Photoshop cs5 by steve Johnson part 25 potx
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (925.24 KB, 8 trang )
ptg
156 Chapter 7
The Lens Correction filter fixes flaws that occur during the shooting of
images, such as geometric distortion, vignetting, and chromatic aberra-
tion. Geometric distortion causes straight lines to bow out toward the
edges of the image. Vignetting is a defect where edges of an image are
darker than the center. Chromatic aberration appears as a fringe of color
along the edges of objects caused by the lens focusing on different col-
ors of light in different planes. You can select options to automatically
correct image problems or apply a Lens Correction Profile (LCP) for a
camera (New!). If a profile for your camera is not available, you can
search online or use Adobe Lens Profile Creator (New!) (available at
www.labs.adobe.com
) to create one. If you know how you want to fix a
problem, you can also manually adjust options to correct it (New!).
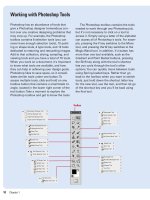
Working with the
Lens Correction Filter
Use the Lens Correction Filter
Open an image.
Click the Filter menu, and then click
Lens Correction.
Select from the following tools:
◆ Remove Distortion Tool. Drag in
the grid left or right to remove
geometric distortion.
◆ Straighten Tool. Drag in the grid
to draw a new horizon line
(image shifts to the horizon).
◆ Move Grid Tool. Drag to
reposition the visible grid.
◆ Hand Tool. Drag to move the
image within the view window.
◆ Zoom Tool. Click in the view
window to zoom in, or Alt+click
(Win) or Option+click (Mac) to
zoom out.
Select from the following options
on the Auto Correction tab (New!):
◆ Correction. Select to correct
Geometric Distortion, Chromatic
Aberration, or Vignette (New!).
◆ Edge. Select to fill in transparent
areas of the image with the
Black or White Color (New!),
Edge Extension, or Transparent.
◆ Search Criteria and Lens
Profile. Search for and select a
lens profile to correct an image
based on a camera and lens, or
click Search Online (New!).
4
3
2
1
3
4
From the Library of Wow! eBook
ptg
Chapter 7 Working with Adjustment Layers, Filters, and Tools 157
Click the Custom tab.
Select from the following tools:
◆ Settings. Choose from Lens
Default, Previous Correction,
Custom, or Default Correction.
◆ Remove Distortion. Drag the
slider left or right to precisely
remove pincushion or barrel
distortion.
Change the Chromatic Aberration
options: drag left or right to remove
Red/Cyan Fringe, Green/Magenta
Fringe (New!), or Blue/ Yellow
Fringe from the image.
Select from the following Vignette
options:
◆ Amount. Drag left or right to
create a light or dark vignette
around the image.
◆ Midpoint. Drag left or right to
select the midpoint for the
vignette.
Select from the following Transform
options:
◆ Vertical Perspective. Drag left
or right to change the image's
vertical perspective.
◆ Horizontal Perspective. Drag
left or right to change the
image's horizontal perspective.
◆ Angle. Drag the angle option to
rotate the image clockwise or
counter clockwise.
◆ Scale. Drag left or right to
change the scale (size) of the
image.
Select the Preview check box to
view changes as they are made.
Select the Show Grid check box to
view or hide (default (New!)) the
grid.
Click the Size list arrow to change
the size of the grid boxes (default
is 64 (New!)).
Click the Color box to change the
color of the grid.
Click OK.
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
6
7
9
8
10 11 12
13
14
5
From the Library of Wow! eBook
ptg
158 Chapter 7
Photoshop provides a variety of filters to blur the look of an image,
including Box, Surface, and Shape. The Box Blur filter blurs an image
based on the average color value of neighboring pixels. Its primary
function is the creation of special effects. You can adjust the size of the
area used to calculate the average value for a given pixel; a larger
radius results in more blurring. The Surface Blur filter blurs an image
while saving the visible edges; this filter is useful for creating special
effects or removing that pesky noise or grain. The Radius option speci-
fies the size of the area sampled for the blur. The Threshold option con-
trols how much the tonal values of neighboring pixels must diverge
from the center pixel value before being part of the blur. Pixels with
tonal value differences less than the Threshold value are excluded from
the blur. The Shape Blur filter uses a specified shape to create the blur.
Choose a kernel from the list of custom shape presets, and use the
radius slider to adjust its size. You can load different shape libraries by
clicking the triangle and choosing from the list. Radius determines the
size of the shape; the larger the shape, the greater the blur.
Using the Box,
Surface, and Shape
Blur Filters
Use the Box Blur Filter
Open an image.
Click the Filter menu, point to Blur,
and then click Box Blur.
Drag the Radius slider left or right
to decrease or increase the
amount of blur applied to the
image.
Click OK.
4
3
2
1
4
3
Results of
Box Blur
1
From the Library of Wow! eBook
ptg
Chapter 7 Working with Adjustment Layers, Filters, and Tools 159
Results of Shape Blur
Use the Surface Blur Filter
Open an image.
Click the Filter menu, point to Blur,
and then click Surface Blur.
Drag the Radius slider left or right
to decrease or increase the
amount of blur applied to the
image.
Drag the Threshold slider left or
right to decrease or increase the
acceptance of the shift in
brightness of the image
information (the edges).
Click OK.
Use the Shape Blur Filter
Open an image.
Click the Filter menu, point to Blur,
and then click Shape Blur.
Select a shape (called a kernel)
from the available options.
Drag the Radius slider left or right
to decrease or increase the
amount of blur applied to the
image.
Click OK.
