bài giảng kỹ thuật lập trình plc chương 5 một số kỹ thuật lập trình
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (1.46 MB, 27 trang )
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 155 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
MỘT SỐ KỸ THUÂT LẬP TRÌNH
DUY TRÌ (LATCH).
Ta phải làm quen với đoạn chương trình duy
trì để sau này có thể sử dụng được.
Ví dụ :
Ngõ ra Q0.0 được tích cực ngay khi ng õ vào
I0.0 được tích cực. Bằng sự duy tr ì Q0.0 vẫn
được tích cực cho đến khi S2 tại ng õ vào I0.1
được tích cực và vì thế dừng duy trì.
Để thực hiện chức năng duy tr ì, ngõ ra (Q0.0
trong trường hợp này) đóng vai trò quan trọng.
Nó được đặt đúng chổ để ngay khi nó đ ược tích
cực, nó làm nhiệm vụ duy trì cho chính nó.
Điều này đạt được nhờ tiếp điểm ngõ ra (Q0.0
trong trường hợp này) được đặt song song với
tiếp điểm ngõ vào làm nhiệm vụ thay thế cho
trạng thái ngõ vào khi có tín hi ệu.(Q0.0 có thể được so sánh với tiếp điểm K1)
Tiếp điểm thường đóng- Normally Closed
(NC) Contact
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 156 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
Để làm cho chức năng duy trì được ngắt trở về trạng thái đầu, ng õ vào I0.1 được đặt làm việc
giống như một chuyển mạch trong đ ường dẫn dòng khi hoạt động.
Nếu đường dẫn dòng bị ngắt (trạng thái “0”) xuất hiện khi chuyển mạch đ ược nhấn, điều này
nói đến tiếp điểm NC.
.
Do đó, có thể nói rằng : Tiếp điểm NC sẽ có giá trị logic bằng đảo của giá trị logic ng õ vào.
Hay nói cách khác, khi giá tr ị ở ngõ vào bằng 24VDC (mức 1) th ì giá trị logic tại tiếp điểm l à
“0”. Khi giá trị ở ngõ vào bằng 0VDC (mức 0) th ì giá trị logic ở tiếp điểm là “1”.
Một tiếp điểm NC ngắt “d òng” trong giản đồ
LAD khi ngõ vào hay ngõ ra được gán “true”
Như trong mạch relay, ta phải đồng thời chuyển
mạch một tiếp điểm ng õ ra (Q0.0) song song
với phần tử I0.0
Nếu trong một vòng quét, ngõ ra Q0.0 được tích cực bởi một toán hạng đ ược được kết nối với
S1 tại I0.0, tiếp điểm Q0.0 song song với I0.0 đ ược cập nhật đóng ở vòng quét kế tiếp, sau
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 157 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
một vài milli giây sau. Đi ều này tạo ra sự duy trì. Tiếp điểm thường đóng I0.1 có thể ngắt
điều này khi chuyển mạch S2 tại I0.1 được tích cực.
Một dạng lệnh khác để thực hiện duy tr ì.
Trong kỹ thuật PLC, duy tr ì thường được dưới nhiều dạng khác nhau :
Thay vì hồi tiếp ngõ ra như trong ví dụ trên, ở đây hai lệnh Set và Reset được sử dụng làm
cho câu lệnh đơn giản hơn.
Khi có lệnh “set” – (S), một xung chuyển mạch tại ng õ vào I0.0 làm cho Q0.0 được tích cực
và tự duy trì.
Ngược lại, khi có lệnh (R), một chuyển mạch xung tại ng õ vào I0.1 làm cho Q0.0 d ừng tích
cực.
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 158 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
ỨNG DỤNG : Khía cạnh an toàn
Dừng chương trình nếu ngắt mạch tại kết nối với S3.
Chuyển mạch với tiếp điểm NC cấp
tín hiệu “0” khi hoạt động.
Trong chương trình LAD, tín hiệu
này được hồi tiếp bằng tiếp điểm NC
ở tại ngõ vào I0.1. Điều này có nghĩa
rằng nếu ta nhấn S3, Q0.0 sẽ reset.
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 159 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
Chú ý an toàn.
