Tạo hình mạch máu
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (137.46 KB, 8 trang )
Tạo hình mạch máu (Angioplasty)
Định nghĩa
Tạo hình mạch máu là một thuật ngữ mô tả thủ thuật làm rộng (nong) bằng cơ học một
mạch máu bị hẹp hoặc tắc hoàn tồn. Thủ thuật này có nhiều kiểu khác nhau và tên gọi
liên quan với kiểu đi vào mạch máu và thiết bị được sử dụng. Ví dụ, tạo hình mạch máu
xuyên lòng mạch qua da (parcutaneous transluminal angioplasty-PTA) là đi vào qua da
rồi điều hướng đến vùng mạch máu liên quan thơng qua mạch máu đó hoặc một máu máu
thơng nối với nó (xun lịng mạch). Trong trường hợp thủ thuật liên quan với động mạch
vành, điểm vào có thể là động mạch đùi ở bẹn và hệ thống ống thông/dây dẫn đi qua
động mạch chủ đến tim và nguyên ủy các động mạch vành ở đáy động mạch chủ ngay
phía ngồi van động mạch chủ.
Thuật ngữ “angioplasty” là từ kết hợp của các từ “angio” (tiếng La tinh/ Hy lạp nghĩa là
mạch máu) và từ “plasticos” (tiếng Hy lạp nghĩa là tạo hình).
Tạo hình mạch máu bằng bóng
Mục đích
Ở những người bị bệnh mạch máu tắc nghẽn như xơ vữa động mạch, dòng máu đến cơ
quan (như tim) hoặc đến phần xa của cơ thể (nhu chi dưới) bị suy yếu vì hẹp lịng mạch
do lắng đọng mỡ hoặc tích tụ calcium. Mạch máu nào cũng có thể bị hẹp. Vì vậy cần
nong mạch máu để dịng máu lưu thơng đầy đủ. Mạch máu có thể bị hẹp lại theo thời
gian ở vị trí này nên thủ thuật này có thể phải làm lại.
Chú ý
Thủ thuật tạo hình mạch máu phải được thực hiện ở bệnh nhân nội trú để dễ theo dõi và
hồi sức. Nếu thủ thuật thực hiện ở động mạch vành, bệnh nhân phải được bác sĩ và ý tá
chuyên khoa và các chuyên gia về mạch máu chăm sóc. Thơng thường, bệnh nhân được
dùng thuốc chống đông trước khi làm thủ thuật để phịng ngừa huyết khối. Tuy nhiên,
việc dùng thuốc chống đơng có thể gây khó bít điểm đi vào mạch máu. Thủ thuật sẽ được
thực hiện dưới sụ hướng dẫn của màn huỳnh quang và thuốc cản quang. Vì việc quyết
định làm tạo hình mạch máu có thể sau khi chụp mạch chẩn đốn, cần phải biết bệnh
nhân có bị mẫn cảm với thuốc cản quang iode khơng. Thủ thuật có thể dùng thuốc cản
quang khơng ion hóa.
Mơ tả
Ban đầu thủy thuật tạo hình mạch máu được thực hiện bằng cách làm giãn mạch máu với
việc đưa vào các ống thông cứng và lớn hơn qua một không gian hẹp. Biến chứng của thủ
thuật này đã làm cho các nhà nguyên cứu phát triển cách làm rộng mạch máu bằng việc
dùng thiết bị có kích thước tối thiểu. Ngày nay, các ống thơng chứa bóng được bơm căng
để làm rộng mạch máu và giá đỡ (stent) để nâng đỡ cấu trúc mạch máu. Laser có thể
được dùng để giúp phá vỡ các mảng vơi hoặc mỡ . Ống thơng có thể được gắn dây quay
hoặc mũi khoan để làm sạch các mảng xơ vữa.
Angioplasty
Definition
Angioplasty is a term describing a procedure used to widen vessels narrowed by stenoses
or occlusions. There are various types of these procedures and their names are associated
with the type of vessel entry and equipment used. For example, percutaneous
transluminal angioplasty (PTA) describes entry through the skin (percutaneous) and
navigates to the area of the vessel of interest through the same vessel or one that
communicates with it (transluminal). In the case of a procedure involving the coronary
arteries, the point of entry could be the femoral artery in the groin and the
catheter/guidewire system is passed through the aorta to the heart and the origin of the
coronary arteries at the base of the aorta just outside the aortic valve.
