Lecture supply chain management chapter 7 sc design and integration
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (3.03 MB, 28 trang )
14-Sep-21
LOGO
Chapter 7: SC design and
integration
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
Contents
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
1
Bullwhip Effect
2
Pull-Push Strategy
3
Supply Chain design
1
14-Sep-21
1. Bullwhip Effect – Case study
Procter & Gamble (P&G) examined order patterns for
Pampers.
Its sales at retail stores were fluctuating, but the variability was
not excessive.
For the distributors' orders, P&G was surprised by the greater
degree of variability.
When they looked at P&G's orders of materials to their suppliers,
such as 3M, the swings were even greater.
While babies consumed diapers at a steady rate, the
demand order variability in the supply chain was
amplified as we move up the supply chain. P&G called
this phenomenon the "bullwhip" effect.
ECR: Potential $30 billion opportunity
Efficient
Consumer
Response
(ECR)
initiative
One motivation for the initiative was the
excessive amount of inventory in the supply
chain.
Studies found more than 100 days of
inventory supply from production lines to
retailers' shelves.
Distorted information led to stockpiling
because of demand uncertainty and
variability
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
2
14-Sep-21
Bullwhip
As we move further away from the endcustomer in the supply chain,
Distortion in demand information,
Increase in variance of orders
1.
2.
Information Coordination: The Bullwhip Effect
Consumer Sales at Retailer
Retailer's Orders to Wholesaler
900
800
800
300
Wholesaler's Orders to Manufacturer
41
39
37
35
33
31
29
27
25
23
21
Manufacturer's Orders with Supplier
1000
1000
Manufacturer Order
900
800
700
600
500
400
300
200
100
900
800
700
600
500
400
300
200
100
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
40
37
34
31
28
25
22
19
16
13
10
7
0
4
41
39
37
35
33
31
29
27
25
23
21
19
17
15
13
11
9
7
5
3
1
0
1
Wholesaler Order
19
1
41
39
37
35
33
31
29
27
25
23
21
19
17
15
13
9
7
11
5
3
0
1
100
0
17
200
100
15
200
400
9
300
500
13
400
600
11
500
700
7
600
5
700
3
Retailer Order
1000
900
Consumer demand
1000
3
14-Sep-21
Causes of the Bullwhip Effect
Best illustration of the bullwhip effect is "beer game."
Participants play the roles of customers, retailers,
wholesalers, and suppliers of a popular brand of beer.
Supplier
They cannot communicate with each other and must
make order decisions based only on orders from the
Manufacturer
next downstream player.
The ordering patterns share a common, recurring
Distributor
theme: the variability of an upstream site is always
greater than those of the downstream site, a simple, yet
Retailer
powerful illustration of the bullwhip effect.
the bullwhip effect is a consequence of the players'
Customer
rational behavior within the supply chains
infrastructure.
So What?
When a supply chain is plagued with a bullwhip
effect and demand information is distorted,
It results in
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
excessive inventory
poor product forecasts
insufficient or excessive capacities
poor customer service
Uncertain and costly production
high costs for corrections (expedited shipments and
overtime)
4
14-Sep-21
What are the causes and solutions
for Bullwhip Effect?
2. Pull and Push System
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
5
14-Sep-21
Pull Strategy
-
Coordinate production and distribution based on actual needs and orders
Receiving orders – Sourcing – Producing/assembling – Delivering
Meet the requirement of market, quick response and high quality service
Reduce stagnant capital, increase inventory turnover.
Strict requirements: flexible organization, scientific production
management, integrated information system, on time
Characteristics of products
and market
- Production and distribution
based on forecasting.
- Low volatile demand
- Low customized
- High Economies of scale
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
- Production and distribution
based on real demand
- High volatile demand
- Customized products
- Low Economies of scale
6
14-Sep-21
Characteristics of
Supply chain
Objective
Push system
Pull system
Minimize cost
Maximize cus service
High
Complex level
Focus
Low
Resource Allocation
Responsiveness
Process
Supply chain planning
Order processing
Storage
Many
Few
Order time
Short
Long
Adaptive level
Pull
Slow adaption
High
Non-stable demand
Low economies of
scale
Customization
Push
Stable market
Low economies of
scale
Non-stable
demand
Large scale
market
Stable market
High economies of scale
Standardized products
and processes
Low
Low
Pull
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
Fast and flexible
High
Push
7
PUSH OR PULL
14-Sep-21
- Make to order
Many time per day, at the Assembly line
Supplier’s
warehouse
Dell’s production
department
Customers
Suppliers
- Buying based on
demand forecast
All components are attached to the orders
No finish product is assembled before the order comes
-
Dell’s production department only stores a small amount of components and they comes
before few hours
The responsiveness of Dell depends directly on supplier’s competence
Absolute synchronization between production and sales, keep the supply chain always
balanced and smooth
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
8
14-Sep-21
Why is there such a
change?
Push and Pull Strategy
Define the
boundary
- Push and pull Coordination: take the advantages of 2
strategies
- The first part of the chain: Push
- Store components based on long term forecasting
- Semi – products are assemble to modules
- The last part of the chain: Pull
- Assemble based on real demand
- Complete products after receiving orders
Forecasting
the customer
demand
Push strategy
Raw
material
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
Pull –
push
Boundar
y
Real demand orders
Pull strategy
Receiving orders point
of time
End
users
9
14-Sep-21
MTS
MTO
less volatility
Customization
ATO
ETO
Customers
Suppliers
Standardization
more volatility
Receiving Order point of time
3. Supply Chain Design
Supply chain strategy must be aligned with overall
corporate strategies
Supply chain performance goals must be stated in
operational terms: projected market coverage, sales
and service support, sale volume, profitability,
inventory turns, cash to cash cycle times and return
on investment.
