Formulation of business strategy in period of 2012-2017, vision to 2012 for investtech gn company limited
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (1.07 MB, 77 trang )
1
FORMULATION OF BUSINESS STRATEGY IN
PERIOD OF 2012-2017, VISION TO 2012 FOR
INVESTTECH GN COMPANY LIMITED
CAPSTONE PROJECT REPORT
H A N O I 2 0 1 2
MEMBERS OF GROUP 10:
1. DO TRUNG HIEU (Group leader)
2. NGUYEN THI MAI HUONG
3. HO HAI QUANG
4. DAM THI HOA
5. LE QUY HOANG
GaMBA.M0210
2
CONTENTS
ASSURANCE 6
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT 7
INTRODUCTION 8
1. Background 8
2. Goal and subject of research 9
3. Scope of research 9
4. Methods of research 10
5. Data processing method 10
6. Topic structure 10
7. Significance of the topic 10
CHAPTER I: BASIC THEORY OF BUSINESS STRATEGY AND
METHOD FOR STRAGIC FORMULATION 12
1.1. STRATEGIC OVERVIEWS 12
1.1.1. The concept of strategy - Strategic Management 12
1.1.2. Strategic requirements 13
1.1.3. Role of strategic management 13
1.1.4. Strategic classification : 14
1.2. ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCH TO IDENTIFY MAIN
OPPORTUNITIES AND THREATS 16
1.2.1. Macro environment: 16
1.2.2. Micro-environment: 17
1.3. INTERNAL CONTROL OF THE ENTERPRISES TO IDENTIFY THE
STRENGTHS AND THREATS 20
1.4. ESTABLISH LONG-TERM PURPOSE: 23
1.5. METHOD OF DEVELOPMENT AND SELECTION OF STRATEGY: 24
1.6. TOOLS FOR BUILDING AND SELECTION OF STRATEGIES 25
1.6.1. The tool providing information to develop strategies 25
1.6.1.1. Matrix of Internal Factor Evaluation Matrix (IFE) 25
1.6.1.2. External Factor Evaluation Matrix (EFE) 26
1.6.1.3. The Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM) 27
1.6.2. The tools to build viable strategis 28
3
1.6.2.1. Matrix of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats (SWOT)28
1.6.3. Tools for selection of strategies: Quantitative Strategic Planning
Matrix (QSPM) 29
CHAPTER II: ANALYSIS OF BUSINESS ENVIROMENT AND
FORMULATION FOR STRATEGIES OFINVESTTECH GN CO.,LTD 31
2.1. OVERVIEW 31
2.2. ANALYSIS OF IMPACTS OF EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT 37
2.2.1. Macro Environment 37
2.2.1.1. Economic Impact 37
2.2.1.2. Elements of law, government and politics 37
2.2.1.3. Social factor: 39
2.2.1.4. Scientific and technological factors: 39
2.2.2. Micro-environment 40
2.2.2.1. Existing rivals 40
2.2.2.2. Client: 43
2.2.2.3. Supplier 44
2.2.2.4. Potential competitors 45
2.3. INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT ANALYSIS 48
2.3.1. Finance: 48
2.3.2. MARKETING: 48
2.3.3. PERSONNEL: 50
2.3.4. MANAGEMENT: 50
2.3.5. INFORMATION SYSTEM: 51
2.3.6. RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT 51
2.4. SWOT MATRIX: 53
2.4.1. Basis: 53
2.4.2. SWOT MATRIX: 54
4
CHAPTER III. ANALYSIS FORMULATED STRATEGIES AND
SELECTION BUSINESS STRATEGY FOR INVESTTECH GN CO.,LTD (GNC)
IN PERIOD OF 2012-2017, VISION TO 2022. 56
3.1. STRATEGY ORIENTATION 56
3.1.1. Basis for strategy orientation construction. 56
3.1.1.1. From technology trend 56
3.1.1.2. From clients 57
3.1.1.3. From terminal distribution market in Vietnam 57
3.1.1.4. From telecommunication development orientation by 2010 58
3.1.1.5. Conception on development 59
3.1.1.6. Development targets by 2017 60
3.1.1.7. Development orientation by 2017 and vision to 2022 61
3.1.1.8. The Company’s strategic orientation by 2017 62
3.2. STRATEGY FORMATION 62
3.2.1. Group of S-O strategies 62
3.2.1.1. Market penetration strategies: 62
3.2.1.2. Market development strategies: 62
3.2.1.3. Joint venture strategy: 63
3.2.2. Group of S-T strategies: Strategy on product differentiations: 63
3.2.3. Group of W-O strategies: Strategy on human resource
development: 64
3.2.4. Group of W-T strategies: Strategy on product differentiation: 64
3.3. SELECTION OF STRATEGIES – MATRIX QSPM 65
3.4. SOLUTIONS FOR STRATEGIC IMPLEMENTATION 67