Trong ví dụ trên, một nút NC S3 được sử dụng để khởi động lại.
Khi I0.0 hoạt động, ngõ ra Q0.0 được tích cực. Nếu có tín hiệu 24VDC tại I0.1, tiếp điểm NC
cấp nguồn cho trạng thái “0” của LAD. Ng õ ra Q0.0 không reset. Đường năng lượng trong
LAD được ngắt và ngõ ra cho việc reset không được tích cực.
Nếu không có tín hiệu (0V) tại I0.1 (S3 hở), tiếp điểm NC của I0.1 trong LAD = “1” v à ngõ
ra được reset.
Khi một chuyển mạch NC đ ược dùng tại I0.1, ngõ ra duy trì Q0.0 được reset (tắt lại) nếu
chuyển mạch S3 được nhấn (I0.1= “0”) hay nếu có một sự đứt quảng trong việc kết nối cáp
giữa I0.1 và chuyển mạch NC. Thì khi có sự kiện ngắt mạch, tiếp điểm tr ên sẽ đảm bảo rằng
thiết bị đang hoạt động trong một trạng thái, chẳng hạn nh ư motor được tắt.
Hoạt động “Reset Q0.0” đ ược đưa vào sau hoạt động “Set Q0.0” bởi điều n ày nghĩa là trong
sự kiện cả hai chuyển mạch đ ược tích cực cùng một lúc, việc làm rõ ràng duy trì được thực
hiện ưu tiên.
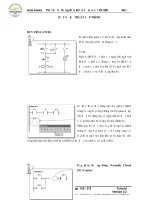
CHUYỂN MẠCH XUNG
Nguyên lý hoạt động
Một đèn tại ngõ ra Q0.5 được bật ngay khi S1 tại
ngõ vào I0.0 hoạt động trong thời gian ngắn.
Nếu S1 (I0.0) được nhấn lại, Q0.5 sẽ ngắt l àm
cho đèn tắt.
Khi chuyển mạch S1 hoạt động, Q0.5 sẽ chuyển
trạng thái. Và đây là nguyên lý hoạt động của
“chuyển mạch xung”.
Giản đồ thời gian
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 160 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
Giản đồ thời gian của một xung tín hiệu tác
động vào ngõ vào.
Trong khoảng thời gian một xung (từ s ườn lên và sườn xuống) tồn tại rất nhiều v òng quét.
Ta biết rằng ở mỗi vòng quét chương trình sẽ dò sự thay đổi ngõ vào và tùy thuộc vào
chương trình sẽ thay đổi ngõ ra. Theo giải thích đó, nếu trạng thái tr ước đó Q0.5 = “1” thì ở
vòng quét kế tiếp sẽ làm Q0.5 = “1”; nếu trạng thái trước đó Q0.5 = “0” th ì ở vòng quét kế
tiếp sẽ làm Q0.5 = “0”.
Và cứ như thế, chương
trình sẽ làm cho việc
đóng mở ngõ ra Q0.5
liên tục theo từng vòng
quét. Một câu hỏi đặt ra
là làm thế nào để mỗi
xung chỉ cho tích cực ở
một vòng quét, tức là chỉ
cho tích cực một lần ????
Ta thấy rằng, mỗi xung tín hiệu luôn có một s ườn lên và một sườn xuống.
Sườn lên là trạng thái chuyển từ trạng thái “0” sang trạng thái “1”.
Sườn xuống là trạng thái chuyển từ trạng thái “1” sang trạng thái “0”.
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 161 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
Như vậy, ta sẽ sử dụng sườn lên hoặc sườn xuống để xác định xung chuyển mạch cho Q0.5.
Nếu ngõ ra Q0.5 là “0”, khi có sườn lên của I0.0, bit nhớ M0.0 đ ược set và điều này làm cho
Q0.5 = “1” tại network 2.
Nếu ngõ ra Q0.5 là “1”, khi có s ườn lên I0.0, bit nhớ M0.0 được reset, và điều này làm cho
Q0.5 = “0” ở network 2.
DÒ SƯỜN XUNG.
Khoảng thời gian chuyển c ủa một tiếp điểm
(ngõ vào, ngõ ra,…) từ “mở” sang “đóng” hay
từ “sai” sang “đúng” đề cập đến s ườn lên hay
sườn dương.
