factors affecting the use of mobile banking services in hanoi, vietnam
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (586.46 KB, 23 trang )
Thai Nguyen University
Socialist Republic of Vietnam
Southern Luzon State University
Republic of the Philippines
DOCTORAL DESSERTATION
(ABSTRACT)
FACTORS AFFECTING THE USE OF MOBILE BANKING
SERVICES IN HANOI, VIETNAM
In Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements for The
Degree of Doctor in Business Administration
Full Name: Vu Manh Cuong
English Name: Cameron
Adviser
Dr. Nelly Mendoza
(Southern Luzon State University)
HANOI, 2013
!
1
Chapter I. INTRODUCTION
Mobile banking services have become the objective and inevitable trend
during the international economic integration more and more deeper in Vietnam. The
development of mobile banking services has brought significant benefits to customers
as a convenient, fast and accurate of the transaction. At the same time it also opens up
new development opportunities for the telecommunications providers, application and
software developers, e-commerce merchants and bankers in Vietnam.
Vietnam has more than 86 million population (GSO, 2012), 120.7 million
mobile subscribers, 15.5 million fixed subscribers, over 31% rate of people use the
Internet regularly, 30.2 million mobile users and (MIC, 2012), 44 bankers with high-
tech infrastructure (SBV, 2013), and more then 400 Value added services providers
(MIC, 2013). It should be a great potential market.
1.1 Background of the study
The study of consumer behavior is an important part of the research needs of
customers. To succeed in any business at all the fields, especially in fast-growing and
dynamic markets as today's, entrepreneurs, marketers need to know clearly about
customers such as the needs, convenience, the difficulty, suitable time, etc.
Numerous theoretical models have been launched and continuous
improvement. Most notably, Theory of Reasoned Action Models introduced Ajzen &
Fishbein (1975), often referred to TRA model, and then extended into TPB model
(Ajzen, 1991). Davis (1989) has applied this theory to build the Technology
Acceptance Model (TAM), and then Venkatesh and Davis (2000) has built
Technology Acceptance Model 2 (TAM2).
Thousands of studies have applied TAM model to explain the behavior of
using integrated technology services on many different areas in many countries
around the world. In the technology service sector in general and mobile banking
services in particular, the choice and use by customer is also comply the basic
principles of psychology and behavior, but specific expression of consume behavior
in these situations, conditions and environment are totally different. This has made the
line of research on consumer behavior continues incessantly.
!
2
In recent years, mobile banking has attracted particular and get the attention of
researchers, managers. There are a lot of research in the world were conducted, but,
in-depth studies of this field in Vietnam were very rare. So far there is no research
about the use of mobile banking services in Hanoi specifically and Vietnam overall.
Stemming from such pressing issues, this study was conducted to explore the factors
influence the use of mobile banking services of customers in Hanoi. The dissertation
contributes to propose the policy to develop this services in the near future.
1.2 Statement of the objectives
- Determine the relationships of the demographic characteristics (age, gender,
occupation, income and educational attainment) of the respondents and the
use of mobile banking services;
- Determine the differences in the purpose of the use of mobile banking services
by customers in Hanoi by gender, age, education, occupation and income;
- Determine the factors affecting the use of mobile banking services by
consumers in Hanoi;
- Analyze the level level of influence of the different factors to the use of
mobile banking services in Hanoi; and
- Propose solutions to improve mobile banking services to increase the number
of users in Hanoi, Vietnam.
1.3 Hypothesis
H1: The use of mobile banking services are affected by the geographical location
and demographic characteristics such as age, gender, education, area,
occupation and income.
H2. Perceived usefulness of mobile banking services has a positive impact on the
use of the services
H3: Perceived of ease of use of mobile banking services has a positive impact to
the use of the services
H4: Perceived costs to use mobile banking services have a negative impact to use
the service
!
3
H5: The trust of customers on mobile banking services has a positive impact to the
use of the services
H6: Perceived risks of customers for mobile banking services have a negative
impact to the use of the services
1.4 Significance of the study
Regarding scientific, dissertation contributed (i) reviewing the basis of the
theory of consumer behavior generally and Theory of Technology Acceptance Model
(TAM) in particular; (ii) providing the research model of consumer's behavior in the
use of mobile banking services in Hanoi.
Regarding practice, dissertation contributed (i) to enrich the practical research
in the field using mobile banking services in Vietnam generally and Hanoi in
particular; (ii) to outline a comprehensive picture of the use of mobile banking
services in Hanoi. And then identify the major factors affecting the use of the services
of customer in the studied area; (iii) to suggest the main recommendations of the
policy for the mobile banking service providers in Hanoi, practical contribution to
improving mobile banking services in Vietnam; (iv) to provide a good reference
material for managers, service providers, researchers and practitioners in the
management agencies, universities of Vietnam and International.
