autocad 2016 a problem solving approach basic and intermediate 2nd edition pdf
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (26.47 MB, 1,376 trang )
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
AutoCAD 2016
A Problem-Solving Approach,
Basic and Intermediate
(22nd Edition)
CADCIM Technologies
525 St. Andrews Drive
Schererville, IN 46375, USA
(www.cadcim.com)
Contributing Author
Sham Tickoo
Professor
Department of Mechanical Engineering Technology
Purdue University Calumet
Hammond, Indiana, USA
AutoCAD 2016: A Problem-Solving Approach, Basic and Intermediate
Sham Tickoo
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
CADCIM Technologies
525 St Andrews Drive
Schererville, Indiana 46375, USA
www.cadcim.com
Copyright © 2015 by CADCIM Technologies, USA. All rights reserved. Printed in the United States of America
except as permitted under the United States Copyright Act of 1976.
No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, or stored in the
database or retrieval system without the prior permission of CADCIM Technologies.
ISBN 978-1-942689-00-3
NOTICE TO THE READER
Publisher does not warrant or guarantee any of the products described in the text or perform any independent
analysis in connection with any of the product information contained in the text. Publisher does not assume,
and expressly disclaims,any obligation to obtain and include information other than that provided to it by the
manufacturer.
The reader is expressly warned to consider and adopt all safety precautions that might be indicated by the
activities herein and to avoid all potential hazards. By following the instructions contained herein, the reader
willingly assumes all risks in connection with such instructions.
The Publisher makes no representation or warranties of any kind, including but not limited to, the warranties of
fitness for particular purpose or merchantability, nor are any such representations implied with respect to the
material set forth herein, and the publisher takes no responsibility with respect to such material. The publisher
shall not be liable for any special, consequential, or exemplary damages resulting, in whole or part, from the
reader’s use of, or reliance upon, this material.
www.cadcim.com
CADCIM Technologies
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
DEDICATION
To teachers, who make it possible to disseminate knowledge
to enlighten the young and curious minds
of our future generations
To students, who are dedicated to learning new technologies
and making the world a better place to live in
SPECIAL RECOGNITION
A special thanks to Mr. Denis Cadu and the ADN team of Autodesk Inc.
for their valuable support and professional guidance to
procure the software for writing this textbook
THANKS
To the faculty and students of the MET department of
Purdue University Calumet for their cooperation
To employees of CADCIM Technologies for their valuable help
Online Training Program Offered by CADCIM Technologies
CADCIM Technologies provides effective and affordable virtual online training on
various software packages including Computer Aided Design and Manufacturing
(CAD/CAM), computer programming languages, animation, architecture, and GIS.
The training is delivered ‘live’ via Internet at any time, any place, and at any pace to
individuals as well as the students of colleges, universities, and CAD/CAM training
centers. The main features of this program are:
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Training for Students and Companies in a Classroom Setting
Highly experienced instructors and qualified engineers at CADCIM Technologies
conduct the classes under the guidance of Prof. Sham Tickoo of Purdue University
Calumet, USA. This team has authored several textbooks that are rated “one of the
best” in their categories and are used in various colleges, universities, and training
centers in North America, Europe, and in other parts of the world.
Training for Individuals
CADCIM Technologies with its cost effective and time saving initiative strives to
deliver the training in the comfort of your home or work place, thereby relieving you
from the hassles of traveling to training centers.
