Văn hóa anh nguyễn thị lan anh
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (10.48 MB, 47 trang )
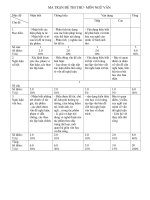
COURSE OUTLINE
Subject
Units of credit
Suggested self- study
Instructor
Contact detail
BRITISH CULTURE
2 (30 periods)
90 periods
Nguyễn Thị Lan Anh
cell phone: 0905369644
Textbooks:
- British studies textbook – compiled by Dr. Peter Stork, 2009
Session
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Topics
Introduction: Sightseeing in Britain
Geography & Climate
Cities, population and countryside
History of Britain
Unification and division in Britain
Festivals and Holidays
Folklore traditions and other festivals
Food and Drinks
Cultural diversity
Education
Government
Chapter
1 (textbook)
2 (textbook)
3 (textbook)
4 (textbook)
5 (textbook)
Hand-outs
6 (textbook)
8 (textbook)
9 (textbook)
7 (textbook)
Subject objectives: The specific objectives of this subject are to help students to get familiar
with some aspects of British Culture, focusing on those which may be more appealing for
the students: sightseeing in Britain, major cities, history, festivals and holidays, British cuisines,
etc.
Language objectives: The students deal with the four skills of the
language: listening, speaking, reading and writing.
Assessment for all students
- Final test : 50%
- Mid-term test: 50%, including:
- 30% of total mark: group presentation
- 10 %: a revision test
- 10 %: individual writing assignments after some lectures
Guidelines for presentation in groups
1
1. A group of 5 students formed by themselves will be working together and given an
individual mark based on their group performance and internal assessment of individual
participation:
- Group performance: good organizations of slide (a clear introduction right at the
beginning of which parts your group members would present; not many words shown in each
slide- should generalize ideas by key words; not many animation effects used in a
presentation – possible for quiz designs; equal division of work to each member’s parts; a
deep understanding of issues presented)
- Individual presentation: clear and good pronunciation, a clear introduction of which
parts you are in charge (a clear outline), interesting or creative presentation, a deep
understanding of issues presented.
Please read the sheet of assessment criteria for presentation below:
Teacher Evaluation Form
Group Number____
Date____________
Topic___________________________________________
Student’s name:___________________________________
Individual assessment through group presentation
Organization: 2 points
______ a clear introduction of which parts you are in
charge.
Content: 6 points
___ variety of reference resources
___ understanding of the issues presented
Presentation: 6 points
___held audiences' attention (interesting and creative
presentation)
___spoke with note cards
___Eye contact
Group assessment: 10
points
Total mark
30 points
____ clear outline
____ effectiveness of
visual aids
____ cooperation
(mutual assistance) for
an understanding of the
common issues
presented in groups
____ equal division of
work to each member’s
parts
____ interesting and
creative design of
group presentation
___ providing class
games or activities to
involve audience.
___time control
___volume of voice
___effectiveness of visual aids
Oral skills: 6 points
____ clear explanation
2
___ fluency
___ accuracy in grammar and pronunciation
Teacher comments:
2. Time duration: 1 period for each group presentation, including a 10-minute design of review
games or activities to involve audiences’ listening
3. Use hand-out materials as an additional reference source for presentation.
Other reference sources:
- projectbritain.com
- British studies textbook – compiled by Dr. Peter Stork
- Oxford Guide to British & American Culture- by Johnathan
Crowther – Oxford University Press- 1999 – 599 pages
- British Culture: an introduction – by David Christopher –
Routledge – 2006 – 292 pages
3
CHAPTER 1: SIGHTSEEING IN BRITAIN
I.
Introduction to England-Scotland-Wales
1. Pre-listening activity 1: Matching the pictures with their names before watching the
video: The Changing of the Guard, Royal Mile (Edinburg), White cliffs of Dover,
Wallace Monument-Stirling- Scotland, Edinburg Castles, Cardiff Castles, Minster
(York), Snowdon (Wales), Edinburgh (Scotland)
2. Pre-listening activity 2: Read the descriptions and fill in the gaps with these words
above
•
_____________ : is one of the greatest cathedral churches in Great Britain
•
__________: starts at 11.30 and lasts about 45 minutes.
•
__________ is a succession of streets which form the main thoroughfare of the Old
Town of the city of Edinburg in Scotland.
___________: is a city and former ancient burgh in Scotland, and is at the heart of
the wider Stirling council area. Stirling is Scotland’s newest city and one of its most
historic cities. The city is clustered around a large fortress and medieval old-town
beside the River Forth. Historically it was strategically important as the "Gateway to
the Highlands", with its position near the boundary between the Scottish Lowlands
and Highlands, and its crossing of the Forth, the nearest to the river mouth.
