LV Thạc sỹ_Solutions for integrating the distribution systems of NKD and NTC
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (956.16 KB, 106 trang )
Subject: Solutions for integrating the distribution systems of
NKD and NTC
INTRODUCTION
1.
Rationale:
The development of domestic companies in producing and distributing thank to
the development of security market made the competition in retail industry
increasingly. Furthermore, the opening of retail market policy of the
Government on the 1st of January 2009 made the competition become fiercer.
The competition happen in many aspects such as: product quality, pricing,
marketing campaign….but the most important one in retail industry is location
– with the current situation of Vietnam now is retailer (point of sale which is
opened by the location owner). In retail industry, the definition of WAR is War
at Retailer, this definition proves that the most fierce competition happen at
retailer where all producers want to penetrate and occupy as large space as
possible. In this competition which producer has more bargain power to retailer
will has an advantage in occupy big scale in sales and large space in
displaying products. Thus, all producers now try to increase their bargaining
power to retailer by supplying wide range of products, enhancing services,
setting good policies to bring good profit to retailer.
Aware of that Kinh Do group set out the direction of enhancing the bargaining
power to retailer by integrating some distribution systems together. This is the
initial step to form Kinh Do Trading Joint stock company which is not only
distributing Kinh Do group products but trading some other product categories
also. The reasons for Kinh Do to do that is:
-
Kinh Do has some subsidiaries that produce Fast Moving Consumer
Goods (FMCG) products such as: NKD produces confectionery, Tribeco
produces beverage, Kido’s produces ice-cream.
-
Kinh Do is the strategic partner of Nutifood a milk producing company.
-
Kinh Do distribution system is considered as one of professional biggest
system in FMCG in Vietnam.
2
-
All of these products (confectionery, beverage, milk and ice-cream) are
distributed to at least 70% the same retailers; this make Kinh Do does the
integration conveniently.
-
North Kinh Do Food Processing Joint Stock Company (NKD) and North
Tribeco Joint Stock Company (NTC) located in the same place is the most
important reason why Kinh Do chose the North market as pilot market in
integrating distribution systems together because Kinh Do does not solve
the warehouse problem anymore.
All of the above reasons led me to choose topic “Solutions for
integrating the distribution systems of NKD and NTC” to
complete my MBA course and fulfill my responsibility at NKD. Choosing this
topic helped me to systematize my knowledge and practically contribute to my
company.
Because this is a strategic direction of Kinh Do group so in this thesis the
solutions were formulated in general and aim to solve almost all problems and
requirements of the integration.
2.
Research objectives:
In order to know the evaluation of retailer, distributor and find out the
challenges when the integrating happen, in this thesis the author focused on
the following objectives:
•
Theoretical summary on integrating the distribution channels and the
requirements of integration.
•
Current situation analysis of distribution system of NKD and NTC.
•
Difficulties and challenges when integrating two systems together.
•
Solutions for integrating the distribution system of NKD and distribution
system of NTC.
3.
Research questions:
To achieve the research objectives this research has to answer these
questions:
•
What requirements Kinh Do should meet when doing the integration?
3
•
What difficulties Kinh Do will face when doing the integration?
•
How to integrating the two distribution systems together to meet with
the needs of the market in a short term and long term also?
4.
Scope of research:
The integration is related to distributor, retailer and the sales forces only, so
the research just focuses on:
•
The evaluation on distribution system of NKD and NTC.
•
Retailer, distributor and managers of NKD, NTC on how to do the
integration.
•
All the data of recent three years: 2006, 2007, 2008.
•
The north market only.
5.
Research methodology:
5.1.
•
Collecting data.
Secondary data: Secondary data has been collected by qualitative
method mainly base on company’s report, news paper, internet,
magazine, from formal publication of Vietnam General Statistic Office,
information from thesis of others students.