Training Offered on Software Packages
CADCIM provides basic and advanced training on the following software packages:
CAD/CAM/CAE: CATIA, Pro/ENGINEER Wildfire, PTC Creo Parametric, Creo
Direct, SOLIDWORKS, Autodesk Inventor, Solid Edge, NX, AutoCAD, AutoCAD LT,
AutoCAD Plant 3D, Customizing AutoCAD, EdgeCAM, and ANSYS
Architecture and GIS: Autodesk Revit Architecture, AutoCAD Civil 3D, Autodesk
Revit Structure, AutoCAD Map 3D, Revit MEP, Navisworks, Primavera, and Bentley
STAAD Pro
Animation and Styling: Autodesk 3ds Max, Autodesk 3ds Max Design, Autodesk
Maya, Autodesk Alias, The Foundry NukeX, MAXON CINEMA 4D, Adobe Flash, and
Adobe Premiere
Computer Programming: C++, VB.NET, Oracle, AJAX, and Java
For more information, please visit the following link:
Note
If you are a faculty member, you can register by clicking on the following link to
access the teaching resources: The
student resources are available at . We also provide Live
Virtual Online Training on various software packages. For more information, write
us at
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Dedication
Preface
Chapter 1: Introduction to AutoCAD
AutoCAD Screen Components
Start Tab
Drawing Area
Command Window
Navigation Bar
ViewCube
In-canvas Viewport Controls
Status Bar
Invoking Tools in AutoCAD
Keyboard
Ribbon
Application Menu
Tool Palettes
Menu Bar
Toolbar
Shortcut Menu
File Tabs
AutoCAD Dialog Boxes
Starting a New Drawing
Open a Drawing
Start from Scratch
Use a Template
Use a Wizard
Saving Your Work
Save Drawing As Dialog Box
Automatic Timed Save
Creating Backup Files
Changing Automatic Timed Saved and Backup Files into AutoCAD Format
Using the Drawing Recovery Manager to Recover Files
Closing a Drawing
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Opening an Existing Drawing
Opening an Existing Drawing Using the Select File Dialog Box
Opening an Existing Drawing Using the Startup Dialog Box
Opening an Existing Drawing Using the Drag and Drop Method
Quitting AutoCAD
Creating and Managing Workspaces
Creating a New Workspace
Modifying the Workspace Settings
AutoCAD Help
Autodesk Cloud
Autodesk Exchange Apps
Design Feed
BIM 360
Additional Help Resources
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 2: Getting Started with AutoCAD
Dynamic Input Mode
Enable Pointer Input
Enable Dimension Input where possible
Show command prompting and command input near the crosshairs
Show additional tips with command prompting
Drafting Tooltip Appearance
Drawing Lines in AutoCAD
The Close Option
The Undo Option
Invoking tools Using Dynamic INPUT/Command Prompt
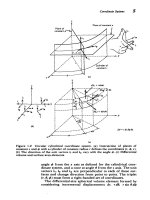
Coordinate Systems
Absolute Coordinate System
Relative Coordinate System
Relative Polar Coordinates
Direct Distance Entry
Erasing Objects
Canceling and Undoing Operation
Object Selection Methods
Window Selection
Window Crossing Method
Lasso Selection Method
Drawing a Circle
Basic Display Commands
Zooming Drawings
Setting Units Type and Precision
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Specifying the Format
Specifying the Angle Format
Setting the Direction for Angle Measurement
Specifying Units for the Drawing or the Block to be Inserted
Sample Output
Specifying Units for Lighting
Setting the Limits of a Drawing
Setting Limits
Limits for Architectural Drawings
Limits for Metric Drawings
Introduction to Plotting Drawings
Modifying AutoCAD Settings by Using the Options Dialog Box
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 3: Getting Started with Advanced Sketching
Drawing Arcs
Drawing Rectangles
Drawing Ellipses
Drawing Regular Polygons
Drawing Polylines
Drawing Donuts
Placing Points
Changing the Point Style and Size
Placing Multiple Points
Placing Points at Equal Distance
Placing Points at Specified Intervals
Drawing Infinite Lines
Drawing Construction Lines
Drawing Ray
Writing a Single Line Text
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 4: Working with Drawing Aids
Introduction
Understanding the Concept and Use of Layers
Working with Layers
Creating New Layers
Making a Layer Current
Controlling the Display of Layers