3.4.1. Solutions and development of human resource: 68
3.4.2. Marketing solutions: 69
3.4.2.1. Solutions on products: 70
3.4.2.2. Solution on price: 70
5
3.4.2.3. Solution on Distribution channel: 71
3.4.2.4. Solution for public relation (PR): 72
3.4.3. Solutions on research and development: 73
3.4.4. The roadmap and budget to implement strategies of the company: 73
3.5. SOME PROPOSALS FOR THE STATE 74
3.6. CONCLUSION 74
REFERENCES 76
APPENDICES 77
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1: Michael E.Porter’s 5 forces model
5
(Duong Ngoc Dung, 2005) 17
Figure 2: Main contents need analyzing on competitors
4
(Nguyen Thi Lien
Diep & the authors, 2006) 19
Figure 3:The "tripod" of business development strategy of company 23
Figure 4: The Strategy - Formulation Analytical framework 24
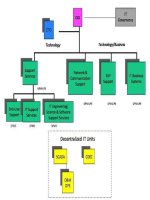
Figure 5: Organization Chart of Gia Nguyen Company 33
LIST OF TABLE
Table 1: GDP growth rate of Vietnam in the period 2003-2011 37
Table 2: GDP per capita of Vietnam in the period 2003-2011 37
Table 1: The Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM) 42
Table 2: EXTERNAL FACTOR EVALUATION (EFE) MATRIX 46
Table 3: INTERNAL FACTOR EVALUATION (IFE) MATRIX 52
Table 4: Growth rate of terminals imported in Vietnam in types in period of
2008-2012 58
Table 5: Market shares of terminal imported in Vietnam in types (forecast
within 5 years) 58
Table 6: A QSPM for GNC strategy 65
6
ASSURANCE
We do assure that the content of the capstone project report has not been
submitted to any high-degree programs as well as any other degree programs.
We do further assure that we have tried our best to apply the knowledge
that we have learned from the program to complete the graduation exercises. All
of our efforts has been reflected in graduation exercises.
7
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Firstly, we do express our gratitude to the Board of Rectors, Professors,
Experts, Lecturers and staff of the ETC Center - Vietnam National
University, Hanoi and the Griggs University (United States) has always been
closely together us during this course.
Through this course, we have accessed a high-quality education with
innovative teaching methods, how to apply and update useful information to
serve the management to improve business production efficiency.
Truthfully yours!
8
INTRODUCTION
1. Background
For years, Vietnam's economy has always achieved high growth and
stability. After joining the World Trade Organization (WTO), Vietnam has
opened up many opportunities for Vietnam enterprises to possibly expand
markets, expand production scale, and confirm its brand, but also come to new
challenges. The volatility of the market will increasingly faster and more
complex, sales is becoming more difficult due to the enterprise’s ability in
supplying goods to the market's growing, diversification in commodity and
quality requirement is increasingly high, the competition to take the customers is
increasingly more aggressive. It requires every enterprise that wants to succeed in
business must have a way of doing business, ways of thinking, new way, to know
how to use the facilities, capture and process information quickly, effective
application of scientific and technological solutions, making the direction and
operations goal consistent in each period to possibly gain advantages in
competition.
Telecommunications technology is the industry which has an important
role to promote the development and promote the effects of many other
technologies, as the decisive basis of the innovative development of many
economic sectors. Moreover, telecommunications technology is also one of the
industry performing the function as necessary means and conditions to ensure the
development of the national economy in the trend of globalization,
regionalization at present.