Vì lẽ đó, trạng thái chuyển từ “đóng” sang “mở” hay từ
“đúng” sang “sai” đư ợc coi như là sườn xuống hay sườn
âm.
Có hai lệnh được dùng để dò sườn trong S7-200.
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 162 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
Ta cần một bit nhớ cho chuyển mạch xung. Ví
dụ ngắn gọn sau sẽ hỗ trợ cách sử dụng
chúng.
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 163 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
Thay vì được dùng như một ngõ ra, bit nhớ “M0.0” được dùng như một vị trí nhớ trong PLC
cho kết quả thời gian chuyển tiếp của phép toán logic “I0.0 AND I0.1”. Bit nhớ c òn có thể
dùng ở nhiều nơi khác trong chương tr ình.
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 164 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
Một lệnh set bit nhớ được đặt ở đây.
Số dưới của lệnh set xác định số bit đ ược
set từ địa chỉ trên.
Ở đây, bắt đầu từ địa chỉ M0.0.
Hoạt động của đoạn ch ương trình bên như
thế nào ?
Giả sử trường hợp đầu Q0.5 = “0”, n ên đảo
của Q0.5 = “1”. Điều n ày có nghĩa là
được tích cực. Khi nhấn I0.0, lệnh EU sẽ lấy một xung s ườn lên tín hiệu của I0.0 (Tại
sao chỉ lấy sườn ?) kết hợp với trường hợp đảo của Q0.5 = 1 th ì lệnh set M0.0 được thực hiện
và ở network kế tiếp Q0.5 = “1”.
Khi Q0.5 = “1”, nếu có một xung từ I0.0 sẽ l àm cho lệnh reset M0.0 thực hiện.
Tại sao lại chỉ lấy một s ườn? Ta biết rằng, vòng quét của PLC sẽ được thực hiện liên tục
các bước đọc ngõ vào, duyệt chương trình, xuất ngõ ra và việc này được thực hiện cứ mỗi
3-6ms tùy theo số lệnh trong chương trình(S7-200). Điều đó có nghĩa rằng cứ mỗi 3 -6ms,
I0.0 sẽ được kiểm tra một lần v à nếu trước đó Q0.5 = “1” thì lệnh reset thực hiện v à
ngược lại. Việc này được thực hiện liên tục như thế làm cho việc thực hiện lệnh của ta
không chính xác. Chính vì v ậy, việc lấy sườn của một tín hiệu v ào để chắc chắn rằng lệnh
chỉ được thực hiện một lần khi I0.0 đ ược nhấn.
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 165 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
1. Vòng quét của một PLC là gì?Ba thành phần chính của vòng quét ?
2. Thế nào là một lệnh duy trì trong công nghệ PLC ?
3. Tiếp điểm thường đóng : được mô tả như thế nào trong giản đồ LAD, nó có hiệu ứng
gì? Ta có thể dùng nó để tăng độ an toàn như thế nào ?
4. Sườn là gì, nó được dò như thế nào và có mục đích gì ?
5. Bit nhớ là gì, chúng dùng cho m ục đích gì ?
6. Lệnh Set và Reset hoạt động như thế nào ?
7. Bạn hiểu về hoạt động của TOF nh ư thế nào? Vẽ giản đồ LAD dùng —( )— hoặc với
(S) và (R).
8. Lưu một dự án như thế nào ?
9. Xác định giá trị đặt trước của bộ định thời ?
10. Viết Comment trên networks ?
11. Draw Diagram Block of basic PLC systems ?
12. The binary number system has a base ………….
13.
Giải thích ngõ vào liên tục cập nhật v à phương pháp copy và x ử lý thông minh .
14. The hexadecimal number system has a base………
15. Chuyển một số decimal th ành các dạng số sau :
a. Binary ____________
b. BCD ____________
c. Hexadecimal ____________
16. 5 loại PLC nằm thuộc họ S7-200 là ____________ , ____________ , ____________
, ____________, và ____________ .
