7 ocean water chemistry
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (2.59 MB, 50 trang )
Ocean Water Chemistry
Figure 4.17a
/>
Distribution of Earth’s Water
• Oceans
• Ice Caps and Glaciers
• Atmosphere
• Rivers and Lakes
• Inland Seas
• Groundwater
97.2 %
2.15 %
0.001 %
0.009 %
0.008 %
0.625 %
Ocean Water is SALTY
• Salinity: Total amount of dissolved solids
• Units: o/oo = 1/1000
• Range: 33 – 37 o/oo
• Increase in salinity:
– Increase in Density
– Decrease in Freezing Point
– Decrease in Vapor Pressure
– Increase in Osmotic Pressure
Origin of Salts in Oceans
• Rivers (largest transport of chemicals to ocean)
– Rain + CO2 H2CO3
– Si, Al, Na, K, Mg
• Volcanoes
– Cl, S, CO2
• Dust / Rain
–
Fe, Si
• Anthropogenic
–
CO2, P
Example Geochemical Cycle
Concept of Steady State
Example 2 Geochemical
Cycle
Residence Time
(T = Ocean amount/Output rate)
• Concentration of elements in seawater is
determined by their removal rate
• Conservative elements:
–
-
Major Elements: Cl, Na, SO4, Mg, Ca, K
Minor Elements: Br, Sr, B, C, F
• Non Conservative Elements
–
–
–
–
Nutrients: N, P, Si
Dissolved gases: O2, CO2, N2
Trace Elements: Fe, Al, Mn
Organic Compounds
Residence Time - Concentration
Element
Res. Time (yrs)
Na 60 000 000
Cl80 000 000
Mg 10 000 000
K 6 000 000
SO4 9 000 000
Ca
Mn
Fe
1 000 000
7 000
100
Concentration
Crust (%)
Ocean (mg/l)
2.4
0.013
2.3
2.1
0.026
4.1
0.5
2.4
10 770
19 500
1 290
380
905
412
0.0002
0.002
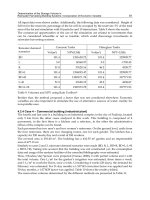
Dissolved Gases
Gas Solubility:
Decreases with Temp. and Salinity
Increases with Pressure
Gases in Atmosphere & Oceans
Percent Gas Phase by Volume
Gas Atmosphere
Surface Ocean
Total Ocean
N2
79%
48%
11%
O2
21%
36%
6%
CO2
0.04%
15%
83%
Seawater pH
• Pure water pH = 7
• Seawater pH = 7.5 – 8.1
• Seawater is very well buffered!
CO2(gas)+H2OH2CO3H++HCO32H++CO32
H2O: Universal Polar Solvent
H20: Temperature and Density
H2O: Frozen & Liquid density
H2O: Heat Capacity
• Heat Capacity: heat needed to change the
temperature of a substance
• Water has higher heat capacity than:
– All solids
– All liquids, except liquid ammonia
• Latent heat of Vaporization: heat needed to
evaporate a liquid
– Water has the highest of all substances
Seawater: Temperature and Density