1.5 Scope and Limitations
The research will be conducted within Hanoi Capital. The respondents were
living in Hanoi and using mobile banking services (included SMS banking and
Internet banking). The survey was conducted in districts: Hoan Kiem, Ba Dinh, Hai
Ba Trung, Dong Da, Cau Giay, Tay Ho, Thanh Xuan, Hoang Mai, and Long Bien.
!
4
Chapter II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
AND STUDIES
2.1 Banks in Vietnam
According to State Bank of Vietnam (SBV), at the end of 2012 in Vietnam,
there are total 44 banks (excluding 1 Vietnam Development Bank, 1 Vietnam Bank
for Social Policies, Joint"venture Bank, Branches of Foreign Bank, Rep. Office of
Foreign Banks), including 5 Stated owned Banks (Agribank, BIDV, Vietinbank,
Vietcombank, and Mekong Housing Bank); 34 Commercial Banks (such as: ACB,
Eximbank, Techcombank, MBBank, Maritime, etc.); and 5 wholly Foreign-owned
banks (HSBC, Standard Chartered, ANZ, Hong Leong, Shinhan).
2.2 Mobile Banking Services
The rapid growing of mobile service in Asia has created opportunities for new
and innovative mobile services. The most promising is Mobile finance service
including mobile banking, mobile payment and mobile commerce services. Mobile
banking allow end-users to get bank information via SMS such as balances,
transaction history, promotion information, confirmation for direct payment (Niina M,
Matti R, Virpi K.T, 2004). The cost is saved average 19% when using the mobile
banking service (McKay, Claudia and Mark Pickens, 2010).
The number of mobile banking users worldwide is forecasted to grow from 55
million in 2009 to 894 million in 2015, at a compound annual growth rate of 59%
(Ann H., 2010). Juniper estimate the number of mobile subscribers who use mobile
banking will exceed 400 million globally by 2013. Mobile banking can perform
account balances and transaction history inquiries, funds transfers, and bill payments
via mobile devices (Laukkanen, 2007; Turban, King, Viehland, & Lee, 2006).
2.3 Mobile Financial Services
Mobile Financial Services where telecom and banking converge, using the
mobile device for formal financial services, Immediate, simple and convenient access
to money-related transactions. Using for shopping online, pay for education, save
money, buy insurances, pay bills, receive and payoff loans, buy tickets, pay for
!
5
parking, transfer airtime, purchase goods, receive salary, pay for transportation, send
money home, etc. (Jorge Campos, 2011).
According to Niina et al., the key players of mobile financial services includes
banks and other financial organizations, the telecom operators, retailers, equipment
manufacturers (hand-set devices), and software vendors that enabling the services are
incremental in building the infrastructure progress.
2.4 Mobile Commerce Services
Mobile Commerce (m-commerce) is defined as a business transaction
conducted through mobile communication networks or the Internet (Siau & Shen,
2003). M-commerce can offer value to consumers through convenience and flexibility
by enabling time and place independence (Kim et al., 2009; Venkatesh et al., 2003).
There are challenges associated with m-commerce, and specifically mobile
banking. Mobile devices with a small screen size, limited screen resolution and
uncooperative keypad may make it difficult for the customer (Kim et al., 2009).
2.5 Mobile banking technology
Currently, mobile banking is implemented through three different technology
solutions: browser-based applications, messaging-based applications and client-based
applications (Kim et al., 2009; Tiwari & Buse, 2007). The browser-based application
is essentially a Wireless Access Protocol (WAP)-based internet access (Kim et al.,
2009). This requires a compatible mobile phone which is WAP-enabled. The mobile
phone is used to access banking portals through the Internet.
Based on assessment of mobile banking is a full-potential field in the world,
many technology teams was focused in research and development of technology
solutions for this type of service. The solutions are continuously improved in line with
the rapid development of mobile, especially the rapid growth of smartphone.
2.6 Mobile Banking in Vietnam
Mobile banking has been introduced in Vietnam quite late compare to other
countries in the region. Four commercial banks only have actually introduced in 2011.
!
6
The mobile banking functions are focusing account inquire, money transactions,
payment for bills and online.
According to while paper on Information & Communication Technology 2012
(MIC, 2013), by August 2012, Vietnam has 25.79 million smart phone subscribers,
contribute to 21% of total mobile phone subscribers and representing an increase 27%
compared to the end. This is quite good for the development of mobile application in
general and mobile banking in particular.
With the interest of bankers, service providers, mobile operators, merchants
and combined the rapid development of technology environments including core
banking, e-commerce, mobile infrastructure, and smart phone, mobile banking is a
potential market in Vietnam.