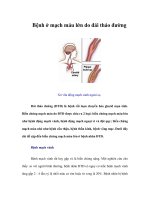
In balloon angioplasty, plaque is pushed out of the clogged artery by the inflation of
the balloon device.
(Illustration by Argosy Inc.)
Purpose
In individuals with an occulsive vascular disease such as atherosclerosis, blood flow is
impaired to an organ (such as the heart) or to a distal body part (such as the lower leg) by
the narrowing of the vessel's lumen due to fatty deposits or calcium accumulation. This
narrowing may occur in any vessel but may occur anywhere. Once the vessel has been
widened, adequate blood flow is returned. The vessel may narrow again over time at the
same location and the procedure could be repeated.
Precautions
Angioplasty procedures are performed on hospital inpatients in facilities for proper
monitoring and recovery. If the procedure is to be performed in a coronary artery, the
patient's care is likely to be provided by specially trained physicians, nurses, and vascular
specialists. Typically, patients are given anticoagulants prior to the procedure to assist in
the prevention of thromboses (blood clots). Administration of anticoagulants, however,
may impede the sealing of the vascular entry point. The procedure will be performed
using fluoroscopic guidance and contrast media. Since the decision to perform
angioplasty may have been made following a diagnostic angiogram, the patient's
sensitivity to iodinated contrast media is likely to known. The procedure may then require
the use of non-ionic contrast agents.
Description
Angioplasty was originally performed by dilating the vessel with the introduction of
larger and larger stiff catheters through the narrowed space. Complications of this
procedure caused researchers to develop means of widening the vessel using a minimally
sized device. Today, catheters contain balloons that are inflated to widen the vessel and
stents to provide structural support for the vessel. Lasers may be used to assist in the
break up of the fat or calcium plaque. Catheters may also be equipped with spinning
wires or drill tips to clean out the plaque.
Key terms
cardiac catheterization — A procedure to pass a catheter to the heart and its vessels for
the purpose of diagnosing coronary artery disease, assessing injury or disease of the
aorta, or evaluating cardiac function.
EKG — Electrocardiogram, used to study and record the electrical activity of the heart.
plaque — In atherosclerosis, a swollen area in the lining of an artery formed by fatty
deposits.
Angioplasty may be performed while the patient is sedated or anesthetized, depending on
the vessels involved. If a percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) is to be
performed, the patient will be kept awake to report on discomfort and cough if required.
PTCA procedures are performed in cardiac catheterization labs with sophisticated
monitoring devices. If angioplasty is performed in the radiology department's
angiographic suite, the patient may be sedated for the procedure and a nurse will monitor
the patient's vital signs during the procedure. If performed by a vascular surgeon, the
angioplasty procedure will be performed in an operating room or specially designed
vascular procedure suite.
The site of the introduction of the angioplasty equipment is prepared as a sterile surgical
site. Although many procedures are performed by puncturing the vessel through skin,
many procedures are also performed by surgically exposing the site of entry. Direct view
of the vessel's puncture site aids in monitoring damage to the vessel or excessive bleeding
at the site. Once the vessel is punctured and the guidewire is introduced, fluoroscopy is
used to monitor small injections of contrast media used to visualize the path through the
vessel. If the fluoroscopy system has a feature called 'roadmap', the amount of contrast
media injected will be greater in order to define the full route the guidewire will take. The
fluoroscopy system will then superimpose subsequent images over the roadmap while the
vessel is traversed, that is, the physician moves the guidewire along the map to the
destination.
Having reached the area of stenosis, the physician will inflate the balloon on the catheter
that has been passed along the guidewire. Balloons are inflated in size and duration
depending on the size and location of the vessel. In some cases, the use of a stent (a mesh
of wire that resembles a Chinese finger puzzle) may also be used. The vessel may be
widened before, during, or after the deployment of the stent. Procedures for deploying
stents are dependent on the type of stent used. In cases where the vessel is tortuous or at
intersections of vessels, the use of a graph may be necessary to provide structural strength
to the vessel. Stents, graphs, and balloon dilation may all be used together or separately.
The procedure is verified using fluoroscopy and contrast media to produce an angiogram
or by using intravascular ultrasound or both. All equipment is withdrawn from the vessel
and the puncture site repaired.
