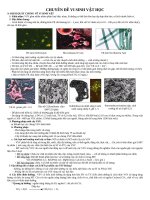
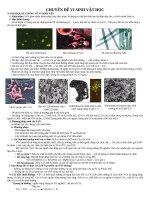
Chuyên đề vi sinh vật học phân tử
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (16.73 MB, 165 trang )
Phần 1:
Các nguyên lý cơ bản
về di truyền học Vi sinh vật
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Cấu trúc tế bào vi sinh vật
Sao chép ADN
Biểu hiện gen
Điều hòa gen
Các dạng đột biến
Tái tổ hợp ADN và chuyển gen
Cấu trúc tế bào vi sinh vật
2
Kích thước của tế bào vi khuẩn:
Đường kính trung bình (0,2-2 µm), chiều dài trung bình (2-8 µm)
Hình thái tế bào vi sinh vật dưới kính hiển vi
Tảo lục
Vi khuẩn quang hợp màu tía
Nấm men
Nấm mốc
4
Hình dạng khuẩn lạc, tế bào nấm men S. cerevisae
Khuẩn lạc trên đĩa thạch
Hình thái hiển vi
Cấu trúc tế bào
Nấm sợi /nấm mốc
(filamentous fungi /mold)
(a) Hình vẽ sơi nấm không vách
ngăn và (b) sợi nấm được chia
thành các tế bào nhờ vách ngăn.
Ảnh hiển vi điện tử (x40,000) sợi
nấm với một lỗ đơn trên vách ngăn.
6
Sinh trưởng đỉnh sợi ở nấm mốc
7
Sinh sản vơ tính ở nấm sợi
8
Genome của vi sinh vật
Dịng chảy thơng tin di truyền
1. Sao chép ADN
Cấu trúc ADN
Sao chép DNA
Sao chép DNA
Sao chép ADN mạch vòng (plasmid)
MOLECULAR MI CROBI OLO
Replication
forks
Origin of
replication
Newly
synthesized
DNA
Theta structure
Origin
(DnaA binding site)
Movement
3
5
5
3
Replication
fork
Lagging 3
Leading
5
5
3
Origin
Leading
Lagging
Movement
3
5
5
3
Replication
fork
Replication of circular DNA: the theta structure. In circular DNA, bidirectional replication from an origin forms
structure resembling the Greek letter theta ( ). Inset shows dual replication forks in the circular chromosome. In
, the origin of replication is recognized by a specific protein, DnaA. Note that DNA synthesis is occurring in both
lagging manner on each of the new daughter strands. Compare this figure with the description of the replisome
Sao chép ADN mạch vòng (plasmid)
Hoạt tính đọc sửa (proofreading) của DNA polymease
- DNA polymerase sao chép DNA với tỷ lệ lỗi: 10-8 – 10-11 lỗi/bp
- Một số có hoạt tính 3‘-5‘ exonuclease để loại bỏ và thay thế các
nucleotide bị sai.
Khởi đầu sao chép ADN
Quá trình sao chép bắt đầu tại vị trí Ori (origin of replication):
• Các protein nhân tố khởi đầu lắp ráp tại Ori DNA sequence
• DNA helicase tháo xoắn AND (theo cả hai chiều)
• Các protein làm bền giữ cho các sợi tách nhau, cho phép quá trình tổng
hợp ADN bắt đầu.
Các protein của nhiễm sắc thể (histone ở sinh
vật nhân thật và cổ khuẩn) được loại bỏ.
DNA polymerase III
3'
Replication fork
5'
DNA helicase
Protein làm bền
Tổng hợp sợi liên tục
Tổng hợp DNA luôn bắt đầu với RNA primer:
• the DNA-synthesizing enzyme DNA polymerase can only add
nucleotides to an existing strand
• Primase produces a short, complementary RNA primer at the Ori
• DNA polymerase extends primer of leading strand in direction of fork
Primase
1
3
3
Replication fork
Triphosphate
nucleotide
Synthesis of leading strand
5
2
Leading strand
P+P
RNA primer
Tổng hợp sợi gián đoạn
Replication fork
Triphosphate
nucleotide
RNA
primer
Okazaki
fragment
6
Lagging
strand
7
3
5
8
Primase
Synthesis of lagging strand
DNA
polymerase III
9
10
DNA ligase
DNA
polymerase I
Gene Expression
5'
3'
DNA
(genotype)
5'
3'
TRANSCRIPTION
3‘
5'
mRNA
TRANSLATION
(by ribosomes)
NH2
Methionine
Arginine
Tyrosine
PHENOTYPE
Leucine
Polypeptide
Khởi đầu phiên mã
1
2
RNA polymerase attaches
nonspecifically to DNA and
travels down its length until
it recognizes a promoter
sequence. Sigma factor
enhances promoter
recognition in bacteria.
RNA polymerase
DNA
Promoter
Sigma factor
Attachment of RNA polymerase
Upon recognition of the
promoter, RNA polymerase
unzips the DNA molecule
beginning at the promoter.
3'
5'
Unzipping of DNA, movement of RNA polymerase
Initiation of transcription
Terminator
Template
DNA strand
Kéo dài mRNA
3
After triphosphate
ribonucleotides align with
their DNA complements,
RNA polymerase links
them together, synthesizing
RNA. The triphosphate
ribonucleotides also provide
the energy required for
RNA synthesis. No primer
is needed.
Elongation of the RNA transcript
3
5
Growing
RNA molecule
Template
DNA
strand
Kết thúc phiên mã
RNA polymerase
released
3'
5'
RNA transcript released
4
In self-termination, the transcription of DNA
terminator sequences cause the RNA to fold,
loosening the grip of RNA polymerase on the DNA.
5
In enzyme-dependent termination, a termination
enzyme pushes between RNA polymerase and
the DNA, releasing the polymerase.
Rho termination
protein
C-G rich
stem-loop
Rho protein moves
along RNA
3'
Termination of transcription
• triggered by stem/loop structure in RNA or termination
factors such as the Rho protein