2.7 Consumer Behavior
The consumer behavior is a research tries to understand the decision-making
processes of buyers, both individually and in-group, including: problem recognition,
information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase
behavior. It studies characteristics of individual consumers such as demographics and
behavioral variables in discovering the people's wants. It also tries to assess
influences on the consumer from related groups such as family, friends, and society.
According to Kotler and Armstrong (1996), the factors affecting the consumer
behavior are cultural, social, personal, and psychological.
The theories and models are most commonly applied in the study and
explanation of consumer behavior since the second half of the twentieth century are
theories of attitude and behavior, such as Expectancy-Value Theories (Tolman, 1932;
Rotter, 1954; Atkinson, 1957), Theory of Reasoned Action (Ajzen & Fishbein, 1980),
Theory of Planned Behavior (Ajzen & Driver, 1992).
2.8 Expectancy-Value Theory
Expectancy Value Theory (EVT) was presented by Tolman (1932), Rotter
(1954) and Atkinson (1957). According to Fishbein & Ajzen (1975), people learn
"expectations," i.e., briefs that a given response will be followed by some events.
Since these "events" could be either positive or negative "reinforcers" (i.e., could have
!
7
positive or negative valence), his argument, essentially, was that people would learn
to perform (or increase their probability of performing) behavior that they "expected"
to lead to positively valence events (Tolman, 1932). In the late 1970s Fishbein and
Ajzen expanded expectancy-value theory into the theory of reasoned action (TRA).
2.9 The Theory of Reasoned Action
The theory of reasoned action (TRA) developed by Fishbein & Ajzen (1969,
1980). This model defines the links between beliefs, attitudes, norms, intentions, and
individuals behaviors. The person’s behavior is determined by its behavioral intention
to perform it. The intention is itself determined by the person’s attitudes and his
subjective norms towards the behavior. TRA also claims that all other factors
influence the behavior only do so in an indirect way by influencing the attitude or
subjective norms. Fishbein & Ajzen (1975) refer to these factors as external variables.
2.10 The Theory of Planned Behavior
Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) was developed from TRA (Venkatesh et
al, 2003) with the aim to improve the predictive power by adding a major predictor,
perceived behavioral control, to the model. It is one of the most predictive persuasion
theories. It has been applied to studies of the relations among beliefs, attitudes,
behavioral intentions and behaviors in various fields such as advertising, public
relations, advertising campaigns and healthcare.
TPB is good in explaining individual acceptance and usage of many different
technologies (Harrison et al., 1997; Mathieson, 1991; Taylor and Todd, 1995).
However, Taylor and Todd (2001) reported that it did not provide a complete
explanation of usage intention as compared TAM (Faziharudean & Tan, 2011).
According to Gregory (2011) both TRA and TPB models have been widely used to
evaluate a range of consumer behaviors.
2.11 Technology Acceptance Model
The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) introduced by Davis (1989). TAM
has been continuously studied and extended to TAM2 by Venkatesh & Davis (2000)
and the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) by
Venkatesh et al. (2003). TAM3 has also proposed by Venkatesh & Bala (2008).
!
8
TAM suggests that perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use are the two
most important factors in explaining individual users’ adoption intentions and actual
usage (Davis, 1989). TAM has been extensively tested and validated and is a widely
accepted model, which can be modified or extended using other theories or constructs
(Taylor & Todd, 1995; Davis & Venkatesh, 2000; Wu & Wang, 2005; Luarn & Lin,
2005; Zhang, Gou & Cheng, 2008). Venkatesh and Davis (2000) introduced such
social and organizational factors as subjective norms, impression, quality of output
and work relevance into the TAM model and proposed TAM2.
Luarn & Lin (2005) conducted a study with perceived usefulness, perceived
ease of use, perceived credibility, self-efficacy, and perceived financial cost. Lee
(2009) investigated the factors influencing the adoption of Internet banking with five
antecedents of perceived risk were discussed: performance risk, social risk, financial
risk, time risk and security risk. Perceived cost is defined as the extent to which a
person believes that using mobile banking will cost money (Luarn & Lin 2005). Kim
et al. (2009) defined the trust as a psychological expectation. The trust was defined as
a feeling of security and willingness (Kim, Chung & Lee, 2010).
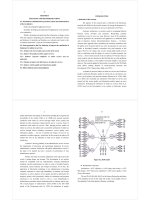
2.12 The conceptual framework
Perceived usefulness
Perceived ease of use
Perceived Cost
Trust
Perceived Risk
Demographic Characteristics
(age, gender, education, area, occupation,
income)
The use of
mobile banking services
H1
H2
H3
H4
H5
H6
!