17. Một switch và một pushbutton là một ngõ vào dạng ____________.
18. Một đèn hay một solenoid là một ví dụ ngõ ra dạng ___________.
19. The ____________ makes decisions and executes control instructions based on the
input signals.
20. ____________ ____________ is a PLC programming language that uses components
resembling elements used in a line diagram.
21. A ____________ consists of one or more instructions that accomplish a task.
22. Memory is divided into three areas: ____________ , ____________ , and
____________ __________ __ space.
23. Which of the following is not available on an S7 -221?
a. Mode Switch
b. Expansion Port
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 166 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
c. Programming Port
d. Status Indicators
24. An S7-222 can have a maximum of ____________ expansion modules and an S7 -224
can have a maximum of ____________ expansion modules.
25. An S7-222 has ____________ DC inputs and ____________ DC outputs.
26. An S7-224 has ____________ DC inputs and ____________ DC outputs.
27. The fourth output of an S7 -200 would be labeled ____________ .
28. S7-200 can be panel mounted or installed on a ____________ r ail.
29. When talking about computer or PLC memory, 1K refers to ____________ bits,
bytes, or words.
30. Software that is placed in hardware is called ____________ .
31. Which of the following is not required when creating or changing a PLC program?
a. PLC b. Programming Device
c. Programming Software d. Connector Cable
e. Printer
32. A special cable, referred to as a ____________ cable, is needed when a personal
computer is used as a programming device.
33. In the following instruction Q0.0 will be true (logic 1) when ______ ______ or
____________ is true, and when ____________ is true.
34. Analog signals are converted into a ____________format by the PLC.
35. Three types of timers available in the S7 -200 are On-Delay, ____________ On -
Delay, and ____________ -Delay.
36. The maximum time available on a 100 millisecond time base timer is ____________
seconds.
37. A count of 25 on a 10 millisecond time base timer represents a time of __________
milliseconds.
38. There are ____________ timers in the S7 -200.
39. The component of a PLC that makes decisio ns and executes control instructions based
on the input signals is the ____________ .
a.CPU b.Input module
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 167 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
c.Programming device d.Operator interface
40. One byte is made up of ____________ .
a.2 bits b.8 bits
c.16 bits d.32 bits
41. 3.The binary equivalent o f a decimal 5 is ____________ .
a.11 b.100
c.101 d.111
42. An input that is either On or Off is a/an ____________ input.
a. Analog b. discrete
c. high-speed d. normally open
43. A programming language that uses symbols resembling elements used in hard -wired
control line diagrams is referred to as a ____________ .
a. ladder logic diagram b. statement list
c. network d. PLC scan
44. A type of memory that can be read from but not written to is ____________ .
a. RAM b. ROM
c. Firmware d. K memory
45. Which type of int erface cable is needed when a personal computer is used as a
programming device for an S7 -200 PLC?
a. PC/PPI b. Parallel
c. Serial d. MPI
46. The CPU 224 AC/DC/RELAY has ____________ .
a. 8 DC inputs and 10 relay outputs b. 8 AC inputs and 6 relay outputs
c. 14 DC inputs and 14 relay outputs d. 14 DC inputs and 10 relay outputs
47. .____________ expansion modules can be used on the S7 -224 and S7-226.
a. None b. 7
c. 10 d. 30
48. The S7-222 has the ability to store ____________ kbytes in user data.
a. 4 b. 8
c. 2 d. 5
49. Which of the following is not part of a PLC scan?
a. Read Inputs b. Execute Program
c. Force Interrupts d. Update Outputs
50. The address designation for output four of an S7 -200 is ____________ .
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 168 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
a. I0.4 b. I0.3
c. Q0.3 d. Q0.4
51. The maximum clock input freq uency for high-speed counters is ____________ .
a. 0.37 ? b. 10 kHz
c. 20 kHz d. 1 ms
52. The maximum value of an S7 -200 timer with a resolution of 1 millisecond is
____________ seconds.
a. 3.2767 b. 32.767
c. 327.67 d. 3276.7
53. An S7-200 timer with a time base of 100 ms can count to a maximum value of
____________ seconds.
a. 3.2767 b. 32.767
c. 327.67 d. 3276.7
54. The time base of TON 32 of is ____________ ms.
a. 0.1 b. 10
c. 1 d. 100
55. 17.The maximum count of an S7 -200 up counter is ____________ .