Supply chain strategies: intensity of distribution,
use of direct or indirect channels, services of
intermediaries in each geographic area and
implementation plans
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
10
14-Sep-21
3. Supply Chain Design
Phase 1: Understanding end customer
Phase 2: Choosing best SC’s strategy
Phase 3: Scoping the SC’s structure
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
11
14-Sep-21
Phase 1: understand the need of customer
The customer is the ultimate judge of the supply
chain’s performance
Organizations must understand the nature of their
products and be able to devise a supply chain
strategy that best fits their customers’ needs or
demands
Primarily functional or primarily innovative
products
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
12
14-Sep-21
Customer service objectives
The level of product availability
The speed and consistency of the customer’s
order cycle
The communication that takes place between
seller and customer.
Availability
Inventory availability within a specified order
cycle time.
KPI: number of total order shipped completed
within a specified time period as a percentage of
total order received.
Reflecting the customer’s view of customer
service. And the product’s importance to the
customer and the customer importance to the
company
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
13
14-Sep-21
Order cycle
The elapses between the customer’s order
placement and the time product is received.
Speed and consistency of the order cycle are
prime factors in SC design
Most customers prefer consistent service to fast
service.
The former allows them to plan inventory levels
to a greater extent than is possible with a fast
but highly variable order cycle
Communication
Firm’s ability to supply timely information to
the customer regarding such factors as: order
status, order tracking, back-order status, order
confirmation, product substitution, product
shortages, and product information requests.
Automated information system usually results
in fewer errors in shipping, picking, packing,
labeling and documentation.
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
14
14-Sep-21
Phase 2: Selecting a supply chain strategy
A supply chain strategy can be defined as a
strategy required to manage the integration of
all the supply chain activities through
improved supply chain relationships in order to
achieve a competitive advantage for the supply
chain (Hines, 2004: 5)
Supply chain strategies may be designed to be
more efficient and/or to be more responsive
Requirement in design a supply chain
Suitable Strategies
Simplicity
Consistency
Throughout from the
origin to the destination
Suitable Strategies
Adapt to important priorities
in competitive strategy
Supply chain makes the
Cost
difference
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
Competition Strategy
SC’ Strategy
SC’ structure
Efficiecy
Effective
Responsi
-veness
15
14-Sep-21
Simplicity
Postponement >< Delay ???
Postponement makes SC:
More Flexible
Reduce cost due to reduce the
complexity
Postponement ways:
Manufacturing Postponement
Logistics Postponement
Consistency
Objectives
Application and process
Data and IT system
High Reliability
Collaboration
Throughout from the origin to the destination
Process and IT are integrated inside and outside the
firm to the customers and main suppliers
Production capacity and inventory are optimized
throughout the SC
Performance indicators and qualitative objectives
are shared throughout the SC
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
16
14-Sep-21
Efficient (or lean) supply chains
An efficient (or lean) supply chain is a set of
organizations directly linked by flows of
information, products and finances that work
collaboratively to reduce cost and waste
Non-value-added
activities
should
be
eliminated, scale economies should be pursued
and optimization techniques should be deployed
to get the best capacity utilization in production
and distribution
Lean supply chains are thus appropriate for and
match functional products
Responsive (or agile) supply chains
The focus of agile supply chains is on time
compression and quick response and on
eliminating the barriers to quick response
Supply chain agility is the ability of the supply
chain as a whole to rapidly align the network and
its operations to the dynamic and turbulent
requirements of customers’ demands
Agile supply chains are relevant for innovative
products
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
17
14-Sep-21
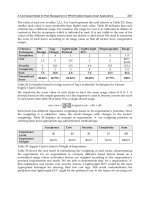
Supply chain strategies
Efficient Supply
chain
Responsive Supply
chain
Main goal
Distribution
strategy
Operation
management
Inventory
management
Response time
Supplier selection
New product
design
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
18
14-Sep-21
Competition
Strategies
Innovation
Strategies and Structure of SC
SC supports to introduce new product
Outsource, expand the size quickly
Suppliers join in designing product process
Product and operational procedures standardization
Cost
Integrating and controlling supply source
Quality
Quality management
Service
Integrating process and customer system
Market Segmentation
Product Origin Traceability
SC’ Strategy
Simplicity
Product standardization
Reduce the number of suppliers
Process Standardization
Establishing general process
applied to all member in SC
Postponement variety of
products at the end stage
Shell supplied inventories automatically to Bayer
Bayer does not need to order
Bayer does not fear of shortage of bunker
E - payment
solution for inventory management
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
19
14-Sep-21
A combination of lean and agile supply chains
Hybrid (or ‘leagile’) supply chains exploit
the benefits of both lean and agile supply
chains
The decoupling point is the point in the
product ow stream to which the customer’s
order penetrates and where real time data and
forecast- driven activities meet
What is the organisation’s position in terms
of the decoupling point?
Which supply chain strategy should be
adopted by the organisation?
MsC. Bui Thi Bich Lien
20