•
Primary data:
-
Questionnaires: The author has applied questionnaire survey to
collect information from retailers, distributors who had given their
opinion about the existing distribution system advantages and
disadvantages, comparing the existing system to others, forecast the
trend of distribution system in the future, giving their ideas about the
challenging and difficulties when two distribution systems integrated
together. Because of time limitation, Author had conducted 200
questionnaires for retailers in which 100 for Hanoi and 100 for
provinces, 60 questionnaires for 90 distributors.
-
The in-depth interview: After conducting questionnaire method and
process the answer, the author has applied in-depth interview method
to collect the information that the questionnaire method did not supply
4
enough. By using this method the question designed for the in-depth
interview were base on the problem/ issues that questionnaire
method
couldn’t
solve.
In-depth
interview
applied
to
some
interviewees such as ASM of NKD, Chief of System Department of
NKD, ASM and SM of NTC.
5.2.
Data analyzing method.
The quantitative and qualitative methods were both used for analyzing data.
The Author used Excel, SPSS software to process data.
6.
Structure of thesis:
The main body of this thesis is divided into four chapters as following:
Chapter 2: Theoretical background.
Chapter 2: NKD and NTC distribution system analysis
Chapter 3: Research summary.
Chapter 4: Solutions to integrate two distribution systems.
5
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Description/ Forms...................................................................................................... 38
Selecting....................................................................................................................... 38
Sales department......................................................................................................... 38
BM.KD.01.01: Distributor set up proposal..................................................................38
Sales dept./ Sales Supervisor..................................................................................... 38
BM.KD.01.02: List of candidates................................................................................. 38
Sales department......................................................................................................... 38
BM.KD.01.03: Candidate information form.................................................................38
Sales Manager.............................................................................................................. 38
BM.KD.01.03:................................................................................................................ 38
Training......................................................................................................................... 38
ASM/ SS........................................................................................................................ 38
BM.KD.01.04:................................................................................................................ 38
Trial contract................................................................................................................ 38
Evaluating..................................................................................................................... 38
ASM/SS......................................................................................................................... 38
BM.KD.01.05:................................................................................................................ 38
Evaluation form........................................................................................................... 38
Sales Manager.............................................................................................................. 38
BM.KD.01.06: Distribution contract............................................................................38
Mar department............................................................................................................ 38
BM.MK.01.03: Customer feedback form.....................................................................38
Appendix 1................................................................................................................... 90
DISTRIBUTOR QUESTIONNAIRES.............................................................................. 90
(For Kinh Do Distributor)............................................................................................ 90
Appendix 2................................................................................................................... 96
QUESTIONNAIRES....................................................................................................... 96
(for retailer)................................................................................................................... 96
6
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
In order to finish this thesis and E-MBA course also, I have received
a lot of support from many people. I would like to take this opportunity to
thank all those who in many ways have helped me complete the Master
program.
I want to express my deeply thanks for my family, especially for my
wife who had found the course on newspaper and encouraged me to
enrolled. It is impossible for me to finish this course without her helps and
encouraging. Besides that the obedient of my lovely daughters has created
an ideal condition for me to finish the thesis.
I would like to thank to Associate Prof. Vu Thanh Hung Ph.D who
has taught strategic management subject and also supervise me to
conduct this thesis. I admire his knowledge and devotion for me.
I would like to thank all my professor of EMBA course, who have
trained and help me to improve my knowledge on business management.
And in fact is that I have applied it for my work effectively.
I also have received supporting from experts, interviewees,
coworkers, and class-mates. I would like to express my sincere thanks to
them who have worked hard with me during the thesis written time.