9
Chapter III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 Research design
To achieve the proposed objectives, the research process was organized into
two steps including qualitative research and quantitative research. The entire research
process is summarized in following figure.
3.1.1 Pilot study
A pilot study was conducted by interviewing 50 customers in Hanoi who are
using mobile banking services to explore preliminarily the main characteristics of the
use of mobile banking services. The pilot study was a basis to design the survey
questionnaire for the next quantitative study.
3.1.2 Variable measurement
There are five independent variables, specifically, "perceived usefulness",
"perceived ease of use", "perceived cost", perceived risk" and "trust of service". Each
Theoretical
model
Orientation
Study materials
and questionnaire
development
Fieldwork and
integrated
analysis
Pilot Study (N=50)
Theoretical framework and research model
(theories of psychology and consumer
behavior, model TRA, TPB and TAM)
Questionnaire
Completing the questionnaire
Formal Study (N = 800)
Formal
Questionnaire
Regression Model
Analysis
Descriptive Statistical
Analysis
Exploratory Factor
Analysis (EFA)
!
10
independent variable measured by three to ten questions related mobile banking
services. A total of 27 questions were conducted to five aspects of the use of mobile
banking services. The dependent variable was designed with three questions to
measure the use of mobile banking services in Hanoi. A five-point Likert scale was
applied to measure the responses of the survey.
3.2 Determination of Sample size
Total population of Hanoi is 6,451,909, in which 69.1% are aged between 15
and 64 (GSO, 2010) equal to 4,458,269. According to the stratified random sampling
method use Slovin’s formula with the error level at 5% showed the sample size is 400
as following formula:
n=
2
1 Ne
N
+
=
4,458,269
1+ 4,458,269 *(0,05)
2
= 399, 96 ≈ 400
However, Hanoi is a big city, the second biggest city in Vietnam, thus to
enhance practical significance as well as to ensure the reliability of data analysis,
Authors have collected data from 800 respondents.
3.3 Sampling design and techniques
The samples were conducted by the method of convenience sampling surveys,
but the adjustment on the surveying area and gender to ensure the sample is spread
evenly over the studied region. The survey was conducted in 9 districts including:
Hoan Kiem, Ba Dinh, Hai Ba Trung, Dong Da, Cau Giay, Tay Ho, Thanh Xuan,
Hoang Mai, and Long Bien. The number of sample was allocated as following table.
3.4 Research Instrument
The measurement tools used Likert scale introduced by Rennis Likert.
Questionnaire was used to collect primary data using five-point Likert scales. The
questionnaire was designed with two parts: (i) the questions related to respondents'
demographic characteristics to classify the group of consumers such as living area,
gender, age, occupation, income and education; (ii) the questions related to
measuring the influence and dimension of factors affecting the use of mobile banking
services in Hanoi.
!
11
The results of the reliability analysis of scale showed that Alpha coefficients
of all components are greater than 0.8, ranged from 0.8311 to 0.8807. The values of
the corrected Item - Total Correlation of variables ranged from 0.4489 to 0.8320,
greater than 0.3. That indicated the reliability of scale was satisfied.
3.5 Data gathering procedure
The study used both primary and secondary data to identify the factors
affecting consumer behavior on the use of mobile banking service in Vietnam. The
primary data was used to assess the influence and level of the factors. The secondary
data was used to analyze the demographic characteristics of respondents, features and
functions of the service model, current status and market potential of the services, the
ability to meet the suppliers in the value chain of mobile banking services, and the
aspects related to the research.
3.5 Data processing method
The collected information should be checked and revised by the review
process to avoid errors and inconsistencies. Then all the collected information is
encrypted answers and entered data into the computer. Authors used Microsoft Excel
2003 software for entering the survey data and processing of raw materials. After the
first phase of the basic data cleaning, data was imported into SPSS 16.0 software for
filtering in second phase, and then create statistical tables and conduct the.
3.6 Statistical treatment
The dissertation used Cronbach's Alpha to analyze the reliability of scale,
exploratory factor analysis to extract the factors, and regression analysis to analyze
and test the hypothesis and factors affecting the use of mobile banking services in
Hanoi. ANOVA analysis was used to determine the difference between the
demographic characteristics and the use of mobile banking services in Hanoi.
!
12
Chapter IV. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Profile of the respondents
4.1.1 Demographic characteristics
The study surveyed 800 respondents in 9 districts of Hanoi, there are 717
responses are useable for data analysis. The profile of the respondents as follows.