a. 32,767 b. 65,534
c. 98,301 d. 1,000,000
56. A/An ____________ is used to assign a mode to a high -speed counter.
a. toggle switch b. interrupt
c. PLC scan d. definition box
57. ____________ instructions allows communication with eternal devices, such as
modems, printers, and c omputers.
a. Transmit b. Interrupt
c. High-speed counters d. High-speed outputs
58. ____________ is used to temporarily override the input or output status in order to
test and debug the program.
a. Transmit b. Forcing
c. Interrupt d. PLC scan
1.What is the purpose of the control transformer in machine control systems?
2.Whys are fuses necessary in controls circuits even though the power mains may already
have circuit breakers?
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 169 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
3.What is the purpose of the shrouded pushbutton actuator?
4.Draw the electrical sy mbol for a two-position selector switch with one contact.
The switch is named “ICE” and the selector positions are “CUBES” on the left and
“CRUSHED” on the right. The contact is to be closed when the switch is in the
“CUBES” position.
5.Draw an electrical diagram rung showing a N/O contact CR5 in series with a N/C
contact CR11, operating a lamp L3.
6.A delay-on (TON) relay has a preset of 5.0 seconds. If the coil terminals are energized
for 8 seconds, how long will its contacts be actuated.
7.If a delay-on (TON) relay with a preset of 5.0 seconds is energized for 3 seconds,
explain how it reacts.
8.If a delay-off (TOF) relay with a preset of 5.0 seconds is energized for 1 second,
explain how the relay reacts.
9.Draw a ladder diagram rung similar to Figure 1-30 that will cause a lamp L5 to
illuminate when relay contacts CR1 is ON, CR2 is OFF, and CR3 is OFF.
10.Draw a ladder diagram rung similar to Figure 1 -30 that will cause a lamp L7 when
relay CR2 is ON or when CR3 is OFF. L7 should be ON at to be OFF
all other times. (Hint: Make a table showing all the possible states of CR2 and CR3 and
mark the combinations that cause L7 to be OFF. All those not marked must be the ones
when L7 is ON.)
11.Draw a ladder diagram rung similar to Figure 1 -30 that will cause relay CR10 to
energize when either CR4 and CR5 are ON, or when CR4 is OFF and CR6 is ON. Then
add a second rung that will cause lamp L3 to illuminate 4 seconds after CR10 energizes.
1.How were early machines controlled before PLC's were developed?
2.When were the first PLC's developed?
3.What is a shoe box PLC?
4.List four types of I/O modules?
5.List five devices that would be typical inputs to a PLC. List five devices that
a PLC might control.
6.What types of memory might a PLC contain?
7.Which type or types of memory would store the program to be executed by
the PLC?
8.What is the purpose of the programming unit?.
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 170 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
9.What type of control system did the PLC replace? Why was the PLC better?
10.What industry was primarily responsible for PLC developmen t?
11.What are the two steps the PLC must perform during operation?
12.Describe I/O Update.
13.What is the Output Image Register?
14.Describe the procedure for solving a rung of logic.
15.What are the allowed direction of current flow in a ladder logic run g?
16.Define scan rate.
17.If a PLC program is 7.5K long and the scan rate of the machine is 7.5
msec/K, what will the length of time between I/O updates be?
18.Define scan time.
1.Is a normally closed contact closed or open when the relay coil is energiz ed?
2.What is the limitation on the number of contacts associated with a particular relay coil
in a PLC program?
3.How is the state of a relay coil represented inside the PLC?
4.If a particular coil is to be an output of the PLC, when is the state of the c oil transferred
to the outside world?
5.Draw the ladder logic rung for a normally open IN1 AND'ed with a normally closed
IN2 driving a coil CR1.
6.Repeat 5 above but OR IN1 and IN2.
7.What physical changes would be required to system wiring if the PLC syst em of
problem 5 had to be modified to operate as problem 6?
8.Draw the ladder logic rung for a circuit in which IN1, IN2 and IN3 all have to be ON
OR IN1, IN2 and IN3 all have to be OFF in order for OUT1 to energize.