7
ABBREVIATION
NKD
North Kinh Do food processing joint stock company
NTC
North Tribeco Joint stock company
BM
Business Manager
SM
Sales Manager
ASM
Area Sales Manager
SD
Sales development
SA
Sales Advisor
DSA
Distributor Sales Administration
POSM
Point of Sales Material
ATL
Above the line
BTL
Below the line
GT
General Trade
MT
Modern trade
KA
Key Account
SYS
System
MAR
Marketing
Admin
Administration
PR
FMCG
Public relation
Fast Moving Consumer Goods
8
LIST OF TABLES
Figure 1.1:
Distribution channel
Figure 1.2:
Distribution channel
Table 2.1:
The development of NKD distribution system
Table 2.1:
NKD product categories
Table 2.3:
The development of NTC distribution system
Table 2.4:
Product categories of NTC
Table 2.5:
Distributor training courses of NKD
Table 2.6:
Distributor motivation factors of NKD
Table 2.7:
Distributor evaluation factors of NKD
Table 2.8:
Record of distributor violation in 2008 of NKD
Table 2.9:
Daily selling route of sales advisor of NKD
Table 2.10:
Daily selling route of NTC
Table 2.11:
NKD policies for channel members
Table 2.12:
Policies for distributor
Table 2.13:
NKD policies for sales forces
Table 2.14:
NKD policies for SD & ASM
Table 2.15:
NTC Policies for sales forces
Table 2.16:
Net sales and coverage of NKD
Table 3.1:
Research results on products
Table 3.2:
Research results on policy
Table 3.3:
Research results on sales forces
Table 4.1:
Criteria for recruiting sales forces
Table 4.2:
Policies for Sales Advisor
Table 4.3:
Policies for SD and ASM
Table 4.4:
Criteria for evaluating distributor
9
LIST OF CHARTS
Chart 2.1:
Business department organization chart of NKD
Chart 2.2:
Organization chart of Business department of NTC
Chart 2.3:
Distributor set up process of NKD
Chart 2.4:
NKD’s organization chart for big territory
Chart 2.5:
NKD’s organization chart for small territory
Chart 2.6:
Recruitment process of NKD
Chart 2.7:
Organization chart of sales department of NTC
Chart 2.8:
Distribution cost structure of NKD in 2008
Chart 2.9:
Research results
Chart 2.10:
Distribution cost structure of NTC in 2008
Chart 2.11:
Channel member satisfying research results
Chart 3.1:
Research results on integration
Chart 3.2:
Benefit of integration
Chart 4.1:
Organization chart of Sales department
10
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
To carry out the strategic direction of Kinh Do Group in establishing Kinh Do
Trading Company, North Kinh Do carried out the integration between NKD and
NTC distribution systems together as the initial step. The integration will not
only help Kinh Do enhance it bargaining power to retailer which plays an
important role in retail industry but also reduce cost of distribution, cost of
transportation and management expenses.
Kinh Do chose the North market with NKD and NTC as the pilot because it has
some advantages such as: at least 70% retailer are the same, the same
distribution system structure and the most important thing is they located in the
same location, this helps Kinh Do free from ware house problem.
Because this is the direction of Kinh Do Group so the author just concentrates
on researching whether retailer, distributor support the integration or not, what
difficulties retailer, distributor, Kinh Do will face when two distribution systems
are integrated together and what are the solutions to solve these problems.
These researches helped me to identify the desire, the buying behavior of
retailer and distributor and it also helped me to know what difficulties Kinh Do
will face and how to solve it. Most of solutions in these researches were
proposed by retailer and distributor and obviously it were modified by the
author to assure the effectiveness when applying it in real condition.
In order to find optimal solutions and modified solutions in the research of
retailer and distributor, the author had carried some in-depth interviews with
managers of NKD and NTC. In these interviews the author had raised the
problems that retailer and distributor had raised to ask the solutions from
managers. With highly educated and experienced people the solutions that
gave out by managers play an important role in my thesis.
After the in-depth interview carried the author finalized solutions and discussed
with Board of Director of NKD and NTC to take the approval. Actually, these
solutions will be applied when the integration carried out. The below are some
main solutions:
11
1. Unifying the management of the new distribution system by integrate North
Tribeco distribution system to North Kinh Do distribution system.