Arranging Layers in Increasing Order
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Arranging Layers in Increasing Order with Respect to First Digit
Merging Layers
Deleting Layers
Managing the Display of Columns
Selective Display of Layers
Layer States
Reconciling New Layers
Isolating and Unisolating Layers
Controlling the Layer Settings
Object Properties
Changing the Color
Changing the Linetype
Changing the Lineweight
Changing the Plot Style
Changing Object Properties using the Properties Palette
Changing Object Properties using the Quick Properties Palette
Global and Current Linetype Scaling
LTSCALE Factor for Plotting
Working with the DesignCenter
Drafting Settings Dialog Box
Setting Grid
Setting Snap
Snap Type
Drawing Straight Lines Using the Ortho Mode
Working with Object Snaps
Running Object Snap Mode
Overriding the Running Snap
Cycling through Snaps
Setting the Priority for Coordinate Entry
Using AutoTracking
Object Snap Tracking
Polar Tracking
AutoTrack Settings
Function and Control Keys
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 5: Editing Sketched Objects-I
Creating a Selection Set
Editing Sketches
Moving Sketched Objects
Copying Sketched Objects
Creating Multiple Copies
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Creating an Array of Selected Objects
Creating a Single Copy
Pasting Contents from the Clipboard
Pasting Contents Using the Original Coordinates
Offsetting Sketched Objects
Through Option
Erase Option
Layer Option
Rotating Sketched Objects
Scaling the Sketched Objects
Filleting the Sketches
Chamfering the Sketches
Blending the Curves
Trimming the Sketched Objects
Extending the Sketched Objects
Stretching the Sketched Objects
Lengthening the Sketched Objects
Arraying the Sketched Objects
Rectangular Array
Polar Array
Path Array
Mirroring the Sketched Objects
Text Mirroring
Breaking the Sketched Objects
Placing Points at Specified Intervals
Dividing the Sketched Objects
Joining the Sketched Objects
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 6: Editing Sketched Objects-II
Introduction to Grips
Types of Grips
Adjusting Grip Settings
Editing Objects by Using Grips
Stretching the Objects by Using Grips (Stretch Mode)
Moving the Objects by Using Grips (Move Mode)
Rotating the Objects by Using Grips (Rotate Mode)
Scaling the Objects by Using Grips (Scale Mode)
Mirroring the Objects by Using Grips (Mirror Mode)
Editing a Polyline by Using Grips
Loading Hyperlinks
Editing Gripped Objects
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Changing the Properties Using the Properties Palette
Matching the Properties of Sketched Objects
Quick Selection of Sketched Objects
Cycling Through Selection
Managing Contents Using the DesignCenter
Folders Tab
Open Drawings Tab
History Tab
Autodesk Seek design content Link
Making Inquiries About Objects and Drawings
Measuring Area of Objects
Measuring the Distance between Two Points
Identifying the Location of a Point
Listing Information about Objects
Listing Information about all Objects in a Drawing
Checking Time-Related Information
Obtaining Drawing Status Information
Displaying Drawing Properties
Basic Display Options
Redrawing the Screen
Regenerating Drawings
Zooming Drawings
Panning Drawings
Creating Views
Understanding the Concept of Sheet Sets
Creating a Sheet Set
Adding a Subset to a Sheet Set
Adding Sheets to a Sheet Set or a Subset
Archiving a Sheet Set
Resaving all Sheets in a Sheet Set
Placing Views on a Sheet of a Sheet Set
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 7: Creating Texts and Tables
Annotative Objects
Annotation Scale
Assigning Annotative Property and Annotation Scales
Customizing Annotation Scale
Multiple Annotation Scales
Assigning Multiple Annotation Scales Manually
Assigning Multiple Annotation Scales Automatically
Controlling the Display of Annotative Objects
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Creating Text
Writing Single Line Text
Entering Special Characters
Creating Multiline Text
Editing Text
Editing Text Using the DDEDIT Command
Editing Text Using the Properties Palette
Modifying the Scale of the Text
