WebSphere Studio Application Developer Version 5 Programming Guide part 34 pps
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (210.42 KB, 10 trang )
304 WebSphere Studio Application Developer Version 5 Programming Guide
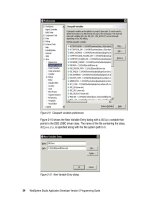
On the Struts Settings page, select
Override default settings
:
– Change the Struts version to 1.1 (beta2).
– Enter itso.strutsweb as the Default Java package prefix.
– Leave itso.strutsweb.resources as the Java package for the resource
bundle.
– Leave ApplicationResources as the resource bundle name.
– Click
Finish
(Figure 10-8).
Click
OK
when prompted to repair the server configuration. This action adds
the new Web project to the server configuration.
Figure 10-8 Setting Struts properties
The new Web project is configured with:
An application resources file:
Java Source\itso.strutsweb.resources.ApplicationResources.properties
An action servlet (in web.xml)
A configuration file (struts-config.xml) and six tag libraries
(struts-xxxx.tld) in Web Content\WEB-INF
The Struts runtime classes (struts.jar and dependent JAR files) in Web
Content\WEB-INF\lib.
we used the Struts
beta support
Chapter 10. Developing Struts applications 305
Copying the facade
We will use the same model and facade as in Chapter 7, “Developing Web
applications” on page 179. The easiest way to get the facade is by copying:
Select the itso.bank.facade package in the ItsoProGuideBasicWeb project
and
Copy
from the context menu.
Select the Java Source folder in the ItsoProGuideStrutsWeb project and
Paste
from the context menu.
Alternatively you can create the itso.bank.facade package manually and import
the Banking class from the \sg246957\sampcode\dev-struts\initial\facade
directory.
Importing RedBank Web content
We want to mirror the image and style sheet of the ItsoProGuideBasicWeb project
in the new ItsoProGuideStrutsWeb project:
Open the Web perspective, J2EE Navigator view, select the
ItsoProGuideStrutsWeb\Web Content directory and
Import
(context).
Select
File system
as source to import from and then click
Next
.
Click
Browse
and locate:
\sg246957\sampcode\dev-struts\initial\Web Content
Expand the Web Content directory and select the check box next to it.
Click
Finish
(Figure 10-9).
Notes:
If you create a Web project with Struts 1.02 support, there will be only one
JAR file (struts.jar) in the lib directory, because Struts 1.02 includes all
dependent classes in this single JAR. In Struts 1.1 these classes are now
split into multiple JAR files.
Although not necessary for our simple application, you would probably
want to upgrade the Struts JAR file to a later version than the 1.1 beta 2
shipping with Application Developer 5.0. At the time of writing, the latest
version of Struts is 1.1 Release Candidate 1.
The Struts action servlet is configured (in web.xml) to intercept all requests
with a URL ending in .do (the servlet mapping is *.do). This is common for
Struts applications, but equally common is using a servlet mapping of
/action/* to intercept all URLs beginning with /action.
306 WebSphere Studio Application Developer Version 5 Programming Guide
Figure 10-9 Importing sample code
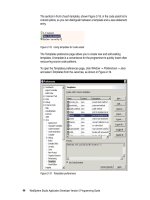
Updating ApplicationResources.properties
The wizard created an empty ApplicationResources.properties file for us and
we have to update it with the texts and messages for our application.
While developing Struts applications, you will usually find yourself having this file
open, because you will typically add messages to it as you go along writing your
code. Figure 10-10 shows an extract of this file.
Chapter 10. Developing Struts applications 307
Figure 10-10 ApplicationResources.properties (extract)
In the Web perspective, expand
Java Source
and then open the
itso.strutsweb.resources.ApplicationResources.properties file.
Replace then contents of the file with the contents in:
\sg246957\sampcode\dev-struts\initial\ApplicationResources.properties
Press Ctrl-S to save the file and then close the editor.
The exception classes we use extend the itso.bank.exception.BankException
class and have a method called getMessageKey. This method returns the key for
the error message so that we can retrieve the clear text message from the
ApplicationResources.properties file when an error has occurred. An example
of the getMessageKey method is:
public String getMessageKey() {
return "error.customerDoesNotExistException";
}
Creating the Struts Web diagram
We take a top-down approach to design the Web application by laying out all the
components in a Web diagram:
Select the WEB-INF folder and
New -> Other -> Web -> Struts -> Web diagram
.
Click
Next
. Enter strutsbank as the file name and click
Finish
.
# Optional header and footer for <errors/> tag.
errors.header=<P><font color="#ff0000"><strong><ul>
errors.footer=</ul></strong></font></P>
error.missing.customerId=<li>You must enter your customer ID.
error.missing.accountNumber=<li>You must select an account to work with.
error.invalid.customerId=<li>Invalid customer ID. Please try again.
error.invalid.amount=<li>Invalid amount. Please correct your entry.
text.pageTitle=ITSO Bank
text.welcome=Welcome to the ITSO Bank
text.customersAccounts={0}'s Accounts
prompt.enterCustomerId=Please, enter your customer ID:
prompt.account=Select the account:
prompt.transaction=Select the transaction:
308 WebSphere Studio Application Developer Version 5 Programming Guide
The Web diagram editor opens on the strutsbank.gph file (.gph is the file
type for Web diagrams).
Notice the icons in the tool bar:
The icons on the right are to place new components into the empty diagram.