2. Set up three main channels to distribute deeper and widely.
3. Salesmen should be shifted to distributor to enhance their responsibilities.
4. Training, recruiting and evaluating sales forces, distributor should be
changed to enhance their capabilities and strength the relationship with
company.
5. The policy for distributor must be changed to improve their profit and
enhance the relationship with Company.
12
CHAPTER 1: THEORETICAL BACKGROUND
1.1.
Overall organization analysis.
Knowing an organization is a good or not good one, people normally not only
base on the result that company has gotten but also look at the vision statement,
mission statement and the strategies of that organization. These are the main
factors which reflect that organization will have a good perspective or not.
1.1.1. Vision statement
Vision statement of an organization is used to answer the question “what do
we want to become?” Vision statement normally is the long term objectives
and it becomes the foundation for all operations of that organization.
Developing vision statement is the first step in the strategy formulation. Vision
statement normally is a single sentence and it is the direction for the
organization to follow.
1.1.2. Mission statement
Mission statements are enduring statements of purpose that distinguish one
business from other similar firms. A mission statement identifies the scope of a
firm’s operations in product and market terms. It addresses the basic question
that faces all the strategists “what is our business?”
Mission statement includes of not only the nature and scope of present
operations but also the future attractiveness of the market. Thus mission
statement is the foundation for setting up the priorities, objectives, strategies,
plans. It is the starting point for designing the organization structure,
managerial competency….
1.1.3. Strategy
1.1.3.1.
Strategy definition
Strategy is the mean of achieving objectives. It answers the questions how
to make the mission statements or long term objectives come true. In
13
generally it is the step of achieving long term objectives. Business strategy
may include geographic expansion, diversification, acquisition, product
development, market penetration, retrenchment, divestiture, liquidation,
and joint venture.
According to Fred r. David there are three main strategies: Differentiation,
Cost leadership and Focus.
1.1.3.2.
Strategic objectives
Strategic objectives are used to concretize the mission statement. They
show that how the organization can fulfill the mission and vision.
According to Gregory G. Dess from University of Texas at Dallas, for
Objectives to be meaningful, they need to satisfy the SMART rule, they are:
•
Specific: This provides a clear massage as to what need to
be accomplished
•
Measurable: There must be at least one indicator that measure
progress against fulfilling the objective.
•
Appropriate/ Achievable: It must be consistent with the vision
and mission of organization.
•
Realistic:
It
must
be
achievable
target
given
the
organization’s capabilities and opportunities in the environment. In
essence, it must be challenging but doable.
•
Timely: There needs to be a time frame for finishing the
objectives.
1.2.
The nature of distribution system.
1.2.1. Distribution system’s concepts.
Distribution systems are behind every product and service that consumers and
business buyers purchase everywhere. Usually, it’s a combination of
organizations or people specializing in manufacturing, wholesaling, retailing
sales forces and logistic tools (transportation, ware house…). In this thesis the
author just concentrate on one main part of distribution system only that is
distribution channel because two companies are located in the same location
so the logistic issues need not to be analyzed any more.
14
Channel is a group of points of purchase that satisfy the same consumer/
shopper needs or requirement.
(1)
“Distribution channels are sets of interdependent organizations involved in the
process of making a product or service available for use or consumption”
(2)
. In
the reality interdependent organizations can be a private business, joint stock
companies especially in Vietnam is family businesses.
This concept shows that a distribution channel cannot be one unit doing its
best in the market place but it must have many entities to do the job of
distribution and each entity depends on the others to do their job. This
definition also mentions that distribution is a process and it takes time to
accomplish.
1.2.2. Number of Channel Levels.
Distribution channel can be characterized by the number of channel levels, the
length of the channel depend on the types of product or services and the
strategy of the producer.
A zero-level channel (also called a direct marketing channel) is a channel
without any intermediary in this case the producers sell their products or
services directly to the end user. The major ways of zero-level channel are
door-to-door, mail order, TV selling and producer owned stores.