Demographic Characteristics
Frequency
Percent
Valid
Percent
Cumulative
Percent
Living area
Suburban
208
29.0
29.0
29.0
Center
509
71.0
71.0
100.0
Gender
Female
373
52.0
52.0
52.0
Male
344
48.0
48.0
100.0
Age
Less than 25
255
35.6
35.6
35.6
From 25 to 35
291
40.6
40.6
76.2
From 35 to 45
116
16.2
16.2
92.3
From 45 to 55
28
3.9
3.9
96.2
Over 55
27
3.8
3.8
100.0
Education
Secondary
22
3.1
3.1
3.1
High School
63
8.8
8.8
11.9
College
35
4.9
4.9
16.8
University
526
73.4
73.6
90.3
Graduated
69
9.6
9.7
100.0
Occupation
Business or Self-Employed
244
34.0
34.0
34.0
Officer or state area
276
38.5
38.5
72.5
Un-employer
30
4.2
4.2
76.7
Pupil or Student
124
17.3
17.3
94.0
Housewife
16
2.2
2.2
96.2
Retirement
27
3.8
3.8
100.0
Income
Less than 5 Million
192
26.8
31.6
31.6
From 5 to 10 Million
246
34.3
40.5
72.2
From 10 to 15 Million
96
13.4
15.8
88.0
From 15 to 20 Million
36
5.0
5.9
93.9
Over 20
37
5.2
6.1
100.0
!
13
4.1.2 The use of banking services
Most of the customers surveyed have at least a bank account with a rate of
84.2%. The customers do not have the bank account is only 15.8%. However, the
transactions in the bank is much less convenient. The results showed that 78.4% of
customers took less than 15 minutes to the nearest branch of bank, while 19% from
15 to 45 minutes. The rate of customer to the nearest branch over 45 minutes is only
small percentage, with 2.6%. This is entirely consistent with a city like Hanoi, the
branch of banks has grown rapidly in recent times. The percentage of customers who
have not used the service but intend to use if it is convenient and safe, is quite high,
with 44.6%. The results showed that 46% of consumers have used mobile banking
services. There are only 9.3% of customers are not interested in using the service.
4.2 Purpose of use mobile banking services
The results showed that purpose of customers are very different including
checking bank account, transfer money, pay for purchases or pay for monthly bills
such as electricity, telephone, TV cable, etc. Up to 448 customers equal to 77.5% use
the service to check account at the bank, 346 people (59.9%) to transfer money; the
purchase and monthly bills accounted respectively 257 and 221 customers, equal to
44.5% and 38.2%; the purpose of the savings is 34.6%. Female use the services for
the purpose of checking accounted 52% higher than male (48%).
Regarding the purpose of transferring money, female accounted 45.7% and
54.3% of male. The purpose of savings deposits female is higher than men, the rate
respectively 53.5% and 46.5%. Customers with high education level accounted the
rate higher than others, such as purpose of checking account up to 88.3%, transfer
money is 81.7%, pay for monthly bills is 53.3% compared with lowest ratio of others
respectively is 33.3% (secondary), 34.3% (high school) and 22.2% (college). The
highest income group accounted 91.7% compare with 57.5% of group has income
between 5 to 10 million. The purpose of pay for monthly billd accounted 36.0% to
52.8% except 21.4% ratio of group with income from 15 to 20 million.
4.3 Analysing the differences in the use of mobile banking services
4.3.1 The difference by living area
To analyse the difference of the trust of customers in the use the services,
research conducted analysis of variance. The results showed the Levene Statistic has
statistical significance levels by 0.001 (Sig.=.001) and Anova Sig.= 0.035. It can be
concluded that there is no difference by living area in the use of the services.
!
14
4.3.2 The difference by gender
Results of variance analysis showed that Levene Statistic has significant
level is 0.020 (Sig. =0.020), the variance of customer's trust for mobile banking
services between male and female is different at 5%. It allowed to conclude there
were not sufficient basic to confirm a difference by gender in the use of the services.
4.3.3 The difference by age
The results of analysis of variance showed Levene Statistic indicators are
significant level of 0.425 (Sig.=.425), Sig. value of .838 by ANOVA (Sig. = .838).
This allows the conclusion that was not enough basis to evaluate the difference
between the group of age in the use of mobile banking services.
4.3.4 The difference by education
The results of analysis of variance showed Levene Statistic indicators are
significant level of 0.106 (Sig.=.106), Sig. value of .334 by ANOVA (Sig. = .334).
This allowed to conclude that was not enough basis to evaluate the difference
between the level of education in the use of mobile banking services.
4.3.5 The difference by occupation
The results of analysis of variance showed Levene Statistic indicators are
significant level of 0.644 (Sig.=.644), Sig. value of .440 by ANOVA (Sig. = .440).
This allows the conclusion that was not enough basis to evaluate the difference
between the type of occupation in the use of mobile banking services.