Aligning Text
Inserting Table in the Drawing
Creating a New Table Style
Setting a Table Style As Current
Modifying a Table Style
Modifying Tables
Creating Text Styles
Creating Annotative Text
Checking Spelling
Text Quality and Text Fill
Finding and Replacing Text
Creating Title Sheet Table in a Sheet Set
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 8: Basic Dimensioning, Geometric Dimensioning, and Tolerancing
Need for Dimensioning
Dimensioning in AutoCAD
Fundamental Dimensioning Terms
Dimension Line
Dimension Text
Arrowheads
Extension Lines
Leader
Center Mark and Centerlines
Alternate Units
Tolerances
Limits
Associative Dimensions
Definition Points
Annotative Dimensions
Selecting Dimensioning Tools
Dimensioning a Number of Objects Together
Creating Linear Dimensions
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Creating Aligned Dimensions
Creating Arc Length Dimensions
Creating Rotated Dimensions
Creating Baseline Dimensions
Creating Continued Dimensions
Creating Angular Dimensions
Creating Diameter Dimensions
Creating Jogged Dimensions
Creating Radius Dimensions
Creating Jogged Linear Dimensions
Generating Center Marks and Centerlines
Creating Ordinate Dimensions
Maintaining Equal Spacing between Dimensions
Creating Dimension Breaks
Creating Inspection Dimensions
Working with True Associative Dimensions
Removing the Dimension Associativity
Converting a Dimension into a True Associative Dimension
Drawing Leaders
Multileaders
Drawing Multileaders
Adding Leaders to Existing Multileader
Removing Leaders from Existing Multileader
Aligning Multileaders
Collecting Multiple Leaders
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing
Geometric Characteristics and Symbols
Adding Geometric Tolerance
Complex Feature Control Frames
Combining Geometric Characteristics
Composite Position Tolerancing
Using Feature Control Frames with Leaders
Projected Tolerance Zone
Creating Annotative Dimensions, Tolerances, Leaders, and Multileaders
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 9: Editing Dimensions
Editing Dimensions Using Editing Tools
Editing Dimensions by Stretching
Editing Dimensions by Trimming and Extending
Flipping Dimension Arrow
Modifying the Dimensions
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Editing the Dimension Text
Updating Dimensions
Editing Dimensions with Grips
Editing Dimensions Using the Properties Palette
Model Space and Paper Space Dimensioning
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 10: Dimension Styles, Multileader Styles, and System
Using Styles and Variables to Control Dimensions
Creating and Restoring Dimension Styles
New Dimension Style Dialog box
Controlling the Dimension Text Format
Fitting Dimension Text and Arrowheads
Formatting Primary Dimension Units
Formatting Alternate Dimension Units
Formatting the Tolerances
Dimension Style Families
Using Dimension Style Overrides
Comparing and Listing Dimension Styles
Using Externally Referenced Dimension Styles
Creating and Restoring Multileader Styles
Modify Multileader Style Dialog Box
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 11: Adding Constraints to Sketches
Introduction
Adding Geometric Constraints
Applying the Horizontal Constraint
Applying the Vertical Constraint
Applying the Coincident Constraint
Applying the Fix Constraint
Applying the Perpendicular Constraint
Applying the Parallel Constraint
Applying the Collinear Constraint
Applying the Concentric Constraint
Applying the Tangent Constraint
Applying the Symmetric Constraint
Applying the Equal Constraint
Applying the Smooth Constraint
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Controlling the Display of Constraints
Applying Constraints Automatically
Applying Dimensional Constraints
Converting a Dimensional Constraint into an Annotational Constraint
Concept of a Fully-Defined Sketch
Under-defined
Fully-defined
Over-defined
Controlling the Display of the Dimensional Constraint
Working with Equations
Adding Equations while Applying Dimensional Constraints
Adding Equations Using the Parameters Manager