A one-level channel contains one intermediary, such as retailer. A two-level
channel contains two intermediaries, typically a wholesaler and a retailer. A
three-level channel contains three intermediaries, typically a distributor, a
wholesaler and a retailer as the exhibit below.
Figure 1.1: Distribution channel
15
Source: from Marketing Management – Philip Kotler 1996
Using zero-level channel producer will face a problem in recruiting and
managing a big amount of sales people. Thus only products with complicated
technology or very high price will apply this model such as: air plane, hydro
power….
One – level model applied when products need high specialized skill of sales
people to consult the end user accuracy such as premium cosmetic, electronic
products….
Two and three level channel is normally applied for consumer products which
are easy to use and need to be distributed as broadly as possible.
1.2.3. Number of intermediaries.
After determining the level of the distribution channel the manufacturer have to
decide on the number of middlemen to use at each channel level.
Exclusive Distribution: It involves severely limiting the number of middlemen
handling the company goods or services. It applies when the producer wants
to maintain a great deal of control over the service level and services outputs
offered by the resellers.
Selective Distribution: It involves the use of more than a few but less than all
of the intermediaries who are willing to carry a particular product.
Intensive Distribution: It is characterized by placing the product in as many
outlets as possible
16
Depend on the product and company strategy the number of intermediary will
be chosen and formed the types of distribution channel.
1.2.4. The power of distribution channel
“Power is the ability of one channel member (A) to get another channel
member (B) to do something which, otherwise, would not have done”
(3)
. Once
one channel member can use it power to force another to do something but
not receive any compensation for it, by this way the relationship will be eroded
gradually. But the judicious way of using power will create the good
relationship among channel members and they will try the best to accomplish
their duties even though sometime it doesn’t make profit.
Five sources of power:
-
Reward power: benefit given to others.
-
Coercive power: punishing others for failure.
-
Expert power: based on the target perception that the influence has
special knowledge, useful expertise that the target doesn’t possess.
Legitimate power: stems from the target company’s sense that it is in
-
some way obligated to comply with the request of the influence.
Referent power exist when B view A as a standard of reference and
-
therefore wishes to identify publicly with A.
It takes time to create power naturally and the smart way of using power is not
forcing but influencing others to do thing that we want.
1.2.5. Distribution channel flows.
Figure 1.2: Distribution channel
•
Forward flow (promotion, delivery, and physical possession).
Producer
•
Wholesaler
Retailer
Backward flow (payment, order)
End User
17
Producer
•
Wholesaler
Retailer
End User
Two-way flow (information, negotiation, finance, risk taking)
Producer
Wholesaler
Retailer
End User
Source: from Marketing Management – Philip Kotler 1996
1.3.
Integrating and managing distribution system.
Integration is a kind of strategies to gain control over another resources such as
distributor, retailer, supplier or competitor. There are 3 types of strategies.
Forward Integration involves gaining ownership or increased control over
the distributors or retailers. This strategy is now used commonly under the
form of franchise or some producers open their own shop to sell their own
products instead of through distributors. Using this strategy the producer wants
to increase their competitive advantages or wants to contact their customer
directly to understand them more.
Backward Integration involves gaining ownership or increased control of a
firm’s suppliers. This strategy is used when the sources of supply do not meet
with the producer’s needs, unreliable or too costly. Using this strategy,
normally the producer buys a certain shares of supplier or signs a strategic
partner contract.
Horizontal Integration refers to a strategy of seeking ownership of or
increased control over a firm’s competitors. This is widely used today as a
growth strategy and one typical model of this strategy is merger and
acquisition.
