag library
266 WebSphere Studio Application Developer Version 5 Programming Guide
Be sure to select
Add an alias URI
so that the tag library is added to the web.xml
file. The entry can be found on the References page.
Click
OK
to close the dialog. Now the tag library has been imported. Select the
jspsql
check box to add it to the JSP (Figure 8-19).
Figure 8-19 Select the jspsql tag library
Select
OK
twice to close the dialog. The following tag is inserted into your JSP:
<%@taglib uri="jspsql" prefix="dab"%>
The full TestTagLib.jsp is available in:
\sg246957\sampcode\dev-webdb
Chapter 8. Developing Web applications with database access 267
Building the JSP with custom tags
Now you can add tags to the JSP by selecting
JSP -> Insert Custom
. You should
see the following dialog (Figure 8-20).
Figure 8-20 Insert custom JSP tags
In the following example we create a JSP that displays a list of transaction
records. We show you some of the main tags that you would use to access the
database. The Application Developer online help contains descriptions for all the
tags that are available.
First, we have to create the connection to the database. To do this we use the
<dab:dataSourceSpec> tag. Select
dataSourceSpec
in the left list, then click
Insert
. Click
Close
, then go to the Source view of the JSP editor. The following
new code has been added:
<dab:dataSourceSpec dataSource="" id="" />
Figure 8-21 shows the correct parameters and values to use for the
<dab:dataSourceSpec> tag. Update the tag in your JSP.
Note: Application Developer version 5 offers an improved New JSP wizard,
which includes a step to add tag libraries to a newly generated JSP file.
268 WebSphere Studio Application Developer Version 5 Programming Guide
Figure 8-21 Establishing a database connection
All the parameters for the connection are retrieved from the data source defined
in the server.
Once you have established a connection, you can execute the query. Click
JSP
-> Insert Custom
again, and this time choose
select
and click
Insert
. Update the
new select tag to be the same as in Figure 8-22.
Figure 8-22 Executing a select statement in a JSP tag
Here you use the connection created previously to issue the SQL select
statement. The input parameter is specified using the <dab:parameter>
tag.
Assuming that you have created an HTML table to display the result, you can
then use <dab:repeat> and <dab:getColumn> to loop through the result set and
display the values. You can either use the insert custom method to get you
started, or enter the code shown in Figure 8-23.
<dab:dataSourceSpec id="DSConnect" scope="page"
dataSource='jdbc/ejbbank'/>
Tip: In the Properties view (
Window -> Show View
) you can see the properties
of each tag when you place the cursor within the tag.
<dab:select id="select_master" scope="request" connectionSpec="DSConnect>">
<dab:sql>
SELECT ITSO.TRANSRECORD.TRANSID, ITSO.CUSTOMER.FIRSTNAME,
ITSO.CUSTOMER.LASTNAME, ITSO.TRANSRECORD.ACCID,
ITSO.TRANSRECORD.TRANSAMT
FROM ITSO.CUSTACCT, ITSO.CUSTOMER, ITSO.TRANSRECORD
WHERE ITSO.CUSTACCT.CUSTOMERID = ITSO.CUSTOMER.CUSTOMERID
AND ITSO.CUSTACCT.ACCID = ITSO.TRANSRECORD.ACCID
AND ITSO.TRANSRECORD.TRANSTYPE = 'C'
AND ITSO.CUSTOMER.LASTNAME LIKE :lastname
</dab:sql>
<dab:parameter position = "1" type="CHAR" value="Brown"/>
</dab:select>
Chapter 8. Developing Web applications with database access 269
Figure 8-23 Displaying result set values
As you can see from the discussion above, both the DB Beans and the
corresponding JSP tags give you an easy and quick way to access relational
data directly from a JSP. As was mentioned earlier, you have to be aware of the
potential problems of combining presentation and business logic in one JSP.