____________: is the highest mountain in Wales and is Great Britain's highest
mountain south of the Scottish Highlands
•
•
-
•
____________ is the capital city of Scotland, the second largest city in Scotland
after Glasgow and the seventh-most populous in the United Kingdom. __________
is a castle fortress which dominates the skyline of the city of Edinburgh, from its
position atop the volcanic Castle Rock. It is said that many people have heard the
sound of ghostly drums within it.
•
__________________: form part of the British coastline facing France. Their face
reaches up to 107 metres (351 ft) and spread east and west from the town in the
county of Kent, an ancient and still important English port. They have great
symbolic value for Britain because they face towards Continental Europe across the
narrowest part of the English Channel, where invasions have historically threatened
and against which the cliffs form a symbolic guard.
•
__________: is the capital, largest city and most populous county of Wales. The city
is Wales' chief commercial centre, the base for most national cultural and sporting
institutions, the Welsh national media, and the seat of the National Assembly for
Wales. It is a significant tourism centre and the most popular visitor destination in
3. Listening activity:
Use the textbook. Watch the video and fill in the gaps with the words given.
London view:
- Pre-listening: Recognize the places, famous person in the picture and guards in Britain.
4
Houses of
Parliament
Westminster
Abbey
Churchill
•
Household
Cavalry =
Life Guards +
Blues & Royals
•
Queen’s
Guard
- Listening activity: Use the textbook. Watch the video and fill in the gaps with the words
given.
London short tour:
Pre-listening: Recognize these places
5
Trafalgar Square
National Gallery
St Paul’s Cathedral
Tower of London
Piccadilly Circus
6
Pre-listening: Recognize these guards and these things
Listening activity: Use the textbook. Watch the video and fill in the gaps with the words
given.
II.
Scotland:
- Watching the video (1 st time)
- Before watching the video again: notice these questions
•
•
•
•
•
People mentioned in the video: Mary, John Knox, William Wallace,
Robert Bruce, Mel Gibson. Who are they?
What is special about them?
What places are mentioned?
What are other things about Scotland?
What is the nickname of Edinburgh for its neoclassical buildings?
7
Listening for the 3rd time: Use the textbook and fill in the gaps with these
words
-
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Royal Mile
Holyrood House
(Palace)
Smoked salmon
Edinburgh
castle
Black pudding
Britannia
Mary
Mel Gibson
Saint Giles
Cathedral
Catholicism
Cannons
Pigeon
Georgian
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Georgian shop
Robert Bruce
Athens of the North
Old Town
New Town
Protestant Church
Stirling castle
Wood cask
Rye (or Barley)
Brave heart (movie)
Bagpipes
Scotch Whiskey Heritage
Center
William Wallace
Stirling Bridge
Lochs
King Arthur
John Knox
Georgian shops
Georgian architecture is the name given in most English-speaking countries for the
architectural styles between 1720 and 1840.
This name is in honor of the British kings George I to George IV. They reigned
between 1714 and1830.
III.
Wales:
- Use the textbook and fill in the gaps with what you can hear
8
IV.
Oxford - More of London- The Bloody Tower:
- Watch the video (1st time): Oxford
- Before watching the 2nd time:
What things about Oxford are mentioned?
Things about Oxford
9
-
Watch the video (1st time): More of Lodon
Before watching the 2nd time:
What things about London are mentioned?
10
Things about London
-
Watch the video (1st time): The Bloody Tower
Before watching the 2nd time:
What things about the Bloody Tower are
mentioned?
11
Things about The “Bloody Tower”
Execution sites:
A complex of Towers:
•
•
•
•
•
-
_________
_________
_________
_________
_________
____ Tower
Tower _____
_____ Tower
_____ Tower
_____ Tower
_____ Tower (or
___Tower)
King Henry Tudor (8th)
12
CHAPTER 2: GEOGRAPHY AND CLIMATE OF BRITAIN
I. The British Isles:
- Read the description in the textbook
- Exercise 1: Label the map with the correct name or phrase from the definitions (textbook).
- Exercise 2:
Name each territory of the British Isles (darkened part) in the maps below.
- Exercise 3: Listening and Watching the video
Activity before listening: Match the words and phrases in the table to their definitions.