The integration strategies are used widely today because the competition is more
and more fierce, the shortage of material is increasingly and the cost of
distribution is higher. But, how to use this kind of strategy effectively is depend on
not only the industry but also the way to do it. In FMCG the sources of suppliers
are abundant and it less important than the output (distributor/ distribution system)
so many producer in FMCG tend to use forward integration to reduce the cost of
distribution, increase competitive advantages, contact customers directly so that
18
they can know exactly what consumers want and fulfill it faster than their
competitors.
Forward integration itself has some kind of integration such as integration to
distributor, integration among product categories of a corporation or integration
among channel of distributions of a corporation.
When integrate two distribution systems together the integrator must pay attention
on the current objectives of each system. If two systems have the same objectives
it is very convenience to integrate together because all the intermediary and sales
forces have the same direction.
The second one is the design of each system; this issue will make the work load
of integration become easy or complicated. If two systems have the same design
the integration will be carried out easily and vice versa.
The policy for distribution system operate effectively is also the important part, if
the policy quite different between two systems the integration will face many
problems when choosing one policy to apply for the new system.
Last but not least is the distribution system management, this issues related to
evaluating and rewarding which play an important role in system development.
To do the integration effectively we must go through all of the above mentioned
issues.
1.3.1. Establishing distribution system objectives.
Distribution system is consisted of many distribution channels which serve
many different needs and requirements of the different consumers, so the
distribution system objectives vary with product characteristics. Perishable
products require more direct channel, bulky products (building material, soft
drinks) require channels that minimize the shipping distance…and high-unitvalue products are often sold through a company sales force rather than
through middlemen.
In a FMCG company the primary objective is to serve the consumer
everywhere. That why some company has a “moving channel” - it means that
company will set up channel to meet with the changing of point of purchase.
The ideal example of this kind of channel is the ice-cream on the summer
19
season. This kind of product moved very slowly on winter especially on the
beach. But in the summer consumer will gather more and more on the beach,
thus this time is the prime time for selling ice-cream and the “moving channel”
will be set up. This kind of channel used one time for a year only, after the
summer it will be disappeared and will appeared one year later.
Once distribution system has been established the objectives must be set up
first and it is the direction for system design. The general objectives of a
distribution system are coverage (include of numeric coverage and weighted
coverage), Sales, competitive advantages and company images. Based on
these objectives the design, the structure of the system and the policy will be
formed up. The Board of Directors of company is the place to set out the
objectives, through objectives people will know the strategy of the company
and the direction to go not only short term but long term also.
1.3.2. Distribution system design decision.
In designing distribution channel the manufacturers have to struggle between
what is ideal, what is feasible, and what is available. A new firm with limited
resources might choose the wholesalers who have been being existed in the
market and doing some related or similarity products to handle their products.
A big famous company when entering to a new market might choose the sole
agent with an allocated area to handle their products. On the other hand, the
distribution channel model is also being affected by the geographical
especially the on the Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG). In the big
condense market the manufacturer might sell their products directly, in the
small market they might sell their product through distributors or wholesalers to
reduce the expenses. They also grant their exclusive franchise in an area and
sell through all outlets willing to handle the merchandise in another area. Thus
the manufacturers’ distribution system evolves in response to local
opportunities and conditions.
Designing a distribution system especially in FMCG Company must be based
on number of retailers, the density of the retailers, geographical, trading
behavior…and the most important thing is the objectives of distribution system
and how to evaluate channel alternatives.
1.3.2.1
Analyzing the number of retailers, geographical, trading behavior…
20
In FMCG, the transportation plays an important role cause it cost from 3% to
15% of sales depend on kind of product. So how to set up a distributor or
wholesaler with an optimal transportation cost is very important because it not
only help the distributor or wholesaler to maximize their profit but company
also. In this case the number of retailer or the density of the retailer in the area
plays an important role. Normally if there are many retailers and the density is
high the company will set up distributor without any wholesaler to increase the
service to the last retailers and vice versa.
Geographical is another factor that company has to pay attention to. In a
mountain or river area company tend to set up a direct sale model for all kind
of product and they have to set up many sub-distributor or wholesaler to
reduce the transportation cost.