9.It is desired to implement a switch s ystem similar to a three -way switch system in house
wiring, that is, a light may be turned on or off from either of two switches at doors on
opposite ends of the room. If the light is turned on at one switch, it may be turned off at
the other switch and v ice versa. Draw the ladder logic rung which will provide this.
Define the two switches and IN10 and IN11 and the output which will control the light as
OUT18.
10.Draw the ladder logic rung for an oscillator which will operate only when IN3 and IN5
are both ON or both OFF.
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 171 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
1.Draw the ladder rung for an R -S type flip flop that will energize when both IN1 AND
IN2 are on and will de -energize when both IN3 AND IN4 are ON. The condition where
all inputs are on will not be a defined state for this problem, i.e., it will not be allowed to
occur so you do not have to plan for it.
2.Draw the ladder diagram for a T flip flop CR1 which will toggle only when IN1 and
IN2 are both OFF.
3.Develop the ladder for a system of two T flip flops which will function as a two bit
binary counter. The least significant bit should be CR1 and the most significant bit
should be CR2. The clock input should be IN17.
4.Viết chương trình dùng LAD cho vi ệc dịch thanh ghiDevelop the ladder diagram for a 3
bit shift register using J -K flip flops that will shift each time IN1 is switched from OFF to
ON. The input for the shift register is to be IN2. The three coils for the sh ift register may
be any coil numbers you choose.
5.Design the ladder diagram for a BCD counter using T flip flops. The LSB of the
counter is to be CR1 and the MSB is to be CR4. The clock input is IN2.
6.Design the ladder diagram for a device that will co unt parts as they pass by an
inspection stand. The sensing device for the PLC is a switch that will close each time a
part passes. This switch is connected to IN1 of the PLC.
A reset switch, IN2, is also connected to the PLC to allow the operator to manually reset
the counter. After 15 parts have passed the inspection stand, the PLC is to reset the
counter to again begin counting parts and turn on a light which must stay on until reset by
a second reset switch connected to IN3. The output from the PLC t hat lights the light is
OUT111.
7.Design the ladder diagram for a program which needs a timer which will
cause a coil CR24 to energize for one scan every 5.5 seconds.
1.What is the voltage resolution of a 10 -bit unipolar 5 volt analog input?
2.How many bits would be needed for an analog output if, after applying the 25% rule of
thumb, we need a resolution of 4.8 millivolts for a signal that has a range of 0 to +10
volts?
4.An 8-bit bipolar 5 volt analog input has an input of -3.29 volts. What will be the
decimal value of the number the converter sends to the CPU in the PLC?
5.You program a PLC to output the binary number 10110101 to its analog output. The
analog output is 8-bits, 10 volts, bipolar. What DC voltage do you expect to see on the
output.
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 172 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
6.An AC motor controller has a frequency control input of 0 -10 volts DC which varies the
output frequency from 0 -60Hz. It drives a 3-phase induction motor that is rated at 1750
RPM at 60 Hz. The DC input to the motor controller is provided by an analog output
from a PLC. The analog output is unipolar, 10 volts, 10 bits. What binary number must
you program into the PLC to cause it to output the appropriate voltage to run the motor at
1000 RPM (assume for the motor that the relationship between frequency and s peed is a
simple ratio)?
7.A pressure sensor is rated at 0 -500 psi and has an output range of 0 -10 volts DC (10
volts corresponds to 500 psi). It is connected to a PLC’s analog input, that is 10 bits, 10
volts, unipolar. If the PLC reads the analog input as 8B3
16 what is the pressure in psi?
1.What is the difference between a discrete sensor and an analog sensor?
2.Manufacturers specify the range of inductive proximity sensors based on what type of
target metal?
3.An inductive proximity sensor has a spe cified range of 5mm. What is it’s range when
sensing a brass target object?
4.Capacitive proximity sensors will sense metal objects as well a inductive proximity
sensors. So why use inductive proximity sensors?
5.Why are ultrasonic proximity sensors not used to sense close-range objects?
6.When the beam of a thru -beam NPN dark-on optical sensor is interrupted by a target
object, it’s output will be logically _____ (high or low).
7.State one disadvantage in using a thru -beam optical sensor.