Risks
During the procedure there is a danger of puncturing the vessel with the guidewire. This
is a very small risk. Patients must be monitored for hematoma or hemorrhage at the
puncture site. There is also a small risk of heart attack, emboli, and although unlikely
death. Hospitalization will vary in length by the patient's overall condition, any
complications, and availability of home care.
Resources
Periodicals
"The angioplasty correct follow up strategy after stent implantation." Heart 84, no. 4
(April, 2001): 363.
Carnall, Douglas. "Angioplasty." The Western Journal of Medicine 173, no. 3 (September
2000): 201.
"New Imaging Technique Could Improve Outcome of Popular Heart Procedure." Heart
Disease Weekly May 13, 2001: 3.
"Success clearing clogged arteries." Science News 159, no. 5 (February 3, 2001): 72.
Other
"Cardiovascular System" Miami Heart Research Institute 2001. [cited July 5, 2001].
〈 />Center/YourCardiovascular…/Cardiovascular.htm〉.
"Coronary angioplasty: Opening clogged arteries" MayoClinic.com, Condition Centers,
Treatments and Tests. 2000. [cited July 5, 2001]. .
"Heart American Heart Association online. 2000. [cited July 5, 2001].
〈 />"STS Patient Information: What to Expect after your Heart Surgery." Society of Thoracic
Surgeons online. 2000. [cited July 5, 2001]. />"When you need to have Angioplast: A patient guide" Heart Information Network. 2000.
[cited July 5, 2001]. />Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights
reserved.
angioplasty /an·gio·plas·ty/ (an´je-o-plas″te) an angiographic procedure for elimination
of areas of narrowing in the blood vessels.
balloon angioplasty inflation and deflation of a balloon catheter inside an artery,
stretching the intima and leaving a ragged interior surface, triggering a healing response
and breaking up of plaque.
Balloon angioplasty, the expanded balloon pressing against a stenotic site in an artery.
percutaneous transluminal angioplasty a type of balloon angioplasty in which the
catheter is inserted through the skin and through the lumen of the vessel to the site of the
narrowing.
percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) percutaneous transluminal
angioplasty to enlarge the lumen of a sclerotic coronary artery.
Dorland's Medical Dictionary for Health Consumers. © 2007 by Saunders, an imprint of
Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
an·gi·o·plas·ty ( n j - -pl s t )
n.
1. Surgical reconstruction of a blood vessel.
2. Balloon angioplasty.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton
Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
angioplasty
[an′jēōplas′tē]
Etymology: Gk, angeion, vessel, plassein, to mold
the reconstruction of blood vessels damaged by disease or injury, often performed by
inflating a balloon within the vessel lumen at the site of narrowing to reconstitute flow.
See also balloon angioplasty.
Mosby's Medical Dictionary, 8th edition. © 2009, Elsevier.
angioplasty (an´jē plas´tē),
n a medical procedure used to treat angina or blockage of the coronary arteries. The
procedure involves the insertion of a balloon-tipped catheter into the body through a
small incision, usually in the groin. The catheter is guided to the blockage using
radiographs and injected dye. Once the blockage is reached, the balloon on the catheter is
gently inflated to open the blood vessel. Also called
percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA).
Mosby's Dental Dictionary, 2nd edition. © 2008 Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
angioplasty
surgical repair of blood vessels or lymphatic channels.
percutaneous transluminal angioplasty
dilatation of a blood vessel by means of a balloon catheter inserted through the skin and
into the chosen vessel and then passed through the lumen of the vessel to the site of the
lesion, where the balloon is inflated to flatten plaque against the artery wall. Called also
PCTA.
Saunders Comprehensive Veterinary Dictionary, 3 ed. © 2007 Elsevier, Inc. All rights
reserved
angioplasty
Any interventional repair of a blood vessel. See Balloon angioplasty, Deferred adjunctive
coronary angioplasty, Immediate adjunctive coronary angioplasty, Kissing balloon
coronary angioplasty, Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty, Primary coronary
angioplasty, Rescue adjunctive coronary angioplasty, Rescue renal angioplasty.
McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc.
Anode
A positively charged electrode that attracts electrons from the negatively charged cathode
which serves as a target source for x-ray photons. There are two types of anodes, rotating
and stationary.
/>