Lecture Human resource management: Gaining a competitive advantage (9/e) – Chapter 8: Performance management
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (1.05 MB, 11 trang )
Chapter 8
Performance Management
Copyright © 2015 McGrawHill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGrawHill Education.
Introduction
82
Performance Management Process
83
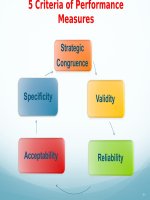
5 Criteria of Performance Measures
84
Competency Model
Competencies are sets of skills, knowledge,
abilities and personal characteristics that enable
employees to successfully perform their jobs.
A competency model identifies competencies
necessary for each model and provides
descriptions common for an entire occupation,
organization, job family or specific job, useful for
recruiting, selection, training and development.
85
Balanced Scorecard Approach
86
Typical Rater Errors
1. Similar to Me
2. Contrast
3. Leniency
4. Strictness
5. Central Tendency
6. Halo
7. Horns
87
Improve Performance Feedback
1. Give feedback frequently, not once a year.
2. Create right context for discussion.
3. Ask employees to rate performance before the
session.
4. Encourage employee to participate.
5. Recognize effective performance through praise.
6. Focus on solving problems.
7. Focus feedback on behavior or results, not on the
person.
8. Minimize criticism.
88
9. Agree to specific goals and set progress review date.
Employee
Characteristics
89
Withstand Legal Scrutiny
1. Conduct a valid job analysis related to
performance.
2. Base system on specific behaviors or results.
3. Train raters to use system correctly.
4. Review performance ratings and allow for
employee appeal.
5. Provide guidance/support for poor performers.
6. Use multiple raters.
7. Document performance evaluations.
810
Summary
Measuring and managing performance are key to gain
competitive edge.
Performance management systems (PMS) serve strategic,
administrative and developmental purposes.
PMS should be evaluated against criteria of strategic
congruence, validity, reliability, acceptability and
specificity.
Effective managers need to
be aware of the issues involved in determining best
methods and legal scrutiny.
feed performance information back to employees
take action based on causes for poor performance: ability,
motivation or both
811