8.What is the difference between a diffuse -reflective and retro -reflective optical sensor?
9.Why do retro-reflective optical sensors use polarizing light filters?
1.When a bi-metallic strip is heated, it bends in the direction of the side that has the
_____ (high or low) coefficient of expansion.
2.What is the Seebeck voltage?.
3.What is chromel? What is alumel?
4.A 200 ohm platinum RTD measures 222 ohms. What is its temperature?
5.A N/O float switch closes when the liquid level is ___ (low or high).
6.A 100mm long meta l rod is compressed and measures 97mm. What is the strain?
7.A 1k ohm strain gage is connected into a bridge circuit with the other three resistors R
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 173 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
= R = R = 1k ohms. The bridge is powered by a 10 volt DC 1 2 3 power supply. The
strain gage has a gage factor k = 1.5. The bridge is balanced (Vout = 0 volts) when the
strain = 0. What is the strain when Vout= +200 microvolts?
8.A 0 to +500psi pressure transducer has a calibration factor of 100 psi/volt.
a) What is the pressure if the transducer out put is 1.96 volts? b) What is the full scale
output voltage of the transducer?
9.Water is flowing at 10 mph in a square concrete drainage canal that is 3/sec?
10' wide. The water in the canal is 5' deep. What is the flow in ft
10.What is an advantage in using a thermal dispersion flow switch as opposed to other
types of flow switches?
11.A slotted disk and opto -interrupter as shown in Figure 9 -27 outputs pulses at 620 Hz.
What is the rotating speed of the disk in rpms?
12.A 3600 pulse incremental encode r is outputting a 2.5 kHz square wave.
What is a) the resolution of the encoder, and b) the speed of rotation?
13.A 10-bit absolute optical encoder is outputting the octal number 137. What is its shaft
position with respect to mechanical zero?
14.A 10 bit absolute optical encoder is outputting the gray code number 1000110111.
What is its shaft position with respect to mechanical zero?
15.A 16 inch magnetostrictive sensor has a full scale output of 10 volts. When it is
outputting 3.55 volts, how far is t he magnet from the sensor element head?
1. Decide whether each of these statements is True (T) or False (F).
The instruction list:
X401LD
X402AND
Y430OUT
describes a ladder diagram rung for which there is an output when:
(i) Input X401 is activated but X 402 is not.
(ii) Input X401 and input X402 are both activated.
A (i) T (ii) T
B (i) T (ii) F
C (i) F (ii) T
D (i) F (ii) F
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 174 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
2. Decide whether each of these statements is True (T) or False (F).
The instruction list:
X401LD
X402OR
Y430OUT
describes a ladder diagram rung for which there is an output when:
(i) Input X401 is activated but X402 is not.
(ii) Input X402 is activated but X401 is not.
A (i) T (ii) T
B (i) T (ii) F
C (i) F (ii) T
D (i) F (ii) F
3. Decide whether each of these statements is True (T) or False (F).
The instruction list:
X401LD
X402ANI
Y430OUT
describes a ladder diagram rung for which there is an output when:
(i) Input X401 is activated but X402 is not.
(ii) Input X401 and input X402 are both activated.
A (i) T (ii) T
B (i) T (ii) F
C (i) F (ii) T
D (i) F (ii) F
4. Decide whether each of these statements is True (T) or False (F).
The instruction list:
X401LDI
X402ANI
Y430OUT
describes a ladder diagram rung for which there is an output when:
(i) Input X401 is activated but X402 is not.
(ii) Input X401 and input X402 are both activated.
A (i) T (ii) T
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 175 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
B (i) T (ii) F
C (i) F (ii) T
D (i) F (ii) F
5. Decide whether each of these statements is True (T) or False (F).
The instruction list:
X401LD
Y430OR
X402ANI
Y430OUT
describes a ladder diagram rung for which there is:
(i) An output when input X401 is momentarily activated.
(ii) No output when X402 is activated.
A (i) T (ii) T
B (i) T (ii) F
C (i) F (ii) T
D (i) F (ii) F
6. Decide whether each of these statements is True (T) or False (F).
The instruction list:
I0.1A
I0.2A
Q2.0=
describes a ladder diagram rung for which there is an output when:
(i) Input I0.1 is activated but I0.2 is not.
