Introducing Windows Azure- P8 pps
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (166.07 KB, 5 trang )
CHAPTER 1 ■ CREATE CLOUD TABLE STORAGE
8
City = city;
State = (int)state;
Zip = zip;
County = county;
Country = country;
}
}
4. In the same project, create a folder called CloudDataService. Add three
interface definitions—IDataTableService, IHasDependencyTableService, and
INoDependencyTableService—to this folder. The interface IDataTableService
exposes three basic data table access functions: Insert, Update, and Delete. All
these functions accept a parameter of type TableStorageEntity defined in the
Microsoft.Samples.ServiceHosting.StorageClient namespace. The two other
interfaces are derived from the interface IDataTableService. The interface
IHasDependencyTableService exposes one method, UpdateDependencyTable(),
which also accepts a parameter of type TableStorageEntity. The third interface,
INoDependency, does not expose any methods but provides a type definition used
for marking a class as having no logical dependency data object.
5. Add two classes into the folder CloudDataServices—DataTableService
and AddressTableService. Mark the first class as an abstract class. The
AddressTableService class is a derived class from the DataTableService class
and implements the interface INoDependencyTableService. In the base class
DataTableService, all three basic data I/O methods—Insert, Update, and
Delete—are implemented. The Insert and Delete methods are marked as
virtual, allowing concrete classes derived from this base class to override them.
The implementation for all interfaces and classes is shown in Listing 1-4.
Listing 1-4. Implementation for All Interfaces and Classes Defined in the Folder CloudDataServices
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CreateDataStorage.Models.CloudDataServices
{
using Microsoft.Samples.ServiceHosting.StorageClient;
public interface IDataTableService
{
bool Insert(TableStorageEntity entity);
bool Update(TableStorageEntity entity);
bool Delete(TableStorageEntity entity);
}
public interface IHasDependencyTableService : IDataTableService
{
bool UpdateDependencyTable(TableStorageEntity entity);
}
CHAPTER 1 ■ CREATE CLOUD TABLE STORAGE
9
public interface INoDependencyTableService : IDataTableService
{
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CreateDataStorage.Models.CloudDataServices
{
using Microsoft.Samples.ServiceHosting.StorageClient;
using CreateDataStorage.Models.CloudDataContext;
abstract public class DataTableService
{
protected UserDataContext userDataContext = null;
protected string Table { get; set; }
public DataTableService()
{
userDataContext = new UserDataContext();
}
public UserDataContext DataContext() { return userDataContext; }
virtual public bool Insert(TableStorageEntity entity)
{
bool success = false;
try
{
if (this is IHasDependencyTableService)
{
(this as IHasDependencyTableService).UpdateDependencyTable(entity);
}
userDataContext.AddObject( Table, entity);
userDataContext.SaveChanges();
success = true;
}
catch { }
return success;
}
public bool Update(TableStorageEntity entity)
{
bool success = false;
try
CHAPTER 1 ■ CREATE CLOUD TABLE STORAGE
10
{
if (Delete(entity))
{
success = Insert(entity);
}
}
catch { }
return success;
}
virtual public bool Delete(TableStorageEntity entity)
{
bool success = false;
try
{
if (this is IHasDependencyTableService)
{
(this as IHasDependencyTableService).UpdateDependencyTable(entity);
}
userDataContext.DeleteObject(entity);
userDataContext.SaveChanges();
success = true;
}
catch { }
return success;
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Configuration;
namespace CreateDataStorage.Models.CloudDataServices
{
using Microsoft.Samples.ServiceHosting.StorageClient;
using CreateDataStorage.Models.CloudData;
public class AddressTableService : DataTableService, INoDependencyTableService
{
public AddressTableService()
{
Table = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["AddressTable"];
}
}
}
CHAPTER 1 ■ CREATE CLOUD TABLE STORAGE
11
6. In the same project, add the class UserDataContext, derived from the Azure
SDK base class TableStorageDataServiceContext. This class encapsulates a
cloud storage query function as Listing 1-5 shows.
Listing 1-5. Class UserDataContext Definition
public class UserDataContext : TableStorageDataServiceContext
{
public DataServiceQuery<Address> AddressTable
{
get
{
return
CreateQuery<Address>(ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["AddressTable"]);
}
}
}
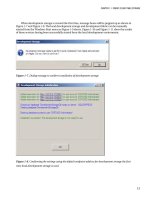
7. Right-click on the CreateDataStorage project node in the Solution Explorer
panel to bring up the Property dialog box. Select Development in the left pane.
Enter the database name, AzureForDotNetDeveloper, into the dialog box, as
Figure 1-4 shows.
Figure 1-4. Enter data table name
8. Add a reference to CloudData.Models.dll to the CloudStorageService WorkerRole
project.
9. Right-click on the CreateDataStorage project and select Create Test Storage Table
as Figure 1-5 shows. The compiler will analyze the code and generate a table for
the database. The generated table in the database is shown in Figure 1-6.
CHAPTER 1 ■ CREATE CLOUD TABLE STORAGE
12
Figure 1-5. Generate SQL storage
Figure 1-6. Data table has been generated in local SQL database