Buying behavior is also affects to, because the primary objective of the
distribution system is to meet the need/ desired of the consumer. If they buy
one time for a week using and buying for everyday use are quite different so
company must know it before setting up a distribution channel is that area.
1.3.2.2
Evaluating the Major channel alternatives.
Setting up a distribution system producer has identified several channel
alternatives and choose the optimal/ best one, normally there are three criteria:
Economic criteria: Each channel member will produce different level of
sales and cost. The distributor, wholesaler and the company direct sales force
will be chosen mostly depend on the return on the investment (cost for
distributor, wholesaler or company directly sales force).
Control criteria: The producer may prioritize the control criteria because the
product need well trained sale representative or facing fierce competition.
Adaptive criteria: In a certain period of time, the channel members must
make some degree of commitment to each other to assure that they have their
own interests and responsibilities. These commitments to assure the
development of the distribution system thus every producer tends to choose
the channel that they can maximize their control to swiftly change their
distribution strategy when the environment change.
21
1.3.3. Setting distribution system policy.
When setting up policies for distribution system we must pay attention on
function of the system and function of each intermediary. Because the policies
will help intermediaries get an equitable return when they accomplish their
functions.
The main function of a distribution channel is to move the product from the
producer to the end user. To do this it has to overcome the time, place and
possession gap between the producer and the end user. Members in
distribution channel play a certain roles and doing some key functions to
accomplish the whole functions of a distribution channel:
-
Physical possession: delivering the goods to the next customers.
-
Information: The collection and dissemination of market research
information about potential and current customers, competitors, market
trend…in the market place.
-
Promotion: The dissemination of promotion campaigns to attract more
customers.
-
Ordering: the communication of channel members to the manufacturer to
buy the products.
-
Financing: the acquisition and allocation of funds required to finance
inventories at different levels of the distribution channel.
-
Solving the complaints: the definition of channel member roles in solving
the complaints of the next customers and the end user.
-
Risk taking: The assumption of risks taken by carry out the channel work
and the responsibilities of each channel members when the lost/damage
happen.
-
Payment: terms and means of payment for possessing the products.
The allocation of functions for channel members depend on the channel
organization, when one member is eliminated its function will be moved to
forward or backward member to assure that the whole functions of distribution
will be maintain the same in any cases and the policy should be changed
accordingly.
22
1.3.4. Distribution system management.
For having a good distribution system the producer must not only careful in
selecting the channel alternatives but also in managing the conflict between
intermediary, training, motivating and evaluating them. All of these actions
must be carried out over time.
1.3.4.1.
Types of conflict and competition.
No matter how well channels are designed and managed, there will be
some conflicts because the interests/ benefits of members in the channel
do not always coincide. The responsibilities of the sales manager are to
classify the types of conflict, determining the cause of conflict and find out
solutions to solve it.
There are many types of conflict happen in the distribution system but we
can classify in three main types: vertical conflict, horizontal conflict and
multi-channel conflict.
Vertical channel conflict happens between different levels within the
same channel. This type of conflict happens when the previous channel
member issue new regulations or having some action which lead to reduce
the profits of the next channel members. For example, the producer may
enforce the distributors to pay more for promotion or increase service to the
retailers; or the distributors cut off the promotion fee as regulated/informed
by the producer.
Horizontal channel conflict exists when there is conflict between
members at the same channel level within the channel. This type of conflict
normally is the territory violation – the distributor sells products to other
distributor territory by lower price.
Multi-channel conflict happens when members of one channel try to sell
products to another channel member territory. It’s only exist when the
producer establish two or more channel.
1.3.4.2.
Causes of channel conflict.
Determining the causes of conflict is very important because only to
determine and distinguish the causes the channel manager find out the
suitable solutions to solves the conflicts.
