Lecture Human resource management: Gaining a competitive advantage (9/e) – Chapter 6: Selection and placement
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (1.13 MB, 11 trang )
Chapter 6
Selection and Placement
Copyright © 2015 McGrawHill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGrawHill Education.
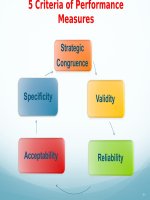
5 Evaluation Selection Method Standards
1. Reliability
2. Validity
3. Generalizability
4. Utility
5. Legality
62
Legality
All selection methods must conform to existing
laws and legal precedents.
Three acts form the basis for a majority of suits
filed by job applicants:
Civil Rights Act of 1991 and 1964
Age Discrimination in Employment Act of
1967
Americans with Disabilities Act of 1991
63
Types of Selection Methods
JOBS
64
Interviews
Selection interviews-a dialogue initiated by one
or more persons to gather information and
evaluate the applicant’s qualifications for
employment.
To increase an interview’s utility:
Interviews should be structured, standardized, and
focused on goals oriented to skills and observable
behaviors.
Interviewers should be able to quantitatively rate each
interview.
Interviewers should have a structured note-taking
65
system that will aid recall to satisfying ratings.
Experience-Based
Situational Interview Items
Table 6.2
Experience Based
Motivating employees:
“Think about an instance when you had
to motivate an employee to perform a
task that he or she disliked but that you
needed to have done. How did you
handle that situation?”
Resolving conflict:
“What was the biggest difference of
opinion you ever had with a co-worker?
How did you resolve that situation?”
Overcoming resistance
to change:
“What was the hardest change you ever
had to bring about in a past job, and
what did you do to get the people
around you to change their thoughts or
behaviors?”
66
Future Oriented
Situational Interview Items
Table 6.2
Future Oriented
Motivating employees:
Suppose you were working with an
employee who you knew greatly disliked
performing a particular task. You needed
to get this task completed, however, and
this person was the only one available to
do it. What would you do to motivate that
person?”
Resolving conflict:
““Imagine that you and a co-worker
disagree about the best way to handle an
absenteeism problem with another
member of your team. How would you
resolve that situation?”
Overcoming resistance
to change:
“Suppose you had an idea for change in
work procedures that would enhance
quality, but some members of your work
group were hesitant to make the change.67
What would you do in that situation?”
Big 5 Dimensions
of Personality Inventories
68
Emotional Intelligence
69
Summary of Selection Methods
JOBS
610
Summary
Job applicants and an organization’s viability are affected
by decisions regarding who is accepted and rejected for
positions.
Five standards should conform: reliability, validity,
generalizability, utility and legality.
Managerial assessment centers use many different forms
of tests over a two or three day period to learn as much as
possible about candidates for important executive
positions.
Validity associated with judicious use of multiple tests is
higher than for tests used in isolation.
611