Perform routine manual metal arc welding (MMAW)
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (4.41 MB, 54 trang )
5.12A Perform routine
Manual Metal Arc Welding
Pre-requisites: Nil
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
Range statement
• Routine MMAW in this unit is intended to apply in a manufacturing or
maintenance environment where welding is not required to meet
Australian Standards or other welding codes, licensing requirements,
Occupational Health and Safety regulations relating to
certificated/coded welding.
• Fillet and butt welds in all positions would typically be performed on low
carbon/mild steels.
• Weld preparation would be minimal and generally restricted to
cleaning, using files and grinders.
• In circumstances where welding is required to meet Australian
Standard 1554 General Purpose or equivalent codes, Occupational
Health and Safety regulations and/or licensing requirements then Unit
5.15A (Weld using manual metal arc welding process) should be
Element 5.12A.1 Identify weld
requirements
In this element you will be required to achieve competency in the
following areas:
1.1
Weld requirements are identified from job instructions. In this
presentation we will look at:
• weld requirements.
1.2
Location of welds are identified in accordance with standard
operating procedures and job specifications. In this
presentation we will look at:
• basic weld symbols.
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
Weld requirements
• Weld requirements for a project can be given in a number
of ways.
• They can be in the form of a:
Weld Procedure
- work instruction or job sheet
within an organisation
ENG
60o
1
n of
atio
&
tific
Cer elders visor
er
W
S up
ding
Unfired
Pressure
Vessels
2
Wel
- an engineering drawing.
Steel
Structures
- welding code
on
AS 1554
c ti
u
r
N
nsSt 1210
L DE
IA
k
r
WE
1.6
Wo
1.6
- weld procedure sheet
796
3S 1
A
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
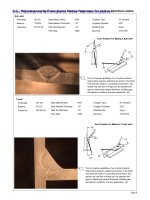
Weld symbols
• Welding symbols enable the engineer/draftsperson to
communicate important detailed information regarding
the weld, to the welder.
Basic weld symbol
10mm fillet weld other side of arrow
6mm fillet weld arrow side
10
6
MMAW
Weld on site
Weld all round
Use the Manual Metal Arc Welding Process
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
Basic weld symbols
Fillet weld
8mm leg length (other side)
Fillet weld both sides
6mm leg length (arrow side)
12mm leg length (other side)
Fillet weld (both sides)
8mm leg lengths
8
12
6
8
8
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
Basic weld symbols
Fillet weld
6mm leg length
Weld all round
Single ‘V’ butt joint (arrow side)
Weld arrow side
Butt joint – Open square
Welded arrow side
6
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
Basic weld symbols
Generally as welding is
being conducted
these areas
Weld all round
are welded
to provide
10mm
fillet a neat
Weld 10mm fillets
finished
project
On-site
Both sides of the plate
10mm
fillet
Weld
6mm
fillet
Weld
6mm
fillets
Weld
6mm
fillets
Arrow
side
Both
sides
of
plate
Both
sides
of
the
plate
Both sides of the
plate
On-site
Top and bottom
of the project
Element 5.12A.2 Prepare materials
for welding
In this element you will be required to achieve
competency in the following areas:
2.1 Materials are cleaned and prepared for welding. In
this presentation we will look at:
•
•
•
•
•
materials cleaning
weld preparations
weld types
weld terminology
methods of material preparation.
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
Plain Carbon Steel
•
It is necessary to ensure that the
material to be welded is clean and
free from:
– oil and grease
– paint
– metallic coatings such as galvanised
and chrome plating
– moisture
– corrosion - rust and mill scale.
•
•
These impurities can readily be
removed by wire brushing, grinding,
solvents, linishing or abrasive
blasting.
If left on, they may cause weld
defects.
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
Weld preparations
Closed butt:
Up to 3mm
- no preparation required
- suitable for up to 3mm plate.
T/2
Open butt:
Up to 6mm
- no preparation required
-- suitable for plate up to 6mm.
-
60o –70o
0 to 3mm
Single vee:
- plate up to 12mm.
Up to 12mm
0 to 3mm
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
Weld types
Corner weld
Lap weld
Fillet weld
Edge weld
Slot weld
Plug weld
0 - 30º
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
Weld terminology – fillet welds
Parent metal
Leg length
Reinforcement
Weld metal
Toe
Fusion zone
Penetration
Heat effected zone
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
Weld terminology – butt welds
Included angle 60 - 70°
Root face
Root gap
Reinforcement
Parent
metal
Fusion zone
Heat effected zone
Weld
metal
Throat
Penetration
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
Weld positions
OVERHEAD POSITION
HORIZONTAL POSITION
VERTICAL POSITION
FLAT POSITION
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
Edge preparation
•
GRINDING
•
FLAME CUTTING
•
– Grinders are used for fast plate removal.
– By holding the wheel on the edge, fast removal of material is possible.
– Using the flat of the wheel allows for removal of uneven surfaces.
– Can be utilised on straight plates or pipes.
