Module 3 - Multiarea OSPF Operation pptx
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (833.58 KB, 34 trang )
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco ConfidentialBSCI
1
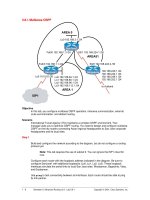
BSCI Module 3 Lesson 6 - Multiarea OSPF
Operation
OSPF
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
2
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
Objective
Large OSPF Network Issues
OSPF LSA Types
OSPF LSA Types (cont.)
Interpreting the OSPF LSDB and Routing Table
Interpreting the Routing Table
Calculating Costs for E1 and E2 Routes
Configuring OSPF LSDB Overload Protection
Changing the Cost Metric
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
3
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
Large OSPF Network Issues
Hierarchical area routing separates a large internetwork
into multiple areas. When you use this technique,
interarea routing still occurs, but many of the internal
routing operations, such as SPF calculations, remain
within individual areas.
–Reduced frequency of SPF calculations
–Smaller routing table
–Reduced LSU overhead
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
4
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
LSA Types
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
5
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
LSA Type 1 Link Types
Link
Type
Description Link-state ID
1
Point-to-point connection to another
router
Neighboring router ID
2 Connection to a transit network IP address of DR
3 Connection to a stub network
IP network/subnet
number
4 Virtual link Neighboring router ID
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
6
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
The Link ID in the OSPF Database
RouterA#show ip ospf database
OSPF Router with ID (10.0.0.11) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
10.0.0.11 10.0.0.11 548 0x80000002 0x00401A 1
10.0.0.12 10.0.0.12 549 0x80000004 0x003A1B 1
100.100.100.100 100.100.100.100 548 0x800002D7 0x00EEA9 2
Net Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum
172.31.1.3 100.100.100.100 549 0x80000001 0x004EC9
Summary Net Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum
10.1.0.0 10.0.0.11 654 0x80000001 0x00FB11
10.1.0.0 10.0.0.12 601 0x80000001 0x00F516
<output omitted>
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
7
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
LSA Type 1: Router LSA
One router LSA (type 1) for every router in an area:
–Includes list of directly attached links
Identified by the router ID of the originating router
Floods within its area only; does not cross ABR
Link-state ID depends on link type
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
8
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
LSA Type 1: Router LSA
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
9
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
Type 1: Router LSAs
The command show ip ospf database router will list all of the Router
LSAs in a database.
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
10
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
LSA Type 2: Network LSA
Advertised by the DR of the broadcast network
Floods within its area only; does not cross ABR
Link-state ID is the DR
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
11
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
LSA Type 2: Network LSA
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
12
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
Type 2: Network LSAs
The command show ip ospf database network is used to observe a
Network LSA.
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
13
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
LSA Type 3: Summary LSA
Advertised by the ABR of originating area.
Regenerated by subsequent ABRs to flood throughout
the autonomous system.
By default, routes are not summarized, and type 3 LSA
is advertised for every subnet.
Link-state ID is the network or subnet advertised in the
summary LSA
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
14
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
LSA Type 3: Summary LSA
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
15
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
Type 3: ABR Summary LSAs
The command show ip ospf database summary is used to display the
network summary LSAs in the database.
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
16
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
LSA Type 4: Summary LSA
Summary (type 4) LSAs are used to advertise an ASBR to
all other areas in the autonomous system.
They are generated by the ABR of the originating area.
They are regenerated by all subsequent ABRs to flood
throughout the autonomous system.
Link-state ID is the router ID of the ASBR.
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
17
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
Type 4: ASBR Summary LSAs
The command show ip ospf database asbr-summary is used to display
ASBR Summary LSAs
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
18
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
LSA Type 5: External LSA
External (type 5) LSAs are used to advertise networks from
other autonomous systems.
Type 5 LSAs are advertised and owned by the originating
ASBR. external LSAs are flooded throughout the autonomous
system
The Link-state ID is the external network number.
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
19
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
Type 5: Autonomous System External LSAs
The command show ip ospf data base externaldisplays AS External
LSAs
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
20
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
LSA Types: 6, 7, 8
Group Membership LSAs are used in an enhancement of OSPF
known as Multicast OSPF (MOSPF). MOSPF routes packets from
a single source to multiple destinations, or group members, which
share a class D multicast address. Although Cisco supports other
multicast routing protocols, MOSPF is not supported as of this
writing.
NSSA External LSAs are originated by ASBRs within not-so-
stubby areas (NSSAs
External Attributes LSAs were proposed as an alternative to
running Internal BGP (iBGP), to transport BGP information across
an OSPF domain. This LSA is not supported in IOS.
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
21
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
Type 7: Not-So-Stubby Area LSAs
The command show ip ospf database nssa-externaldisplays NSSA
external LSAs
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
22
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
LSA Operation Example
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
23
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
LSA Types: 9, 10, 11
Opaque LSAs are a class of LSAs that consist of a standard LSA
header followed by application-specific information.
The Information field can be used directly by OSPF or indirectly by
other applications to distribute information throughout the OSPF
domain.
Opaque LSAs have been used to add various extensions to OSPF,
such as traffic engineering parameters for Multiprotocol Label
Switching (MPLS) networks
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
24
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
Interpreting the OSPF Database
RouterA#show ip ospf database
OSPF Router with ID (10.0.0.11) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
10.0.0.11 10.0.0.11 548 0x80000002 0x00401A 1
10.0.0.12 10.0.0.12 549 0x80000004 0x003A1B 1
100.100.100.100 100.100.100.100 548 0x800002D7 0x00EEA9 2
Net Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum
172.31.1.3 100.100.100.100 549 0x80000001 0x004EC9
Summary Net Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum
10.1.0.0 10.0.0.11 654 0x80000001 0x00FB11
10.1.0.0 10.0.0.12 601 0x80000001 0x00F516
<output omitted>
ADV Router: Advertising router; the source router of the LSA
Link count: Total number of directly attached links, used only on
router LSAs
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.BSCI
25
CCNP – BSCI Bachkhoa Networking Academy
Học viện mạng Bách Khoa - www.bkacad.com
Interpreting the Routing Table
When an ABR receives summary LSAs, it adds them to
its LSDB and regenerates them into the local area.
When an ABR receives external LSAs, it adds them to
its LSDB and floods them into the area.