From a model-view-controller perspective, a JSP should ideally only implement
the presentation layer of your application, while the database access should be
handled by JavaBeans. However, if your application is small, or if you are building
a prototype, using the database access facilities described here may be a good
solution.
<TABLE border="1">
<TR>
<TH>TransID</TH><TH>Firstname</TH><TH>Lastname</TH>
<TH>Account</TH><TH>Amount</TH>
</TR>
<dab:repeat name="select_master" index="rowNum" over="rows" >
<TR>
<TD>
<dab:getColumn index="1"/>
<INPUT TYPE="hidden" NAME="ITSO_TRANSRECORD_TRANSID<%=rowNum%>"
VALUE='<dab:getColumn index="1"/>'/>
</TD>
<TD>
<dab:getColumn index="2"/>
</TD>
<TD>
<dab:getColumn index="3"/>
</TD>
<TD>
<dab:getColumn index="4"/>
</TD>
<TD>
<dab:getColumn index="5"/>
</TD>
</TR>
<%select_master.next();%>
</dab:repeat>
</TABLE>
270 WebSphere Studio Application Developer Version 5 Programming Guide
Running the JSP
Figure 8-24 shows the output of the JSP run execution.
Figure 8-24 JSP with DB Beans run
Summary
In this chapter we used the wizards within Application Developer to create
dynamic Web pages using SQL queries. We showed how to access databases
from a Web application, both by using the database Web page wizard and by
creating your own JSPs using tag libraries.
We also described the configuration of a test server with a data source.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 2003. All rights reserved. 271
Chapter 9. Developing applications
with stored procedures
In this chapter, we discusses the following topics:
What is a stored procedure?
Creating a Java stored procedure
Accessing a Java stored procedure
Creating a stored procedure with multiple statements
9
Tip: When building stored procedures with DB2 be sure to use the DB2 app
JDBC driver. Using the BD2 net JDBC driver is unstable and may not work.
272 WebSphere Studio Application Developer Version 5 Programming Guide
What is a stored procedure?
A stored procedure is a block of procedural constructs and embedded SQL
statements that are stored in a database and can be called by name. Stored
procedures allow an application program to be run in two parts, one on the client
and the other on the server, so that one client-server call can produce several
accesses to the database. This is good for performance because the traffic
between the client and the server is minimized.
Stored procedures can be written as SQL procedures, or as C, COBOL, PL/I, or
Java programs. In the following sections we will look at how to write and use a
Java stored procedure.
Creating a Java stored procedure
In this section we create a simple stored procedure that takes a customer ID and
returns all customer information. Later we create a Web application that uses the
stored procedure.
Importing the database definition into a Web project
We use a new Web project ItsoProGuideStoredProcWeb for the stored procedure
examples. Create the project by following the instructions in “Creating a Web
project” on page 248.
Open the Data perspective and go to the DB Servers view.
Select the existing connection Con2 and
Reconnect
(context). Alternatively,
create a new connection as described in “Creating a database connection” on
page 145 (without a filter to get all the tables).
Import the EJBBANK database into the ItsoProGuideStoredProcWeb project.
– Select the EJBBANK and
Import to Folder
, then select the
ItsoProGuideStoredProcWeb project and click
Finish
.
– The database is imported into Web Content/WEB-INF/databases.
Figure 9-1 shows the Data Definition view in the Data perspective after the
EJBBANK database has been imported.
Note: The support for stored procedures varies between different data base
management systems. We are using DB2 stored procedures in the example.
Chapter 9. Developing applications with stored procedures 273
Figure 9-1 Data Definition view after importing
EJBBANK
database
Using the Stored Procedure Wizard
We are now ready to create the stored procedure. Select the Stored Procedures
folder and
New -> Java Stored Procedure
(or by selecting
File -> New -> Other ->
Data ->
Java Stored Procedure
).
Enter getCustomer as the name of the stored procedure (Figure 9-2).
Figure 9-2 Specify stored procedure name
folder for stored procedures
imported database