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 12: Hatching Drawings
Hatching
Hatch Patterns
Hatch Boundary
Hatching Drawings Using the Hatch Tool
Panels in the Hatch Creation Tab
Creating Annotative Hatch
Hatching the Drawing Using the Tool Palettes
Drag and Drop Method
Select and Place Method
Modifying the Properties of the Predefined Patterns available
in the Tool Palettes
Hatching Around Text, Dimensions, and Attributes
Editing Hatch Patterns
Using the Hatch Editor Tab
Using the Edit Hatch Tool
Using the Properties Tool
Editing the Hatch Boundary
Using Grips
Trimming the Hatch Patterns
Using AutoCAD Editing Tools
Hatching Blocks and Xref Drawings
Creating a Boundary Using Closed Loops
Other Features of Hatching
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 13: Model Space Viewports, Paper Space Viewports, and Layouts
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Model Space and Paper Space/Layouts
Model Space Viewports (Tiled Viewports)
Creating Tiled Viewports
Making a Viewport Current
Joining Two Adjacent Viewports
Splitting and Resizing Viewports in Model Space
Paper Space Viewports (Floating Viewports)
Creating Floating Viewports
Creating Rectangular Viewports
Creating Polygonal Viewports
Converting an Existing Closed Object into a Viewport
Temporary Model Space
Editing Viewports
Controlling the Display of Objects in Viewports
Locking the Display of Objects in Viewports
Controlling the Display of Hidden Lines in Viewports
Clipping Existing Viewports
Maximizing Viewports
Controlling the Properties of Viewport Layers
Controlling the Layers in Viewports Using Layer Properties Manager Dialog Box
Paper Space Linetype Scaling (PSLTSCALE System variable)
Inserting Layouts
Importing Layouts to Sheet Sets
Inserting a Layout Using the Wizard
Defining Page Settings
Working with the MVSETUP Command
Converting the Distance Between Model Space and Paper Space
Controlling the Display of Annotative Objects in Viewports
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 14: Plotting Drawings
Plotting Drawings in AutoCAD
Plotting Drawings Using the Plot Dialog Box
Adding Plotters
Editing the Plotter Configuration
Importing PCP/PC2 Configuration Files
Setting Plot Parameters
Working with Page Setups
Using Plot Styles
Adding a Plot Style
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Plot Style Table Editor
Applying Plot Styles
Setting the Current Plot Style
Plotting Sheets in a Sheet Set
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 15: Template Drawings
Creating Template Drawings
Standard Template Drawings
Loading a Template Drawing
Customizing Drawings with Layers and Dimensioning Specifications
Customizing a Drawing with Layout
Customizing Drawings with Viewports
Customizing Drawings According to Plot Size and Drawing Scale
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 16: Working with Blocks
The Concept of Blocks
Converting Entities into a Block
Inserting Blocks
Creating and Inserting Annotative Blocks
Block Editor
Dynamic Blocks
Adding Parameter and Action Simultaneously Using Parameter Sets
Inserting Blocks Using the DesignCenter
Using Tool Palettes to Insert Blocks
Inserting Blocks in the Drawing
Modifying Properties of the Blocks in the Tool Palettes
Adding Blocks in Tool Palettes
Drag and Drop Method
Shortcut Menu
Modifying Existing Blocks in the Tool Palettes
Layers, Colors, Linetypes, and Lineweights for Blocks
Nesting of Blocks
Inserting Multiple Blocks
Creating Drawing Files Using the Write Block Dialog box
Defining the Insertion Base Point
Editing Blocks
Editing Blocks in Place
Exploding Blocks Using the XPLODE Command
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Renaming Blocks
Deleting Unused Blocks
Applying Constraints to Blocks
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 17: Defining Block Attributes
Understanding Attributes
Defining Attributes
Editing Attribute Definition
Using the Properties Palette
Inserting Blocks with Attributes
Managing Attributes
Extracting Attributes
Controlling the Attribute Visibility
Editing Block Attributes
Editing Attributes Using the Enhanced Attribute Editor