Starting from the role and position of telecommunications technology to
the requirements of national economy, the government of Vietnam has issued a
number of policies in order to guide, facilitate and encourage
telecommunications technology development towards "Strong development for
high-tech industries, especially information technology, telecommunications,
electronics and automation; paying much attention to the production of computer
9
software into the economic sector with remarkable growth rate”.
However, according to some recent studies, about one third of small
companies have failure within the first two years and about half of the remaining
companies have failed in the next five years. Thus, to succeed and develop in
current business conditions, it is not easy to implement at all, only about 30%
successful companies. Therefore, as a newly-established enterprise, lacking many
elements of technology, human resources, finance, etc. and a long-term
development strategy for the future, INVESTMENT TECHNOLOGY AND
EQUIPMENT GIA NGUYEN CO.,LTD needs to build up a suitable and proper
business strategy for itself, to effectively use its resources to exploit opportunities
and strengths, limits the risks and weaknesses as an urgent work for the company
to stand in the market and keep up developing in the future.
By these reasons, we do choose the topic: “Formulation business
strategy in period of 2012-2017, vision to 2022 for Investtech GN Company
Limited” for our research.
2. Goal and subject of research
Through the theoretical and practical research, the subject analyzes the
issues related to the operating environment and the state of INVESTMENT
TECHNOLOGY AND EQUIPMENT GIA NGUYEN CO.,LTD, from that to
propose the goals and strategies for development of the Company in the period
of 2012-2017, vision to 2022; as well as making a solutions for successfully
carrying out the business strategies of INVESTMENT TECHNOLOGY AND
EQUIPMENT GIA NGUYEN CO.,LTD.
3. Scope of research
In the framework of this thesis, our group only research the issues related
to the procedure of making plan for business strategy and manipulate to make
plan for business strategy for INVESTMENT TECHNOLOGY AND
EQUIPMENT GIA NGUYEN CO.,LTD in the period of 2012-2017, vision to
2022, paying attention to the feasibility and effectiveness of the strategies.
10
4. Methods of research
To collect information, our group has used the following methods:
- Collecting primary data: using qualitative and quantitative methods to
collect primary data through questionnaire sent to randomly selected people
(members of the company and members outside the company). The main content of
the survey is to collect information about: evaluation of customer satisfaction,
technical quality, operational policies, leadership at the company, the functional
quality improvement.
- Collecting secondary data: internal documents of GNC.
- Using acquired knowledge for researching, analyzing the internal and
external business environment of the company and formulating company’s business
strategy in period of 2012 – 2017, vision 2020.
5. Data processing method
Mainly using statistical methods, synthesis, comparison, analysis to
collect assessment of inside and outside information related to the company's
business operation.
6. Topic structure
The contents of topic, except for the introduction and conclusion, should be
stated including 3 main Chapter as follow
:
- Chapter I: Basic theory of business strategy and method for strategic
formulation
- Chapter 2: Analysis of business environment and formulation for
strategies of Investtech GN Co.,ltd
- Chapter 3: Analysis formulated strategies and selection business strategy
for Investtech GN Co.,ltd (GNC) in period of 2012-2017, vision to 2022
7. Significance of the topic
Scientific significance: Strategic Planning is an effective way for the
enterprise to use resources efficiently as well as correctly identify its
direction. But because of various reasons that many Vietnamese
11
enterprises are not properly interested in application. In the current
reality, there are very few Vietnamese enterprises that undertake
planning their strategy for developing seriously and scientifically.
Therefore, this topic will present an approach for making plan for
business strategy of the enterprise basing on logic basis and specific
application, from that bringing the experience of business strategy for
other enterprises.
Practical significance: Originating from the practical requirements
of business activities in INVESTMENT TECHNOLOGY AND
EQUIPMENT GIA NGUYEN CO.,LTD, the group is trying to build
a suitable business strategy, focusing on the feasibility to help
companies survive during the current economic crisis and have the
ability to develop more powerful in the future.