4.3.6 The difference by income
The results of analysis of variance showed Levene Statistic indicators are
significant level of 0.261 (Sig.=.261), Sig. value of 0.937 by ANOVA (Sig. = .937).
This allowed to conclude that was not enough basis to evaluate the difference
between the level of income in the use mobile banking services.
4.4 Exploratory Factor Analysis
Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) is used to extract the factors. This study
used Principal component method with Variamax rotation stops when value in the
eigenvalue ≥ 1. According to Hair et al (1998), Factor loading is the norm to ensure
!
15
the practical significance of EFA. Factor loading > 0.3 are considered to achieve the
minimum level, Factor loading > 0.4 are considered important, > 0.5 are considered
to have practical significance.
The results of exploratory factor analysis are presented in following table.
Variable
Component
1
2
3
4
5
6
RISKSE1
.765
RISKSE2
.722
RISKSE3
.715
RISKSO1
.672
RISKSO2
.653
RISKTI1
.511
RISKTI2
.504
TRUST4
.764
TRUST5
.761
TRUST6
.725
TRUST3
.697
TRUST2
.668
TRUST1
.634
USEFUL2
.893
USEFUL1
.874
USEFUL3
.840
USEFUL4
.516
COSTPE1
.853
COSTPE3
.843
COSTPE2
.794
EASE1
.813
EASE3
.794
EASE2
.665
RISKFIN2
RISKPE2
.811
RISKPE1
.714
RISKFIN1
.606
Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy.
.866
Bartlett's Test of Sphericity
Approx. Chi-Square
10476.605
df
351
Sig.
.000
Analysis of 27 observed variables combined, the result is extracted 6 factors.
Analysis results showed coefficient KMO = 0.866 at significant level of Sig. = 0.000.
Thus the hypothesis of the overall correlation matrix is the homogenous matrix is
rejected, i.e. the variables are correlated with each other and satisfy the conditions in
the factor analysis. The analytical results have been extracted 6 factors with the factor
loading coefficients are higher than selected standards (≥ 0.5).
!
16
4.5 Correlation analysis
The correlation analysis showed that most of these variables are strongly
correlated and statistically significant at the 1% (Sig.2-tailed = .000) for variable
TRUOVER except variable COSTPE.
USEFUL
EASILY
RISK1
RISK2
COSTPE
TRUST
TRUOVER
USEFUL
Pearson
Correlation
1
.000
.000
.001
.000
.000
.262(**)
Sig.
(2-tailed)
.
1.000
1.000
.983
1.000
1.000
.000
EASILY
Pearson
Correlation
.000
1
.000
001
.000
.000
.304(**)
Sig.
(2-tailed)
1.000
.
1.000
.974
1.000
1.000
.000
RISK1
Pearson
Correlation
.000
.000
1
.002
.000
.000
164(**)
Sig.
(2-tailed)
1.000
1.000
.
.961
1.000
1.000
.000
RISK2
Pearson
Correlation
.001
001
.002
1
.001
.000
136(**)
Sig.
(2-tailed)
.983
.974
.961
.
.982
.998
.000
COSTPE
Pearson
Correlation
.000
.000
.000
.001
1
.000
.010
Sig.
(2-tailed)
1.000
1.000
1.000
.982
.
1.000
.782
TRUST
Pearson
Correlation
.000
.000
.000
.000
.000
1
.360(**)
Sig.
(2-tailed)
1.000
1.000
1.000
.998
1.000
.
.000
TRUOVER
Pearson
Correlation
.262(**)
.304(**)
164(**)
136(**)
.010
.360(**)
1
Sig.
(2-tailed)
.000
.000
.000
.000
.782
.000
.
** Correlation is significant at level of 0.01 (2-tailed)
4.6 Regression analysis
4.6.1 Regression model
The R2 Adjusted coefficient shows the data explained 33.1% of the impact of
independent variables on the dependent variable, the statistic F = 71.832 at
significance level 0.000 with the assumption of multiple regression were satisfied. In
particular, most of the explanatory variables have expected sign as predicted and
statistically significant at the 1% level, except the factor COSTPE has the
!
17
phenomenon of multi-collinearity. With the analysis results above, the regression
model is written as follows:
TRUOVER = .262 USEFUL + .304 EASILY - .163 ISK1 - .136 RISK2 + .360 TRUST
The regression models showed the variables marked as expected. The factor
USEFUL is the third impact among analysis variables, EASILY have been positively
impact, RISK1 has the opposite impact, RISK2 marked as expected - negative sign,
TRUST has a positive impact. In 6 factor were analysed, there are 5 factors are
actually influence to the use of mobile banking service including: Perceived
usefulness of the service (USEFUL), Perceived ease of use of the service (EASILY),
Perceived risk of social and safety (RISK1), Perceived risk of performance and
finance (RISK2), Trust on the service (TRUST).
