Telephone (kỹ THUẬT TRUYỀN số LIỆU SLIDE)
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (752.13 KB, 26 trang )
Using Telephone and Cable Networks
for Data Transmissions
Outline
Telephone lines
Dial-up modems
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
Cable TV networks
2
Telephone Lines
Traditional telephone lines can carry frequencies between 300
and 3300 Hz
Giving them a bandwidth of 3000 Hz
All this range is used for transmitting voice
A great deal of interference and distortion can be accepted without
loss of intelligibility
3
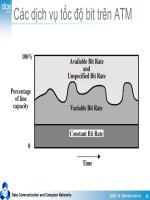
Telephone Line Bandwidth
4
Dial-Up Modems
Modem
stands for modulator/demodulator.
5
V.32 and V.32bis
6
56K Modems
7
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
Provides higher-speed access to the Internet
Supports high-speed digital communication over the existing local
loops
The existing local loops can handle bandwidths up to 1.1 MHz.
8
ADSL
ADSL – Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line
Downstream bit rate > upstream bit rate
Designed for residential users
Unsuitable for businesses
ADSL operates on existing local loops
Local loops can handle up to 1.1 MHz of bandwidth
The distance limit is ~18,000 feet
The system uses a data rate based on the condition of the local loop
line
9
Bandwidth Division in ADSL
10
Discrete Multi-Tone Modulation
Or DMT, based on OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency-Division
Multiplexing) technique
11
Bandwidth Division
4 kHz
Allocation and modulation of each channel
are determined adaptively
12
Bandwidth Division
Voice – Channel 0
Idle – Channels 1-5
Upstream – Channels 6-30
24 data channels, 1 control channel
1.44 Mbps (max) upstream bit rate
Actual bit rate: 64 Kbps to 1 Mbps
Downstream – Channels 31-255
224 data channels, 1 control channel
13.4 Mbps (max) downstream bit rate
Actual bit rate: 500 Kbps to 8 Mbps
13
ADSL Customer Residence
14
DSL Access Multiplexer
Or DSLAM
15
Other DSL Technologies
HDSL – High-bit-rate DSL
VDSL – Very-high-bit-rate DSL
SDSL – Symmetric DSL
Source: AWARE. ADSL2 and ADSL2+ The new ADSL
standard.
ADSL2
ADSL2+
See also
/>
16
OFDM
Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing
Widely used in wideband digital communications
Digital TV
ADSL
Powerline communications
Wireless networks: Wi-Fi, WiMAX
4G mobile communications
17
OFDM Concept
Sub-carriers are orthogonal to each other
No cross-talk; guard bands not necessary
Source:
18
Orthogonality in OFDM
20 ms
Modulated @500 Hz
t
Modulated @550 Hz
t
Modulated @600 Hz
t
200
300
400
500
600
700
Frequency (Hz)
19
800
OFDM Implementation
Transmitter
Receiver
Source: Wikipedia
20
Cable TV Networks
Started as a video service provider, then moved to the business
of Internet access
Communication is simplex
21
Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial Network
Or HFC
Bidirectional communication is achieved
22
Data Transfer over CATV
Standard: DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification)
Division of coaxial cable band by Cable TV
Theoretical downstream data rate is 30 Mbps
Theoretical upstream data rate is 12 Mbps
23
Cable Modem
24
Cable Modem Transmission System
Or CMTS
25