12
CHAPTER I: BASIC THEORY OF BUSINESS STRATEGY
AND METHOD FOR STRAGIC FORMULATION
1.1. STRATEGIC OVERVIEWS
1.1.1. The concept of strategy - Strategic Management
The term "strategy" has appeared for a long time, it originates in the
military field. Currently, there are many strategic concepts. At present, there are
many concepts on strategy: According to FredR.David: Business strategy is the
means to achieve long-term goals
1
(FredR.David,2006).
According to
AlfredChadler
6
(HaroldKoontz, 1993):
Business strategy is
the determination of the basic and long-term objectives of the enterprise as well
as map out and choose a method, the process of action and distribution of
resources to fulfill that goals.
According to MichaelE.Porter
3
: Strategy is the creation of the position and
unique value include different activities, as a choice, trade-offs in the
competition, as creating fit among all the company's activities.
The definition of strategy but different wording, but in general, it is a
combination of strategy and policy objectives as well as major plans to achieve
that goals, it shows that the company is or will be made what business activities,
and the company will fall into what the business sector
4
(Nguyen Thi Lien Diep
& the authors, 2006).
Definition on strategy management
Strategic Management is an art and science of establishment,
implementation and evaluation of decisions regarding functions that allows an
organization to achieve set objectives
1
(FredR.David, 2006).
Also, at present, there are many different concepts of strategy
management, it can be divided in three common approaches, including: the
environmental approach, approach by the objectives and measures, approach by
13
actions and it can be integrated into the concept of strategy management as
follows: “Strategic Management is the process of studying the current
environment as well as future, planning the objectives of the organization;
proposing, implementing and controlling the implementation of decisions to
achieve the environmental objectives in the current and future situation to
increase forces for the enterprise”
4
(Nguyen Thi Lien Diep & the authors,
2006).
1.1.2. Strategic requirements
Business strategy to achieve increased power for the enterprise and win
the competitive advantages.
Business strategy to secure business safety for the enterprise, potential
risks can occur but still low, impossibly build the strategy in the state of "Take
all, falls to zero”
Strategy formed on the basis of determining business scope, objectives
and the basic conditions to achieve the objectives, overcoming the spread or
unused resources.
The strategy must be built based on a right mindset, the certain
information and knowledge to anticipate changes of business environment in the
future, limiting the actual error to the current situation.
Effective strategy to combine maturity with time i.e. when the planning
strategy must seize the opportunity to properly implement, do not take much time
processing the details and expect to complete a perfect strategy.
1.1.3. Role of strategic management
Strategic Management helps the administrators define the purpose and
direction of the organization to reach a certain position.
The environmental conditions constantly change with the opportunities
and threats for organizations. Therefore, the orientation of the strategy will help
organizations take advantage of the opportunities and advantages in business to
make the policy consistent with development, simultaneously predict the
14
uncertainties and risks to face with the action for the situation based on own
potential.
Help the administrators to effectively use the existing resources of the
enterprises, allocating them appropriately, since then, the coordination with
functions in the enterprise in the best way for a common goal of the organization.
The study found that the companies use strategy management is
achieving better results than the previous results and than the results of the
companies that do not use strategic management.
1.1.4. Strategic classification :
- Base on the scope of strategy:
+ Overall strategy: referring to the common goals, key issues with survival
meaning for the enterprise.
+ Partly strategy: The specific strategy on price, products, distribution, etc.
for each short-term or medium term stage of the overall strategy.
- Base on the growth goals:
+ Focused growth goals:
Market Entry Strategy: to increase market share for available products
or services in the current market.
Market Development Strategy: to bring available products or services
on the new market.
Strategy for product development: to develop current market for new
products.
+ Integrated development strategy:
Strategy of combining forward: to increase the ownership or control of
the organization's customers.
Strategy of combining backward: to increase the ownership or control
of those units to provide inputs.
The strategy of combining horizontally: to increase the ownership or
control for the same industry competitors.
15
+ Growth strategy by diversification way:
Strategy on concentric diversification: to market new products or new
Printing & Advertising in the industry, with existing processes or new
technology but are related to each other.
Strategy on horizontal diversification: to target your products or
services with new technology process in new or existing production
but in the current market.
Mixed Diversification strategy aimed new products or services with a
completely new technology in new business.