(ii) Input I0.1 and input I0.2 are both activ ated.
A (i) T (ii) T
B (i) T (ii) F
C (i) F (ii) T
D (i) F (ii) F
7. Decide whether each of these statements is True (T) or False (F).
The instruction list:
I0.1A
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 176 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
I0.2O
Q2.0=
describes a ladder diagram rung for which there is an output when:
(i) Input I0.1 is activated but I0.2 is not.
(ii) Input I0.2 is activated but I0.1 is not.
A (i) T (ii) T
B (i) T (ii) F
C (i) F (ii) T
D (i) F (ii) F
8. Decide whether each of these statements is True (T) or False (F).
The instruction list:
I0.1A
I0.2AN
Q2.0=
describes a ladder diagram rung for which there is an output when:
(i) Input I0.1 is activated but I0.2 is not.
(ii) Input I0.1 and input I0.2 are both activated.
A (i) T (ii) T
B (i) T (ii) F
C (i) F (ii) T
D (i) F (ii) F
9. Decide whether each of these statements is True (T) or False (F).
The instruction list:
I0.1AN
I0.2AN
Q2.0=
describes a ladder diagram rung for which there is an output when:
(i) Input I0.1 is activated but I0.2 is not.
(ii) Input I0.1 and input I0.2 ar e both activated.
A (i) T (ii) T
B (i) T (ii) F
C (i) F (ii) T
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 177 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
D (i) F (ii) F
10Decide whether each of these statements is True (T) or False (F).
The instruction list:
I0.1A
Q2.0O
I0.2AN
Q2.0=
describes a ladder diagram rung for which there is:
(i) An output when input I0.1 is momentarily activated.
(ii) No output when I0.2 is activated.
A (i) T (ii) T
B (i) T (ii) F
C (i) F (ii) T
D (i) F (ii) F
11. Decide whether each of these statements is True (T) or False (F). For the sequential
function chart shown in Figure 6.22:
(i) State 1 is realised when the condition X1 is realised.
(ii) Output 1 occurs when the condition X2 is realised.
A (i) T (ii) T
B (i) T (ii) F
C (i) F (ii) T
D (i) F (ii) F
Figure 6.22 : Problem 11
12. Decide whether each of these statements is True (T) or False (F).
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 178 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
Figure 6.23 Problem 12
For the sequential function chart shown in Figure 6.23, if State 1 is active:
(i) State 2 is realised when the condition X2 is realised.
(ii) State 3 occurs whe n the condition X3 is realised.
A (i) T (ii) T
B (i) T (ii) F
C (i) F (ii) T
D (i) F (ii) F
13. For the ladder program described in Figure 6.24(a), which of the sequential function
charts in Figure 6.24(b) will represent it?
Figure 6.24 Problem 13
Auto books Thiết kế hệ thống điều khiển c ơ bản với S7-200 No1
Copyright 2007 by AUTOMANVN page 179 / 375 Tutorial
Status: 18/08 Version 2.2
Tài liệu này được xây dựng để hỗ trợ sinh vi ên học tập, nghiên cứu. Ngoài đối tượng sinh viên, mọi sự sao chép, sử dụng thông tin tr ên tài liệu, đề nghị liên hệ :
ho ặc số điện thoại 0974.858.101.
Problems 14, 15 and 16 concern the sequential function chart shown in Figure 6.25.
Figure 6.25 Problems 14, 15 and 16
14. Decide whether each of these statements is True (T) or False (F). For the sequential
function chart shown in Figure 6.25, o utput Y2 will occur if output Y1 has been realised
and:
(i) Both X2 and X3 have been realised.
(ii) Just X2 has been realised.
A (i) T (ii) T
B (i) T (ii) F
C (i) F (ii) T
D (i) F (ii) F
15. Decide whether each of these statements is True (T) or False (F). For the sequential
function chart shown in Figure 6.25, output Y4 will occur if output Y2 has occurred and:
(i) Output Y3 has occurred.
(ii) X4 has been realised.
A (i) T (ii) T
B (i) T (ii) F
C (i) F (ii) T
D (i) F (ii) F