Activity after listening: Comprehension task (Multiple choices and Matching)
13
II. Physiographic features of England
14
•
•
•
•
A seafaring nation (*)
Northern + Western: mountainous (*)
Eastern: (*) Flatland,
Rolling hills
Southern: Elevated plateau
Barren uplands
Marsh land
Moors (moorland)
Chalk hills (*)
Seaports of England
Liverpool
Dover
Newcastle-Upon-Tyne
Plymouth
Bristol
15
Mountain ranges or mountains
e.g. Pennine
e.g. Lake District
Flatland
e.g. Portbury Common, North Somerset
16
1
Rolling Hills
e.g. The North Downs
marshland
e.g. The Fens
Chalk hills
e.g. Dover
17
English landscapes
1
Elevated plateau
2
Barren uplands
e.g. Cornwall
e.g. Devon
e.g. Bristol Channel
3
Moors
e.g. North York Moors –
(in Yorkshire)
Watch the video: Yorkshire: North York Moors known as “Garden of England”.
Describe the features of moorlands in England as you can see.
III. Physiographic features of Scotland
- Read the text and fin dout the main physiographic facts of Scotland: Edinburgh,
Glassgow, Ben Nevis, The Tay, The Clyde, Loch Lomond, Loch Ness, The Hebrides,
Orkneys, Shetlands
- What is the general statement best describing Scotland’s physiography?
18
Scottish landscapes
1
2
3
19
Scottish
landscapes
1
2
‘About three quarters of Scotland is made
up of bog, rock and heather and peat
soils’
Match the words bog, peat and heather to
the pictures and their descriptions
3
20
Scottish landscapes
1
2
1
3
‘Scotland has a very irregular coastline
with inlets from the sea called firths…
The Highlands contains narrow lakes or
Lochs….’
Match the words irregular coastline firths
and Lochs to the pictures.
III. Physiographic features of Wales
-
Read the text and find out the main physiographic facts of Wales
What is the general statement best describing Wales’s physiography?
Exercises:
21
Exercise 2: Fill in the blanks for the paragraph below using the following words.
Atlantic Britain Britain canals Cambrian Devon Downs England England
English Channel Cornwall Fens Highlands Ireland Irish island firths lochs
North Northern Ireland Pennines rivers Scotland seas Uplands
The Geography of Britain
Britain is an ___ country that is surrounded by three seas: the ____ Sea, the ____ Ocean and the
___ Sea. ___separated from ____and ____ by the ____ Sea and from France by the ___. The
most mountainous areas of are in the north of Britain: the ____and Southern ___ of ___. The
southern part of Britain contains smaller mountain ranges such as the ___in ___ and ____
Mountains in Wales and the rolling hills of England such as the ____. ____ also has most of the
flatland such as drained marshlands called the ____ and the moors of ____and ____. The south
part of ____ also has the greatest number of ____ and ____ while the northern part has many
narrow lakes called ___ and sea inlets called ____.
22
IV. The Climate and weather in Vietnam and in Britain:
- Read the text
- Understanding vocabulary: mid-latitude oceanic climate, the Gulf Stream, fogs, mist,
overcast skies, rain, drizzle, tropical monsoon climate, moist (Discuss in pairs)
- Exercise 1: (Discuss in groups)
(v) How do you think that the climate of Britain and Vietnam influence its people?
-
Exercise 2: Fill in the blanks with the words given
23
- Exercise 2: Writing assignment
Use the graphs in the textbook, compare and contrast the climate in an essay of 150 words.
You can choose to compare your major cities in Vietnam with those in Britain.
Here is an example:
24
CHAPTER 3: CITIES AND COUNTRYSIDE
I.
Major cities in Britain
Activity 1: Group work
- Ss work in group of 5. In the hand out, there are 5 excerpts on 5 major cities of Britain,
including London, Cardiff, Edinburgh, Manchester & Birmingham, Belfast. Each
member reads an excerpt of information on a major city of Britain. After reading, they
report to the whole group about key points. The group has to take notes.
- Ss make questions to other groups about what they have found from reading and
reporting in the groups.
Activity 2: Ss read the text in the textbook.
Exercise 1:
1. Name the 6 Major cities of United Kingdom and 12 Other Interesting Cities on the map
2. Name the 9 major Financial and Commercial centers of United Kingdom starting from
the top of the map, ie, from Scotland.
3. How many 1. Major cities and 2. Other Interesting Cities are financial and commercial
centres.
4. Which of the three regions of Britain has the most financial centres?
5. Name the 8 major centers of tourism and the arts in the United Kingdom starting from
the top of the map, ie, from Scotland.
6. How many Major cities and Other Interesting Cities are centres of tourism and arts?
7. Which of the three regions of Britain has the most centres of tourism and arts?
Exercise 2: Writing assignment
Question: What does the distribution of major cities, other cities, financial centres, arts and
tourism centres across the United Kingdom imply? Write a 3-paragraph essay of
approximately 180 words.
-
II. Living in Cities and Towns – Village life
Ss read the text
Discuss in groups the questions:
25