23
A major cause of conflict is goal incompatibility. Normally the producer set
target that the distributor have to try their best to reach the target, some
time they face some problems that they cannot reach the target. In this
case the distributor will find some solutions to reach the target to take the
reward. There are many ways for the distributor to reach the target in this
case such as: increase stock level, do promotion themselves, sell to other
distributors territory….unfortunately, all distributor usually choose the third
solution – sell to other distributors’ territory.
The conflict can also stem from differences in perception. The producer
may be optimistic about the short-term business and ask the distributor to
increase stock level to prepare for capturing the market opportunities. But
the distributor may be pessimistic and they don’t want to increase the stock
level
1.3.4.3.
Managing channel conflict.
Certain channel conflict can be solved and on the other hand it help
producer to find the market gap, to increase sales….To manage the conflict
doesn’t mean that to solve the conflict when it happen but to prevent it
happen. Many producer issue the regulations, policies and a strictly
punishment for all the channel members to prevent the conflict. But the
smart way of managing the conflict is to let the conflict happen at a certain
level because conflict has its own advantages. Through conflict producer
know the market gap, determine the strong point and the weak point of
every distributor…so the producer can has solution to improve it
distribution system.
1.3.4.4.
Selecting and training channel members.
The ability of attracting middlemen of producer varies from producer to
producer. This is true not only in different industry but also in the same
industry. This is resulted from the brand name of the producer, the ability of
profit creation of producer products.
Whether it is easy or difficult to recruit middlemen the producer should
point out the characteristic and criteria for each level of middlemen and
base on that to recruit the most suitable middlemen for each level. The
24
characteristic and criteria also vary from company to company because of
the situation and the strategy, some company want to recruit big and
famous distributor but some just want to recruit the distributor who has
enough financial ability but has a strong will.
The cooperation between intermediaries and the producer plays an
important role in business development. To have this there must be a
mutual understanding between them so every company organize training
course for their intermediaries especially distributor every year or on the
time that company change their strategy or before an important season.
1.3.4.5.
Motivating channel members.
The middlemen must be motivated continuously to do their best job and
increase the cooperation. Depend on the size, the growth rate and the
ability to expand the business, the producer may use different motivated
tools. If it is a small producer the best way of motivating middlemen is to
increase their profit by adding some KPI such as: sales target reach,
coverage, inventory, paying on time…If it is a big, famous and has ability to
expand the business producer except the KPI like small producer the big
one can use some tools such as: partnership the distributor (by selling
share to distributor), install management software for distributor…..all of
these have only one purpose is to increase the cooperation and make it
last as long as possible to prevent the competitor to buy the distributor.
1.3.4.6.
Evaluating channel members.
To assure the channel operate smoothly, the producer must evaluate the
channel members periodically. Based on the criteria and the regulations
has been committed the producer carry out the evaluation, the most
common criteria are target sales reach, average inventory level, customer
delivery time, treatment of damaged goods, paying time, promotion
cooperation….By only do this the producer will know how well the channel
is and has an action plan to rearrange it.
25
Evaluating the channel also help the producer to determine the ability of
carrying new products category of the channel, the ability of the channel to
adapt with the changing strategy of the producer….
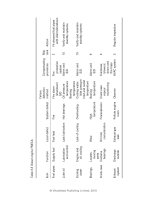
Some main KPI to evaluate the performance of the distribution system as
below:
Table 1.1: Criteria for evaluating channel results
Author’s analysis
1.3.4.7.
Modifying channel arrangements.
Market changes every day, the buying pattern change also and the new
competitor arises, product matures, new-innovative distribution channel
emerge and strategy change…make the producer to change their
distribution channel. Modifying channel arrangement related to change
distribution channel, adding, dropping or increasing the intermediaries.
When setting up the distribution channel the buying power at that territory
was low and the producer just set up a wholesaler there, but after one or
two years later it is a new town and buying power increasingly. In this case
the producer must change it channel from wholesaler to distributor and