The icons are connections, actions, form beans, JavaBeans, JSPs,
sub-diagrams, and Struts modules.
Adding the components
Use the icons in the toolbar to add four JSP pages, three actions, and two form
beans on the empty surface (Figure 10-11):
When you drop a JSP page or an action, you can change its name to the
name shown in Figure 10-11.
When you drop a form bean, you are prompted for a name and scope. Enter
customerInfoForm and transactionForm as names and select request as
scope.
Figure 10-11 Web diagram with initial components
Components in gray are not yet implemented, meaning they are only available in
the Web diagram and not as an underlying file such as a Java class or JSP.
Chapter 10. Developing Struts applications 309
Designing the application flow
When the components are laid out, it is time to connect them to define the flow of
the application. Figure 10-12 shows the layout with connections.
Figure 10-12 Web diagram with components connected
Select index.jsp and select
Connection
(context). A line appears connecting
index.jsp to the mouse cursor. Click the listAccounts action to complete the
connection. A dotted line appears from index.jsp to listAccounts. (You can
also use the
Connection
icon and click the two items to connect.)
Connect listAccounts.jsp to the accountDetails action, the
accountDetails.jsp to the performTransaction action, and the
listTransactions.jsp to the accountDetails action.
Connect the listAccounts action to listAccounts.jsp. Connecting an action
to a JSP page creates a forward, and you are prompted to enter a name for it.
Overtype <new> with the name success. The listAccounts action can then
lookup the listAccounts.jsp by referring to the name success.
Connect the accountDetails action to the accountDetails.jsp and enter
success as the name for this forward as well.
The performTransaction action uses four different forwards depending on
which transaction was performed:
– Connect the performTransaction action to listTransactions.jsp and call
this forward listTransactions.
310 WebSphere Studio Application Developer Version 5 Programming Guide
– Add three forwards from performTransaction back to accountDetails.jsp
and call the forwards deposit, withdraw, and transfer, respectively.
Connect the customerInfoForm to the listAccounts action and also to the
accountDetailsAction. The customerInfoForm is used by both actions.
Connect the transactionForm to the performTransaction action.
Save the Web diagram by pressing Ctrl-S.
Implementing the Struts Web diagram
When the Web diagram is laid out, it is time to start implementing the
components. This can be done in a different order, and the support you get from
Application Developer’s Struts tools depends on the order you choose:
You can implement the form beans first. When you later implement the JSPs,
you can choose which fields from the form beans should be present on the
pages.
You can implement the JSPs first. When you later implement the form beans,
you can choose which fields from the JSP pages should be added to the form
beans as properties.
We choose to implement the form beans first to have full control over their
contents and structure.
Developing the form beans
We start by implementing the customerInfoForm form bean:
Double-click the customerInfoForm form bean in the Web diagram. This
opens up the New ActionForm Class dialog as shown in Figure 10-13.
Tip: You can select a component in the diagram and from the context menu
select:
Change Path
to change the name of a JSP or action
Edit the forward name
to change the name of a connection
Change Description
to add descriptive text to any components
To improve the layout of the application flow, you can drag components to
another spot and you can rearrange connections by dragging their middle
point.
Chapter 10. Developing Struts applications 311
Figure 10-13 New ActionForm Class wizard
Application Developer automatically generates a Struts form bean class
called itso.strutsweb.forms.CustomerInfoForm and implement skeleton
methods for its reset and validate methods. The default values in the dialog
are fine, so click
Next
to proceed.
On the next page we can select the fields from the JSPs we want to include in
the form bean. Because we do not yet have any implemented JSPs, we
cannot use this feature, so just click
Next
(Figure 10-14).
312 WebSphere Studio Application Developer Version 5 Programming Guide
Figure 10-14 Selecting fields from JSPs
On the third page of the wizard we can enter the fields we want our form bean
to hold. Click
Add
and add each of the following fields (Figure 10-15):
customerNumber String
customerName String (firstname lastname)
accountNumber String (after selection)
accountNumbers String[] (list retrieved from customer)
validateKey String (1 or 2, which action)
Figure 10-15 Adding form bean fields
Click
Next
.
Note: Make sure you press Enter after entering the text in each field.
Otherwise, when you click
Next
, Application Developer may not include the
last field you updated.
Chapter 10. Developing Struts applications 313
On the next page (Figure 10-16) you are prompted to add a mapping for the
form bean to the Struts configuration file. Accept the defaults and click
Finish
.
Figure 10-16 Adding struts-config.xml mapping
The form bean wizard creates a new Java class extending the
org.apache.struts.action.ActionForm class and opens it up in the editor.
Replace the validate method (not the whole class) with the code shown in
Figure 10-17. The code is available in:
\sg246957\sampcode\dev-struts\initial\forms\CustomerInfoForm.txt
Figure 10-17 CustomerInfoForm validate method
public ActionErrors validate( ActionMapping mapping,
HttpServletRequest request) {
ActionErrors errors = new ActionErrors();
// Validate the customerNumber
if ("1".equals(validateKey)) {
if (customerNumber == null || customerNumber.trim().length() == 0)
errors.add(
ActionErrors.GLOBAL_ERROR,
new ActionError("error.missing.customerId"));
else if (customerNumber.trim().length() != 3)
errors.add(
ActionErrors.GLOBAL_ERROR,
new ActionError("error.invalid.customerId"));
}
// Validate the accountNumber - defer to action class
if ("2".equals(validateKey)) {}
return errors;
}