Human resource management gaining a competitive advantage 2014 chapter 6
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (1.57 MB, 25 trang )
Human Resource Management:
Gaining a Competitive Advantage
Chapter 06
Selection and Placement
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
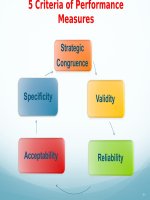
5 Evaluation Selection Method
Standards
1. Reliability
2. Validity
3. Generalizabil
ity
4. Utility
5. Legality
6-2
Reliability
Reliability is the degree to which a measure
of physical or cognitive abilities or traits is
free from random error.
The correlation coefficient is a measure of
the degree to which two sets of numbers are
related.
A perfect positive relationship equals +1.0
A perfect negative relationship equals - 1.0
Test-retest reliability is knowing how
scores on the measure at one time relate to
scores on the same measure at another time.
6-3
Validity
Validity is the extent to which a
performance measure assesses all the
relevant—and only the relevant—aspects
of job performance.
Criterion-related validation is a method
of establishing the validity of a personnel
selection method by showing a substantial
correlation between test scores and jobperformance scores. The types include:
Predictive validation
Concurrent validation
6-4
Criterion-Related Validity
Predictive
Test
Applicant
s
Measure
Performanc
e
of Those
Hired
TIME
Concurrent
Test
Existing
Employees
Measure
Their
Performance
TIME
6-5
Concurrent Validation
6-6
Predictive Validation
6-7
Content Validation
Content validation is a test-validation
strategy performed by demonstrating
that the items, questions, or problems
posed by a test are a representative
sample of the kinds of situations or
problems that occur on the job.
Best for small samples
Achieved primarily through expert judgment
6-8
Legality
All selection methods must conform to
existing laws and legal precedents.
Three acts have formed the basis for a
majority of the suits filed by job
applicants:
Civil Rights Act of 1964 and 1991
Age Discrimination in Employment Act of
1967
Americans with Disabilities Act of 1991
6-9
Civil Rights Act of 1991
Protects individuals from discrimination based
on race, color, sex, religion and national
origin.
Differs from the 1964 act in three areas:
1. Establishes employers' explicit obligation
to establish neutral-appearing selection
method.
2. Allows a jury to decide punitive damages.
3. Explicitly prohibits granting preferential
treatment to minority groups.
6-10
Age Discrimination in
Employment Act of 1967
Covers over age 40 individuals.
No protection for younger workers.
Outlaws almost all “mandatory
retirement” programs.
6-11
Americans with Disabilities
Act
Protects individuals with physical or mental
disabilities (or with a history of the same).
Reasonable accommodations are
required by the organization to allow the
disabled to perform essential functions of
the job.
An employer need not make accommodations
that cause undue hardship.
Restrictions on pre-employment
inquiries.
6-12
Types of Selection Methods
JOBS
6-13
Interviews
Selection interviews-a dialogue initiated by one
or more persons to gather information and
evaluate the applicant’s qualifications for
employment.
To increase an interview’s utility:
Interviews should be structured, standardized, and
focused on goals oriented to skills and observable
behaviors.
Interviewers should be able to quantitatively rate
each interview.
Interviewers should have a structured note-taking
system that will aid recall to satisfying ratings.
6-14
Situational Interview
A situational interview confronts
applicants on specific issues, questions, or
problems likely to arise on the job.
Situational interviews consist of:
experience-based questions
future-oriented questions
6-15
Other Selection Methods
Individuals should manage their digital identity the
same way they manage their résumé.
References, biographical data, and applications
gather background information on candidates.
Physical ability tests are relevant for predicting job
performance, occupational injuries and disabilities.
Physical ability tests include:
muscular tension, power, and endurance
cardiovascular endurance
flexibility
balance
coordination
6-16
Other Selection Methods
A cognitive ability test differentiates individuals
based on mental rather than physical capacities.
Commonly assessed abilities:
verbal comprehension
quantitative ability
reasoning ability
Personality inventories categorize individuals by
personality characteristics.
Work samples simulate a job in miniaturized form.
6-17
Cognitive Ability Tests
3 Dimensions Cognitive Ability Tests:
Verbal Comprehension -a person’s capacity
to understand and use written and spoken
language.
Quantitative Ability - speed and accuracy
with which one can solve arithmetic problems.
Reasoning Ability - a person’s capacity to
invent solutions to diverse problems.
6-18
Physical Ability Tests
Two Questions to Ask:
1. Is physical ability essential to perform the job?
2. Is it mentioned prominently enough in the job
description?
Tests Measure:
muscular power and endurance
cardiovascular endurance
flexibility
balance
coordination
6-19
Personality Inventories
Big 5 Dimensions of
Personality
6-20
Emotional Intelligence
6-21
Work-Sample Tests
Work-sample tests attempt to
simulate the job in a pre-hiring context
to observe how the applicant performs.
Assessment center-is a process in
which multiple raters evaluate
employees’ performance on exercises.
6-22
Honesty Tests
Polygraph Act of 1988 banned the
use of polygraph tests for private
companies except pharmaceutical and
security guard suppliers.
Paper-and-pencil honesty testing
attempts to assess the likelihood that
employees will steal.
6-23
Drug Tests
Drug-use tests tend to be reliable and valid.
Major controversies about drug tests include:
Is it an invasion of privacy?
Is it an unreasonable search and seizure?
Is it a violation of due process?
Tests should be administered systematically to all
applicants applying for the same job.
Testing is likely to be more defensible with safety
hazards associated with failure to perform.
Test results should be reported to applicants,
who should have an avenue to appeal.
6-24
Summary of Selection Methods
JOBS
6-25