4.6.2 Tesing the assumptions of the regression model
! Testing the assumption of a linear regression model of constant variance:
The chart of standardized residuals and predicted values residuals showed random
residual dispersion in the surrounding area of the original release. It allowed to
conclude that the assumption of a linear regression model of constant variance is
satisfied.
! Testing the error variance in the model: The results of the test Spearman
showed that assumptions about the correlation of the overall is zero is rejected. This
allows the conclusion that the research model variance of the error does not change.
! Testing the standardized distribution of residuals: From chart of residual
distribution shows the average value of residuals is 0 (Mean=0.00) and histogram of
standardized residuals follow near the standardized distribution. This allows conclude that
the standardized distribution assumption of the regression model was not violated.
! Testing the independence of the error in the model: The value Durbin-
Watson shows D = 1.978, the value D in the acceptable range: 1< D <3. This allowed to
conclude there is no autocorrelation between the residuals.
! Testing the multi-collinearity: Base on all the value of VIF less than 3, It
showed that there is no phenomenon of multicollinearity between the independent
variables. It allowed to conclude that the regression model was not violated the
classical statistical hypothesis. Therefore, the research model is consistent.
!
18
Chapter V. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND
RECOMMENDATIONS
5.1 Summary of findings
(1) There is not enough evident to conclude the difference of the use of mobile
banking services between central and suburban living areas, between male and
female, between level of education, between income and between occupation for the
customers in Hanoi.
(2) Most consumers in Hanoi use the mobile banking services to check bank
account and transfer money. In particular, the purpose of checking account is largest
up to 77.5%. The other purposes such as pay for monthly bills, pay for shopping,
money savings are modest. The rate of money savings purpose is only 34.6%.
(3) The major customer use the mobile banking services are people living in
urban areas, where people have a high awareness levels, accounted 71%. Female use
mobile banking services is higher than male, the rate of female accounted 52%.
Young people below the age of 35 represent a high proportion (76%) on the use of
mobile banking services.
(4) The most consumers use mobile banking services is high education. The
customer with education level of university accounted a high percentage (73.4%). The
customers working in business or state organizations are main group of these services
in Hanoi area (72.5%).
(5) The dissertation indicated that in six factors studied, there are five factors
affecting the use of mobile banking services with statistically significant at 1% level,
including (i) "trust of consumers" on the services has a greatest positive influence, (ii)
"perceived ease of use" has a second greatest positive influence, (iii) "perceived
usefulness" has a third greatest positive influence, (iv) "perceived risks of social and
safety" has a strongest negative influence, and (v) "perceived risks of operation and
finance" has a weakest negative influence. The factor "perceived cost" was only found
insignificant to the use of mobile banking service for customers in Hanoi.
!
19
5.2 Conclusion
First, dissertation indicated that there is not enough evident to conclude the
relationships between demographic characteristics and the use of mobile banking for
customers in Hanoi.
Second, dissertation indicated that checking account is first purpose of
customers and money transfer is second. The purposes such as pay for monthly bills,
pay for shopping, money savings are modest. These results indicated that there is not
enough evident to conclude the difference between the use of mobile banking services
by customers in Hanoi by gender, age, education, occupation and income.
Third, dissertation has determined five factors affecting to the use of the
mobile banking services, including: (1) perceived usefulness, (2) perceived easy of
use, (3) perceived risk of social and safety, (4) perceived risk of performance and
finance, and (5) trust. The study indicated that factor "perceived cost" had no
significant relationship with the use of the mobile banking services.
Fourth, dissertation has determined the factor "trust" is strongest positive
impact, "perceived ease of use" is second positive impact, and "perceived usefulness"
is the third positive impact to the use of mobile banking services. The factor
"perceived risk of social and safety" has strongest negative impact and "perceived risk
of performance and finance" has second negative impact to the use of this service.
Fifth, dissertation provide the solutions to improve the services, the solutions
to minimize the risks for consumers during the use of these services, the policies to
raise awareness of consumers and enhance the trust of consumers for the use of
mobile banking services.
5.3 Recommendations
5.3.1 Improving the mobile banking services
Mobile banking service providers have a key role in the supply chain of
mobile banking services. They provide convenient facilities for consumers to perform
banking services through mobile device. The service system has to connect all the
banks to ensure processing banking services with any banks. They must be installed
physical cable or channel with all mobile operators to offer the ability send requests
and receive results between the consumers' mobile device and core banking system.
!
20
Providers must provide the multiple interfaces to communicate flexibly with most
common merchants to offer a convenient payment capability using mobile phones for
customers.
