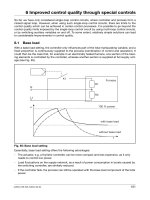
Lecture management a pacific rim focus chapter 6 establishing organisational goals and plans
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (336.38 KB, 24 trang )
CHAPTER 6
ESTABLISHING
ORGANISATIONAL GOALS &
PLANS
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
1
Lecture outline
•
•
•
•
•
The planning process
The nature of organisational goals
How goals facilitate performance
Linking goals & plans
Management by objectives
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
2
The planning process
• Mission
The organisation’s purpose or fundamental reason
for existence.
• Goal
Future target or end result an organisation wishes to
achieve.
• Plan
Means devised for attempting to reach a goal.
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
3
The planning process
mission
goals
plans
Goal attainment
(organisational
efficiency
& effectiveness)
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
4
The planning process
‘Setting goals & developing plans leads to
goal attainment and ultimately, to
organisational efficiency & effectiveness.’
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
5
Organisational mission
‘Essentially, planning builds on the
organisation’s mission, the organisation’s
purpose or fundamental reason for existence.’
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
6
Organisational mission
Mission statement may:
• Be unwritten.
• Address customers, products/services,
location, technology, concern for survival,
philosophy, self-concept, concern for public
image, concern for employees (David 1989).
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
7
Nature of organisational goals
• Benefits of goals
–
–
–
–
Increases performance
Clarifies expectations
Facilitates control
Increases motivation
• Levels of goals
– Operational goals (base)
– Tactical goals (mid)
– Strategic goals (top)
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
8
Levels of goals
• Top managers
Organisational perspective
strategic
goals
strategic
plans
• Middle managers
Departmental perspective
• 1st level managers
Unit/individual perspective
tactical
goals
operational
goals
tactical
plans
operational
plans
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
9
Goals and performance
Key aspects:
• Goal content
• Goal commitment
• Work behaviour
• Other process components
• Possible problems
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
10
Goal content
Content should be:
• Challenging
• Attainable
• Specific/measurable
• Time limited
• Relevant
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
11
Goal commitment
Influenced by:
• Supervisory authority
• Peer & group pressure
• Public display
• Expectations of success
• Incentives & rewards
• Participation
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
12
Goals & work behaviour
Goals & commitment affect work behaviour:
• Direction
• Effort
• Persistence
• Planning
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
13
Goals & other process components
Job process components affect performance:
• Job knowledge & ability
• Task complexity
• Situational constraints
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
14
Goals & possible problems
Possible problems with goals:
• Excessive risk taking
• Increased stress
• Undermined self-confidence
• Ignored non-goal areas
• Excessive short-run thinking
• Dishonesty & cheating
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
15
Linking goals & plans
•
•
•
•
Levels of plans
Extent of recurring use
Time spans of goals & plans
Plans & innovation
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
16
Linking goals & plans
Levels of plans:
• Strategic
• Operational
• Tactical
Recurring use:
• Single use
• Standing planspolicies,
procedures, rules
Time span of goals
/plans:
• Short
• Intermediate
• Long range
Innovation supported by:
• Mission statement
• Goal content & process
• Planning content & process
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
17
Possible obstacles to planning
Environmental change
Manager hostility
Pressure of day-to-day work
Low levels of manager skill & knowledge
Domination by specialists
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
18
Management by objectives
‘Process through which specific goals are set
collaboratively for the organisation as a whole
and every unit within it; the goals are then
used as a basis for planning, managing
organisational activities, and assessing and
rewarding contributions.’
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
19
Management by objectives
Steps in the MBO process:
• Develop organisational goals
• Establish specific goals for departments
• Formulate action plans
• Implement & maintain ‘self-control’
• Review progress periodically
• Appraise performance
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
20
Management by objectives
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
• Helps link goals & plans
• Clarifies priorities,
expectations
• Fosters organisational
communication
• Builds member motivation
• Needs strong, enduring
commitment
• Requires training of
managers
• May be misused
(i.e. for punishment)
• Risk of dominance of
quantitative goals
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
21
Management by objectives
MBO assessed:
• Can heighten organisational performance
• Short-term focus of US, Australian & NZ
organisations limits application
• 20–25% success rate
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
22
Lecture summary
• The planning process
–
–
Major components
Organisational mission statement
• The nature of organisational goals
–
–
–
–
–
–
Benefits of goals
Levels of goals
Goals & performance
Work behaviour
Other work processes
Possible problems with goals
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
23
Lecture summary
• How goals facilitate performance
– Direction, effort, persistence & planning
• Linking goals & plans
– Levels, recurrent use, time spans, promoting
innovation
– Possible obstacles to planning
• MBO: Management by objectives
– The key steps in MBO process
– Strengths & weaknesses
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd. PowerPoint
24