+ Reduction strategy:
Strategic of Joint Venture: Two or more companies form a sponsoring
independent company for the purpose of cooperation.
Cutting operation strategy: selling a subsidiary or a company.
Strategic narrow down activities: strengthening the business through
cost cutting, the existing assets of the business in case of revenue and
profit reduces.
Strategy of liquidation: piecemeal sale of assets of the enterprise.
The competitive strategy under point of view M.Porter
3
(Michael E.Porter,
2009):
M.Porter gives three general directions for the strategy's success can help
companies operate more efficiently to other companies in an industry:
+ Low-cost strategy: This strategy is to focus how the total cost of the
lowest in the industry through a group policy that aims to feature this base.
+ Differentiation strategy products and services: This strategy is aimed at
creating products and services that the industry must be considered
unique. Product differentiation has many forms: design or brand image,
technology, customer service, etc.
+ The strategy focuses on a specific market segment: This strategy is
focused on a group of buyers, a segment of the industry, or geographic
16
market.
1.2. ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCH TO IDENTIFY MAIN
OPPORTUNITIES AND THREATS
The research environment of the business activities focus on the
identification and evaluation of trends and events beyond the control of a single
company, The evaluation of external factors suggests that the assembly and the
threat that an important experience to the organization can draft management
strategy to take advantage of opportunities and avoid or lessen the threat.
Operating environment of the business is divided into two types:
1.2.1. Macro environment:
The important influence of the macro environment is:
- Economic impact: The impact of major economic: inflation,
interest rates, the stage of economic cycle, the balance of payments, fiscal
policy and monetary policy.
- The effects of law, government and politics: The elements of law,
government and political influence is growing to the operation of the
business. Enterprise must comply with tax rules, loans, safety, price,
advertising, where plants and protection of the environment.
- Social Influence: The social effects primarily include demographic
trends, recreational interests, ethics, attitudes and standards of living,
business community and women workers. The social factors are often
slow to change are difficult to identify.
- Natural Effects of natural factors: environmental pollution
problem, lack of energy, waste natural resources, along with the growing
demand for limited resources.
- Impact of technology: More advanced Real Photo Technology was
born, creating opportunities and risks for all industries and businesses.
The development of new technologies can make a new market, resulting
in a proliferation of new products, changing relationships in the industry
17
and competition for existing products become obsolete.
1.2.2. Micro-environment:
We apply the model of five competitive forces MichaelE.Poter to analyze
micro-environment of the enterprise (also known as analysis of industry
structure).
Figure 1: Michael E.Porter’s 5 forces model
5
(Duong Ngoc Dung, 2005)
- Threat of new entrants: When the new competitors entering the
industry, they will reduce the market share, profits of the enterprise. To protect
their competitive position, the enterprises have to increase barriers through
measures such as product diversification, exploiting the inherent advantages of
scale, market share, geographic location , the brand, etc. to make new entrants
who wish join the sector requires the large initial investment cost, slow capital
recovery, less competition, etc. leading to withdrawal from the market.
- Threat of substitutes: Because the science and technology are rapidly
developing, it will be the conditions for the introduction of substitute products.
The substitute products would threaten the market share and limit the profit
potential of the enterprise. Therefore, the enterprises must continually apply the
scientific and technological applications to improve labor productivity to the
18
lower cost of the products and services, while improving quality and usability of
the product to increase the competitive capacity.
- Customers: The trust of customers is significant for the enterprises.
However, when customers get the advantages, they will put pressure and affect
the enterprise, for example, they will squeeze the prices, request long-term
payment, etc.
- Suppliers: Including units providing inputs such as raw materials,
machinery, finance, human resources, etc. When the suppliers have the
advantages, they will cause adverse pressure on enterprises such as selling at
high price, short-term payment, etc.
− Competitors
19
Figure 2: Main contents need analyzing on competitors
4
(Nguyen Thi Lien
Diep & the authors, 2006)
- Purchasers (Customers): The customer’s trust is the valuable asset of
the Company. However, the purchasers shall have the advantages,
possibly make the profits of the sector reduce by price squeeze or require
higher quality and supply more services.
- Suppliers: The supplier includes the following subjects: The sale of
supplies and equipment; public finance staff. When the supplier has an
advantage, they can cause stress and disadvantage businesses.