The new mobile technologies allows multiple ways to access services such as
mobile applications, WAP, WEB, SMS, USSD, NFC, etc. then the supplier must
design service models to adapt most platforms and give customers more options to
use the service. Mobile networks are an indispensable part of the mobile banking
service system. It has a role to serves to convey information between the end-users
and the core-banking system. Network quality affects greatly the transaction quality
of the mobile banking services.
As the results of analysis in this study, the satisfaction level of users for
mobile network was not really high. Therefore, mobile operators need to upgrade the
infrastructure to ensure that banking transactions through mobile network to achieve
high levels of satisfaction. In addition, mobile operators need to have the priority
policies for this service instead treated as the same other value added services. That
will support to high speed transactions such as OTP (once time password) or high
security requirements can be well done.
As the findings of this study, most customers have the needs use mobile
banking services to check the bank account and transfer money. So, the application
developers should focus on designing these features, such as put the high priority for
the appearance of these features on the top, it will minimize number of actions for
end-users when complete successfully a request. Thereby, helping customers save
time in the use of the features with high frequency of use.
Since the research findings, the purpose of shopping payment was modest,
partly due traders have not focused embedding the online payment functions in their
selling activities. It reduced the chances of online payments for consumers. Authors
recommend that service providers should actively connect with the online sales
system, especially the common goods, to add mobile banking functions to give the
ability online buying and pay through mobile for consumers. As major customers use
the mobile banking service living in urban areas and female rate is higher, so
application developers should focus on designing the user-friendly interface and style.
The items appear in the features may be more appropriate preferentially for female.
!
21
The ease of use of the service has a second greatest positive impact to the use
of the mobile banking services. It was one of the important findings of this research.
That recommend to service providers and developers to make the application with the
focus on the aspects of the ease when use the tools to do an action by the mobile
banking services.
The complex procedures of payment transactions, bank transfers are safer to
bankers but it is a barrier for customer convenience. It suggests banks and service
providers should apply a simple procedure for end-users. When customers feel free in
using the chance to keep customer is higher and each customer will be come a
effective marketer for the mobile banking services.
5.3.2 Minimizing the risks to customer in using mobile banking services
The risk of social and safety have a negative impact to the use of mobile
banking services. It reflects a fact that consumers are still concerned about the risk of
losing money when using electronic banking services. Especially in recent years,
some money burglary in the bank account or fake cardholders to pay for goods that
increases the level of consumers' concerns for electronic payment transactions in
general and mobile banking in particular.
Authors propose that mobile banking service providers should apply
integrated solutions using the high security technology, such as multi-door security
solutions and encoding information at a high level, to ensure that the tampering,
hacking or illegal transaction could not perform.
With the risk on operation and finance, authors suggest developers should
design the application for mobile banking service with a clear sequence on interface
and certain confirmation for each action related to the money of customer. That will
support to avoid the mistakes by operating from consumers. The information of
account and balance should be display clearly. The important information such as
value of money on transferring feature should be highlight.
To ensure that the information is completely confidential, service providers
should cooperate with banks to develop the communications solution with high
security protocol. It will help to combat the theft for customer information on
telecommunication networks could not happen.
!
22
5.3.3 Raising the awareness of consumers
Psychology of Vietnamese in general are still not exit the "cash payment
style". Many people have bank account and cards, but they use for receive monthly
salary as the main purpose. As the results of study, the majority of consumers use
mobile banking service is high education. It showed that the high awareness will be
easily accept this type of service. This proves that raising the consumers' awareness
for mobile banking services is very important.
As the findings, the perceived usefulness have a positive impact on the use of
mobile banking service. Therefore, service providers and banks should focus on the
media programs to promote the benefits and advantages that can be gained from the
use of mobile banking services. Hence, raising awareness of the vast majority of
customers, especially people have a bank account but do not use the services.
5.3.4 Enhancing the trust of consumers on the services
As the finding, the trust of consumer on the service has a greatest positive
impact to the use of the mobile banking services for customers. It is important to
create and develop the trustworthy business reputation with a long-term vision. Banks
and service providers should have an effective communication strategy for the
security and safety solutions for mobile banking services in order to create the believe
for customers when using the services.
Besides applying advanced technology solutions, service providers and banks
should have a long-term policy creating the trust of customers for mobile banking
services. The policy of fair treatment for customers, resolve complaints quickly and
reasonably, customer support is thoughtful and dedicated that are suggestions to help
service providers and banks to strengthen credibility and improve customer
confidence.
The insurance policy for social, financial, security and operations will increase
the trust of customers by removing the concerns of losing money. Authors suggest
that service providers and banks apply the suitable insurance package for mobile
banking services.
The trust of customers brings the chance to develop the service. It
recommends that banks and service providers should consider these actions as the top
priority activity.