Editing Attributes Using the Edit Attributes Dialog Box
Global Editing of Attributes
Redefining a Block with Attributes
In-place Editing of Blocks with Attributes
Inserting Text Files in the Drawing
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 18: Understanding External References
External References
Dependent Symbols
Managing External References in a Drawing
The Overlay Option
Attaching Files to a Drawing
Working with Underlays
Editing an Underlay
Opening an Xreffed Object in a Separate Window
Using the DesignCenter to Attach a Drawing as an Xref
Adding Xref Dependent Named Objects
Clipping External References
Displaying Clipping Frame
Demand Loading
Editing References In-Place
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Chapter 19: Working with Advanced Drawing Options
Understanding the Use of Multilines
Defining the Multiline Style
Drawing Multilines
Editing Multilines by Using Grips
Editing Multilines by Using the Dialog Box
Cross Intersection (CC/OC/MC)
Tee Intersection (CT/OT/MT)
Corner Joint (CJ)
Adding and Deleting Vertices (AV/DV)
Cutting and Welding Multilines (CS/CA/WA)
Creating Revision Clouds
Rectangular Revision Cloud
Polygonal Revision Cloud
Freehand Revision Cloud
Creating Wipeouts
Creating NURBS
Editing Splines
Editing Splines using 3D Edit Bar
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 20: Grouping and Advanced Editing of Sketched Objects
Grouping Sketched Objects Using the Object Grouping Dialog Box
Grouping Sketched Objects Using the Group Button
Selecting Groups
Changing Properties of an Object
Exploding Compound Objects
Editing Polylines
Editing Single Polyline
Editing Multiple Polylines
Undoing Previous Commands
Reversing the Undo Operation
Renaming Named Objects
Removing Unused Named Objects
View items you can purge
View items you cannot purge
Setting Selection Modes Using the Options Dialog Box
Noun/verb selection
Use Shift to add to selection Option
Implied windowing
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Press and drag
Object grouping
Associative Hatch
Pickbox Size
Window selection method
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
Chapter 21: Working with Data Exchange & Object Linking and Embedding
Understanding the Concept of Data Exchange in AutoCAD
Creating Data Interchange (DXF) Files
Creating a Data Interchange File
Information in a DXF File
Converting DXF Files into Drawing Files
Importing CAD Files
Other Data Exchange Formats
DXB File Format
Creating and Using an ACIS File
Importing 3D Studio Files
Creating and Using a Windows Metafile
Creating and Using a V8 DGN File
Creating a BMP File
Raster Images
Attaching Raster Images
Managing Raster Images
Editing Raster Image Files
Clipping Raster Images
Adjusting Raster Images
Modifying the Image Quality
Modifying the Transparency of an Image
Controlling the Display of Image Frames
Changing the Display Order
Other Editing Operations
Scaling Raster Images
DWG Convert
Conversion Setup Options
Working with PostScript Files
Creating PostScript Files
Object Linking and Embedding (OLE)
Content Explorer
Self-Evaluation Test
Review Questions
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Index I-1
Preface
AutoCAD 2016
AutoCAD, developed by Autodesk Inc., is the most popular PC-CAD system available
in the market. Today, over 7 million people use AutoCAD and other AutoCAD-based
design products. 100% of the Fortune 100 firms and 98% of the Fortune 500 firms are
Autodesk customers. AutoCAD’s open architecture allows third-party developers to
write application software which has significantly added to its popularity. For example,
the author of this book has developed a software package “SMLayout” for sheet metal
products that generates a flat layout of various geometrical shapes such as transitions,
intersections, cones, elbows, tank heads, and so on. Several companies in Canada and
United States are using this software package with AutoCAD to design and
manufacture various products. AutoCAD also facilitates customization that enables the
users to increase their efficiency and improve their productivity.