- Potential rivals: Potential rivals may be factors that reduce the
What do competitors want to
achieve
Future purpose
At all levels of management and
multi-direction
What are competitors
doing and able to do?
Current
strategy
How do the enterprises
compete?
Several issues needed to answer about competitors
- Do the content agree with the current situation?
- How is the competitors’ ability in shifting and
changing strategies?
- What are weaknesses of the competitors?
-What could help the competitors retaliate most
powerful and effective?
Identification
Its effects and the industry
Potentials
Strong and weak aspects
20
profitability of the company, they put into operation new production
capacity, with the desire for market share and resources needed.
- Substitute products: Substitute products to limit profit potential of the
sector controlled by the highest price for companies in the industry.
A company does not only compete with rivals in the industry but also
compete with manufacturers of products and services instead. There are two
types of replacement that is:
+ The substitute products
+ The alternatives products
11
(W.Chan Kim– 2006, p87-97).
+
1.3. INTERNAL CONTROL OF THE ENTERPRISES TO IDENTIFY THE
STRENGTHS AND THREATS
According to FredR.David
1
, the internal situation of the enterprise shall include
the main factors such as: Administration, marketing, finance – accounting,
manufacture, research and development, human resource, and information
system.
- Management:
+ Making plans: Including all management activities related to the
preparation for the future such as: forecast, set up goals, propose the
strategies, development for the policies, establish the plans.
+ Organization: Included all political activities creating the structure of power
and responsibility relations. The specific work is: Organizational design,
work details, control expansion, command unification, coordination,
arrangement, work design and work analysis.
21
+ Leadership: Leadership includes efforts to orientate human activities,
specifically leadership, contact, working groups, change of activities,
authorization, improvement of work quality, satisfaction of needs,
modification of structure and spirit of staffs and management spirit.
+ Inspection: Inspection is related to management activities to ensure that
actual results are consistent with planned results. Main activities include
quality control, financial supervision, sale supervision, inventory, costs,
analysis of changes, bonus and discipline.
- Marketing:
“Marketing is a human activity in order to meet needs and desires through
exchange”
5
(PhilipKotler,2001). However, to complete the exchange process, it
requires much efforts and professional qualification in “analysis, development of a
plan, and implementation of such plan, valuation, promotion and distribution of
goods, services and ideas to create exchange among target groups, meet needs of
customers and organizations, that means marketing management”
5
(Philip
Kotler,2001). The process of marketing management includes main basic tasks (1)
analysis of market capacity (2) selection of target market (3) preparation of
marketing mix (including 4 basic components: product, price, distribution and
advertisement) (4) implementation of marketing activities.
In addition, strategic marketing also includes following 4 components:
1. Probing: analysis of market
2. Partitioning: market segmentation
3. Prioritizing: selection of priority segments
4. Positioning: positioning enterprises and services of enterprises in such
priority segments
6
(TonThat Nguyen Thiem, 2005)
- Finance- Accounting
Financial condition is often considered as the best method for evaluating the
competition position and as the best condition to attract investors. The main
functions of finance- accounting include decision on investment, sponsorship and
decision on share earnings.
22
Analysis of financial indexes is the most popular method to identify the
strengths and weakness of the unit in term of finance and accounting. Important
financial index groups include solvency (evaluation of solvency for short-term and
due debts), Degree of Financial Leverage (showing scope of sponsorship by debts),
index of operations (measurement of effectiveness of resources), profitability ratios
(showing general efficiency of management) and growth indexes of economy).
- Production - Operation
Production- Operation includes all activities related to management of
inputs, organization and combination of such factors in order to convert such factors
into outputs which are products or services with the highest efficiency and profit.
The process of production- operation includes 5 types of decision: forecast,
inventory, materials, decisions on general planning strategies (refer to decisions
on production volume and production time), decision on production progress.
Strengths and threats in this functional year are decisive factors to success or failure
or an organization.
- Research & Development (R & D):
Research and development for purpose of development of new products
before rivals, improvement of product quality, and proper control of price or
innovation of production process to reduce costs. Quality of efforts in research and
development made by the company can help it affirm its leading position or make it
lag behind other leading rivals in the industry.