– Grinding may be necessary if uneven surfaces
(nicks) are the result of this process.
Reproduced with the
kind permission of BOC
MACHINING PREPARATION
– Nibblers are by far the quickest method of removal:
• material thickness from 3 to 40mm possible
• angles of 22o to 45o possible.
– Pipe bevelling machines can be used for preparation of pipes:
• machines are very expensive to purchase.
– Lathe machining can be used:
• time consuming
• plate set up as well as machine set up is required.
Reproduced with the kind permission of
Trumpf
Element 5.12A.3 Prepare equipment
for welding
In this element you will be required to achieve competency in
the following areas:
3.1 Welding equipment is set up correctly. In this
presentation we will look at:
• definition
• MMAW line diagrams
• equipment.
3.2 Settings and consumables are selected to suit application.
In this presentation we will look at:
• welding fundamentals.
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
The process
•
•
•
•
Is a fusion welding process.
Uses the heat of an electric arc
between a consumable electrode
and the work piece.
The molten pool and arc is protected
by a gaseous shield generated by the
decomposition of the flux covering
on the electrode.
The operator must maintain a
constant arc length and travel speed
as the electrode is consumed into
the weld pool.
Reproduced with the kind permission of the
Australasian Welding Journal
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
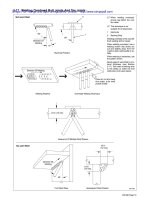
The basic MMAW plant layout
The
power
source
can
be
an
TheAn
The
The
electrode
The
welding
electrode
holder
current
clamp
lead
grips
isisconnected
connected
conducted
the
electrode
totothe
the
in place.
arc
isreturn
struck
between
a flux
covered
AC
DC
Transformer
Rectifier
They
electrode
are
the
fully
work
electrode
holder
insulated
piece
with
terminal
and
and
copper
work
should
on
terminal
or
an
aluminium
be rated for at
electrode
and
the
work
piece
AC
Transformer
least theAC
multi
maximum
via
transformer
the
strand
return
current
insulated
lead
machine
of
which
the
cables
and
power source
or a the circuit
ACDC
completes
transformer
rectifier
DC Generator
for MMAW
Power source
Primary lead
Electrode holder
Electrode
Electrode
Electrode lead
Work piece
Return lead
Return clamp
Work
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
Equipment
Power Source in the form of a:
• DC Generator
• AC/DC Transformer Rectifier
• AC Transformer
Electrode lead and Electrode holder
Return lead and Return clamp
Welding Helmet
Recommended Minimum Protective Filters for MMAW
Safety Glasses
Approximate Range of
FilterScull Cap
Leather
Welding Current
Recommended
Up to 100 amps
8 Jacket
Leather
100 – 200 amps
10
200 – 300 amps
11
300 – 400 amps
12
Over 400 amps
13
Leather Apron
Reproduced with the kind permission of ESAB
Reproduced with the kind permission of ESAB Australia Pty Ltd
Leather
Gloveswith the kind permission of ESAB
Reproduced
Chipping hammer and Wire brush
Welding shield with correct lens
Personal protective equipment
Overalls
Leather Spats
Reproduced with the kind permission of ESAB
Steel capped safety boots
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
Fundamentals of MMAW
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
To produce a quality weld the operator must
consider the following fundamentals:
Material preparation.
Type of electrode.
Size of electrode.
Amperage.
Angle of electrode.
Arc length.
Travel speed.
Striking the arc video
Reproduced with the kind permission of
the Australasian Welding Journal
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
Fundamentals of MMAW
Material preparation
Preparing material incorrectly may lead to weld failure.
Electrode manipulation is impeded if the edges are not prepared correctly.
Material should be cleaned and free from paint, grease, oil, heavy oxidation
and mill scale.
60o –70o
0 to 3mm
Up to 12mm
0 to
3mm
Gouge marks need to be ground smooth or if too
deep, may require filling with weld and dressed.
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
Fundamentals of MMAW
Type of electrode
• The type of electrode to be used on a
particular job may be specified on a:
• work instruction or job sheet within an
organisation
• a welding code
• an engineering drawing
• a weld procedure sheet.
• It may be the responsibility of the
operator to select the appropriate
electrode for the job.
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
Fundamentals of MMAW
Type of electrode continued
•
•
There are four basic types of electrodes.
Classified according to their flux compositions:
– Cellulose.
– Rutile.
– Iron powder.
– Hydrogen controlled.
5.12A Perform routine MMAW
Fundamentals of MMAW
Type of electrode continued
Function of the flux coating
•
•
•
•
•
•
Forms a gaseous shield around the molten weld pool,
electrode tip and molten droplets protecting it from the
atmospheric contamination.
Controls penetration, surface finish of the weld and arc
stability.
To form a molten slag which floats to the surface to provide a
protective cover whilst the weld cools.
Acts as a cleanser by dissolving impurities and surface rust.
Controls the bead shape.
Controls the chemical and mechanical properties by
replacing lost elements as required.