5
4
3
2
1
5
4
3
2
1
1
1
Results of Surface Blur
5
5
4
3
4
3
From the Library of Wow! eBook
ptg
160 Chapter 7
Using the Gaussian
Blur and Despeckle
Filters
Use the Gaussian Blur Filter
Select the portions of the image
you want to blur or leave the
image unselected to apply the
filter to the entire image.
Click the Filter menu, point to Blur,
and then click Gaussian Blur.
Select the Preview check box to
view the results.
Drag the Radius slider or enter a
pixel value to increase or
decrease the amount of Gaussian
blur applied to the image.
Click OK.
Use the Despeckle Filter
Select the Layers panel.
Select the layer to which you want
to apply the Despeckle filter.
Click the Filter menu, point to
Noise, and then click Despeckle.
Photoshop applies the Despeckle
filter to the image.
3
2
1
5
4
3
2
1
You can also apply the Gaussian Blur filter that blurs an image or a
selection by a controllable amount. While not strictly a restoration tool,
the Gaussian Blur filter can be used to add a sense of depth to the
image. For example, you could select and blur the background of an
image while leaving the foreground in focus. The outcome of the filter
is to create a hazy, out-of-focus effect on the image or selection.
Another filter, the Despeckle filter, detects the edges in an image and
blurs the entire image except those edges. Of course, there are no real
edges in a Photoshop document—the Despeckle filter works along
areas where there is a significant shift in the brightness of the pixels.
Since a shift in brightness usually signifies an edge, the Despeckle filter
performs a very accurate blurring of the image while preserving detail.
5
3
Area to despeckle
1
4
2
From the Library of Wow! eBook
ptg
Chapter 7 Working with Adjustment Layers, Filters, and Tools 161
The Unsharp Mask filter creates a visually sharper image by locating
pixels that differ in value from surrounding pixels. When the filter is
applied to the image, the bordering pixels specified by the threshold
option get lighter and the darker pixels get darker. It's important to
understand that the Unsharp Mask does not actually sharpen the
image; it only attempts to create the illusion of sharpness. Be careful;
an over-application of this filter creates harsh images with ragged
edges and shadows. Also, the effects of the Unsharp Mask filter
appear more severe when viewed with the low resolution of a com-
puter than when the document is output to a printer.
Using the Unsharp
Mask Filter
Use the Unsharp Mask Filter
Select the Layers panel.
Select the layer you want to
sharpen.
Click the Filter menu, point to
Sharpen, and then click Unsharp
Mask.
Select from the following options:
◆ Preview. Select the option to
view changes to the image
directly in the active document
window.
◆ Amount. Drag the slider or
enter a value to determine how
much to increase the contrast
of pixels.
◆ Radius. Drag the slider or enter
a value to determine the
number of pixels surrounding
the edge pixels that affect the
sharpening.
◆ Threshold. Drag the slider or
enter a value to determine how
different the sharpened pixels
must be from the surrounding
area before they are
considered edge pixels and
sharpened by the filter.
Click OK.
5
4
3
2
1
4
5
The Unsharp Mask filter applied
to the image.
From the Library of Wow! eBook
ptg
162 Chapter 7
The Smart Sharpen filter attempts to sharpen the pixels of an out-of-
focus image in much the same way as the Unsharp Mask filter. The
major difference is the ability of Smart Sharpen to remove previously
applied Gaussian, Lens, and Motion Blur filters. For example, you've
applied the Lens Blur filter to an image, but later decide to reduce the
effect. The problem is that Unsharp Mask will attempt to sharpen what
it assumes to be an out-of-focus image. Unfortunately, an image taken
with an out-of-focus lens, and a Lens blur are two different things, and
that's where the Smart Sharpen filter comes to the rescue.
Using the Smart
Sharpen Filter
Use the Smart Sharpen Filter
Select the Layers panel.
Select the layer you want to
sharpen.
Click the Filter menu, point to
Sharpen, and then click Smart
Sharpen.
Select the Preview check box to
view the results.
Select the Basic or Advanced
option.
Click the Settings list arrow, and
then select from a list of user-
defined settings.
Select from the following Sharpen
options:
◆ Amount. Drag the slider to
determine the amount of
sharpness applied to the image.
◆ Radius. Drag the slider to
determine the width of the
sharpening effect.
◆ Remove. Click the list arrow
and then select what type of
blur effect you are removing
from the image.
◆ Angle. Enter the angle of the
Motion Blur filter to remove.
◆ More Accurate. Select for a
more accurate (slower)
sharpening effect.
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
4
5
6
7
Original
image
From the Library of Wow! eBook
ptg
Chapter 7 Working with Adjustment Layers, Filters, and Tools 163
Select the Shadow panel and then
select from the following Shadow
options:
◆ Fade Amount. Drag the slider to
determine the amount of
shadow correction applied to
the image.
◆ Tonal Width. Drag the slider to
set the width of the tonal
values in the image shadows.
◆ Radius. Drag the slider to
choose the scale size for the
shadows.
Select the Highlight panel, and
then select from the following
Highlight options:
◆ Fade Amount. Drag the slider to
determine the amount of
highlight correction applied to
the image.
◆ Tonal Width. Drag the slider to
set the width of the tonal
values in the image highlights.
◆ Radius. Drag the slider to
choose the scale size for the
highlights.
To save a copy of the current
Smart Sharpen settings, click the
Save button.
To delete the active saved Sm ar t
Sharpen settings, click the Delete
button.
Click OK.
12
11
10
9
8
12
10
11
8
Image using Smart Sharpen
From the Library of Wow! eBook