- Human resources:
Human resources play an important role in success of the company. A right
strategy is unable to bring about effectiveness without good employees. The main
functions of human resource management include recruitment, inspection, selection,
orientation for training and development, attention, evaluation, reward and
discipline, transfer, promotion, demotion and dismissal of employees.
- Information system:
The information system is an important strategy because it receives rude data
from external and internal environment of an organization, helping to keep track of
23
changes in environment, detect risks in competition and support implementation,
evaluation and supervision of strategy. In addition, an effective information system
allows the company to gain special ability in various fields such as low cost,
services meeting needs of customers.
Otherwise, long-term and sustainable development must be based on core
capacity and professional skills of enterprises. The process of cultivation and
improvement of core capacity and professional skill is the basis for not only
gaining/ keeping the market share but also mainly extending market to facilitate
enterprise development that is identification of strengths of enterprises.
Figure 3:The "tripod" of business development strategy of company
(Core capacity and professional skill include knowledge, technology, skill,
and experience gained by enterprise in professional fields which the enterprise
considers as a launching ramp to create development strategy for the enterprise)
8
(TonThat Nguyen Thiem, 2005).
1.4. ESTABLISH LONG-TERM PURPOSE:
Long-term objectives reflect expected results of pursuing strategies.
Strategies show methods to obtain long-term objectives. Timeframe for objectives
24
and strategies must be in consistent with each other, normally from 2 to 5 years.
Every objective is often accompanied by a period and some items such as
capital growth, growth of consumption revenue, profitability, market share, level
and nature of vertical combination…
1.5. METHOD OF DEVELOPMENT AND SELECTION OF STRATEGY:
Figure 4: The Strategy - Formulation Analytical framework
According to Fred R. David, Process of formulating and selecting strategy
consists three stages:
Stage I: THE INPUT STAGE
The input tools require strategists to quantify subjectivity during early stages of
the strategy-formulation process. Making smalls decisions in the input matrices
regarding the generate and evaluate alternative strategies. Good intuitive judgment
is always needed in determining appropriate weights and ratings.
Stage II. THE MATCHING STAGE
The matching stage of the strategy-formulation framework consists of five
technique that can be used in any sequence: the SWOT matrix, the SPACE matrix,
the BCG matrix, the IE matrix, and the Grand Strategy Matrix. These tools rely
upon information derived from the input stage to match external opportunities and
threats with internal strengths and weaknesses. Matching internal and external
25
critical success factor is the key to effectively generating feasible alternative
strategies.
Stage III. THE DECISION STAGE
Analysis and intuition provide a basis for making strategy-formulation decisions.
The matching technique just discussed reveal feasible alternative strategies. The
Quantitative Strategic Planning Matrix (QSPM) uses input from stage I, analyses
and matching result from stage II, analyses to decide objectively among alternative
strategies. The QSPM is a tool that allows strategists to evaluate alternative
strategies objectively, based on previously identified external and internal critical
success factors. The QSPM requires good intuitive judgment.
Because the company's resources are restricted and we may not choose all
strategies and we can just select some strategies for implementation.
Conclusion: The process of strategic management is continuous and
dynamic. A change in a major component in the model may require a change in one
or all of other components. Thus activities of formation, implementation and
evaluation of strategies should be implemented continuously. Strategic management
process never really ends.
1.6. TOOLS FOR BUILDING AND SELECTION OF STRATEGIES
2
(according to Fred R.David).
1.6.1. The tool providing information to develop strategies
1.6.1.1. Matrix of Internal Factor Evaluation Matrix (IFE)
Internal Factor Evaluation Matrix (IFE): A summary step in conducting an
internal strategic management audit is to construct an internal factor evaluation (
IFE) matrix. This strategy formulation tool summarizes and evaluates the major
strengths and weaknesses in the functional areas of a business, and it also provides a
basis for identifying and evaluating relationships among those areas. An IFE matrix
can be developed in five steps:
Step I: List key internal factor as identify in the internal-audit process. Use a
total of from 10 to 20 internal factor including both strengths and weaknesses. List
strengths first and then weaknesses.