Lecture Mechanics of materials (Third edition) - Chapter 8: Principle stresses under a given loading
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (770.36 KB, 10 trang )
<span class='text_page_counter'>(1)</span><div class='page_container' data-page=1>
<b>MECHANICS OF </b>
<b>MATERIALS</b>
<b>Ferdinand P. Beer</b>
<b>E. Russell Johnston, Jr.</b>
<b>John T. DeWolf</b>
<b>Lecture Notes:</b>
<b>J. Walt Oler</b>
<b>Texas Tech University</b>
CHAPTER
Principle Stresses
Under a Given
</div>
<span class='text_page_counter'>(2)</span><div class='page_container' data-page=2>
Principle Stresses Under a Given Loading
Introduction
Principle Stresses in a Beam
Sample Problem 8.1
Sample Problem 8.2
Design of a Transmission Shaft
Sample Problem 8.3
</div>
<span class='text_page_counter'>(3)</span><div class='page_container' data-page=3>
Introduction
• In Chaps. 1 and 2, you learned how to determine the normal stress due
to centric loads
In Chap. 3, you analyzed the distribution of shearing stresses in a
circular member due to a twisting couple
In Chap. 4, you determined the normal stresses caused by bending
couples
In Chaps. 5 and 6, you evaluated the shearing stresses due to transverse
loads
</div>
<span class='text_page_counter'>(4)</span><div class='page_container' data-page=4>
Principle Stresses in a Beam
• Prismatic beam subjected to transverse
loading
<i>It</i>
<i>VQ</i>
<i>It</i>
<i>VQ</i> <i>I</i>
<i>Mc</i>
<i>I</i>
<i>My</i>
<i>m</i>
<i>xy</i>
<i>m</i>
<i>x</i>
=
−
=
=
−
=
τ
τ
σ
σ
• Principal stresses determined from methods
of Chapter 7
• Can the maximum normal stress within
the cross-section be larger than
<i>I</i>
<i>Mc</i>
<i>m</i> =
</div>
<span class='text_page_counter'>(5)</span><div class='page_container' data-page=5></div>
<span class='text_page_counter'>(6)</span><div class='page_container' data-page=6>
Principle Stresses in a Beam
• Cross-section shape results in large values of
τ
<i><sub>xy</sub></i>near the surface where
σ
<i><sub>x</sub></i> is also large.</div>
<span class='text_page_counter'>(7)</span><div class='page_container' data-page=7>
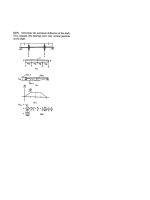
Sample Problem 8.1
SOLUTION:
• Determine shear and bending
moment in Section <i>A-A’</i>
• Calculate the normal stress at top
surface and at flange-web junction.
A 160-kN force is applied at the end
of a W200x52 rolled-steel beam.
Neglecting the effects of fillets and
of stress concentrations, determine
• Evaluate the shear stress at
flange-web junction.
</div>
<span class='text_page_counter'>(8)</span><div class='page_container' data-page=8>
Sample Problem 8.1
SOLUTION:
• Determine shear and bending moment in
Section <i>A-A’</i>
(
)(
)
kN
160
m
-kN
60
m
375
.
0
kN
160
=
=
=
<i>A</i>
<i>A</i>
<i>V</i>
<i>M</i>
• Calculate the normal stress at top surface
and at flange-web junction.
</div>
<span class='text_page_counter'>(9)</span><div class='page_container' data-page=9>
Sample Problem 8.1
• Evaluate shear stress at flange-web junction.
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
MPa
5
.
95
m
0079
.
0
m
10
7
.
52
m
10
6
.
248
kN
160
m
10
6
.
248
mm
10
6
.
248
7
.
96
6
.
12
204
4
6
3
6
3
6
3
3
=
ì
ì
=
=
ì
=
ì
=
ì
=
<i>It</i>
<i>Q</i>
<i>V</i>
<i>Q</i>
<i>A</i>
<i>b</i>
ã Calculate the principal stress at
flange-web junction
( )
(
)
9
.
102
9
.
102 2
2
2
2
1
2
1
max
⎞
⎛
+
+
</div>
<span class='text_page_counter'>(10)</span><div class='page_container' data-page=10>
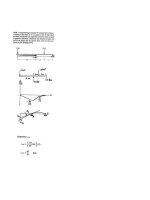
Sample Problem 8.2
The overhanging beam supports a
uniformly distributed load and a
concentrated load. Knowing that for
the grade of steel to used
σ
<i><sub>all</sub></i> = 24 ksiand
τ
<i><sub>all</sub></i> = 14.5 ksi, select thewide-flange beam which should be used.
SOLUTION:
• Determine reactions at <i>A</i> and <i>D.</i>
• Find maximum shearing stress.
• Find maximum normal stress.
• Calculate required section modulus
and select appropriate beam section.
• Determine maximum shear and
</div>
<!--links-->