The AutoCAD 2016: A Problem-Solving Approach, Basic and Intermediate
textbook contains a detailed explanation of AutoCAD commands and their applications
to solve drafting and design problems. Every AutoCAD command is thoroughly
explained with the help of examples and illustrations. This makes it easy for the users to
understand the functions and applications in the drawing. After reading this textbook,
you will be able to use AutoCAD commands to make a drawing, dimension a drawing,
apply constraints to sketches, insert symbols as well as create text, blocks and dynamic
blocks.
The book also covers basic drafting and design concepts that provide you with the
essential drafting skills to solve the drawing problems in AutoCAD. These include
dimensioning principles, and assembly drawings. While going through this textbook,
you will discover some new unique applications of AutoCAD that will have a significant
effect on your drawings. In addition, you will be able to understand why AutoCAD has
become such a popular software package and an international standard in PC-CAD.
Formatting Conventions Used in the Textbook
Refer to the following list for the formatting conventions used in this textbook.
• Command names are capitalized and written in boldface letters.
• A key icon appears when you have to respond by pressing the ENTER or the
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
RETURN key.
• Command sequences are indented. The responses are indicated in boldface. The
directions are indicated in italics and the comments are enclosed in parentheses.
• The methods of invoking a tool/option from the Ribbon, Menu Bar, Quick Access
Toolbar, Tool Palettes, Application menu, toolbars, Status Bar, and Command
prompt are enclosed in a shaded box.
Ribbon: Draw > Line
Menu Bar: Draw > Line
Tool P alettes: Draw > Line
Toolbar: Draw > Line
Command: LINE or L
Example: The MOVE command
Command: MOVE
Select object: G
Enter group name: Enter a group name (the group name is group1)
Naming Conventions Used in the Textbook
Tool
If you click on an item in a toolbar or a panel of the Ribbon and a command is
invoked to create/edit an object or perform some action, then that item is termed as
tool.
For example:
To Create: Line tool, Circle tool, Extrude tool
To Edit: Fillet tool, Array tool, Stretch tool
Action: Zoom tool, Move tool, Copy tool
If you click on an item in a toolbar or a panel of the Ribbon and a dialog box is
invoked wherein you can set the properties to create/edit an object, then that item is
also termed as tool, refer to Figure 1.
For example:
To Create: Define Attributes tool, Create tool, Insert tool
To Edit: Edit Attributes tool, Block Editor tool
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Figure 1 Various tools in the Ribbon
Button
If you click on an item in a toolbar or a panel of the Ribbon and the display of the
corresponding object is toggled on/off, then that item is termed as Button. For
example, Grid button, Snap button, Ortho button, Properties button, Tool Palettes
button, and so on; refer to Figure 2.
Figure 2 Various button displayed in the Status Bar and Ribbon
The item in a dialog box that has a 3d shape like a button is also termed as Button. For
example, OK button, Cancel button, Apply button, and so on.
Dialog Box
The naming conventions used for the components in a dialog box are mentioned in
Figure 3.
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Figure 3 The components of a dialog box
Drop-down
A drop-down is the one in which a set of common tools are grouped together. You can
identify a drop-down with a down arrow on it. These drop-downs are given a name
based on the tools grouped in them. For example, Circle drop-down, Fillet/Chamfer
drop-down, Create Light drop-down, and so on; refer to Figure 4.
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com
Figure 4 The Circle, Fillet/Chamfer, and Create Light drop-downs
Drop-down List
A drop-down list is the one in which a set of options are grouped together. You can set
various parameters using these options. You can identify a drop-down list with a down
arrow on it. To know the name of a drop-down list, move the cursor over it; its name
will be displayed as a tool tip. For example, Lineweight drop-down list, Linetype
drop-down list, Object Color drop-down list, Visual Styles drop-down list, and so on;
refer to Figure 5.
www.EngineeringBooksPDF.com