Day 2 3 parts of speech
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (609.29 KB, 18 trang )
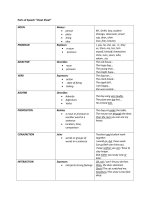
CHAPTER 2: PARTS OF SPEECH TABLE
Part of speech
Function
Example words
Example sentences
Verb
action or state
(to) be, have, do, like,
work, sing, can, must
I’m a student.
I like music.
She works at an office.
Noun
thing or person
pen, dog, work, music,
town, London, teacher,
John
This is my dog. He lives in myhouse. We
live in London.
Adjective
describes a noun
a/an, the, 2, some,
good, big, red, well,
interesting
I have two dogs. My dogs are big. I
like big dogs.
Adverb
describes a verb,
adjective or adverb
quickly, silently, well,
badly, very, really
My dog eats quickly. When he
isvery hungry, he eats reallyquickly.
Pronoun
replaces a noun
I, you, he, she, some
Tara is Indian. She is beautiful.
Article
identifies a noun
a, an, the
Tara is a beautiful girl.
Preposition
links a noun to
another word
to, at, after, on, but
We went to school on Monday.
Conjunction
joins clauses or
sentences or words
and, but, when
I like dogs and I like cats. I like
cats and dogs. I like dogs but I don't like
cats.
Interjection
short exclamation,
sometimes inserted
into a sentence
oh!, ouch!, hi!, well
Ouch! That hurts! Hi! How are you? Well,
I don't know.
Determiners may be treated as a separate part of speech, instead of being categorized under Adjectives.
PARTS OF SPEECH
NOUNS
What is a noun? A noun is a word that names a person, an animal, a place, or a thing. There are more nouns in the
English language than any other word.
VERBS
What is a verb? A verb is a word that shows action or being. Whatever you’re doing can be expressed by a verb.
Without a verb, a group of words cannot be a sentence. A sentence can be as short as one word, as long as that one
word is a verb.
ADJECTIVES
Edited and Complied by EQuest Academy
21
What is an adjective? An adjective is a word that tells us more about a noun or a pronoun. An adjective describes
or limits the use of a noun.
An adjective answers three questions.
1) What kind of?
I saw a big dog.
2) How many?
I’d like six ice cream cones, please.
3) Which one?
I’ll take that pair of jeans.
ADVERBS
What is an adverb? An adverb is a word that tells us more about a verb. An adverb tells us:
1) How
The pig danced terribly.
2) Where The pig danced here.
3) When
The pig danced yesterday.
PRONOUNS
What is a pronoun? A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun. Almost anything a noun can do, a pronoun
can do, too. Pronouns are handy little words because when you use them, you don’t have to keep repeating nouns
all the time.
PREPOSITIONS
What is a preposition? A preposition is a word that shows the relationship of one word in a sentence to another
word. A preposition tells four things:
1) LocationThe pig is outside its cage.
2) DirectionThe pig ran to its cage.
3) TimeI’ll wait until noon, and then I’ll leave.
4) Relationship- I went to the party with my friend.
ARTICLES (a, an, the)
These are special words called articles. They are noun signals. They can often tip you off that there’s a noun is
coming up in a sentence.
CONUNCTIONS
What is a conjunction? A conjunction is a word that joins other words or parts of sentences together. It is a
“bridge” word.
David and Jennifer are brother and sister.
It will rain or snow today.
I ran as fast as I could. However I still missed the train.
I’ll call the Health Department if you don’t clean up your yard.
INTERJECTIONS
What is an interjection? Interjections are special words that show strong feelings or emotions like excitement,
happiness, horror, sadness, disgust, pain, anger. Interjections usually come at the beginning of a sentence. You use
them to add energy to your sentence. Don’t use them too much, or they’ll loose their power. Sometimes
interjections are just shouts or sounds.
Exercise 1: Parts of Speech- Decide which parts of speech are the underlined words
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
You have to believe in yourself if you ever expect to be successful at something.
We left for the mountain just before six in the morning.
We first went to the store to buy a few things.
We had a breakfast at a café near the rail station.
My friend wasn't strong enough to lift his heavy rucksack.
Edited and Complied by EQuest Academy
22
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
I helped him carry it.
The weather was very cold.
My friend said, "Oh! What a cold weather!"
We didn't spend the night there.
We got back home late at night but we didn't go to sleep immediately. We were very hungry.
1. NOUNS
A noun is a word used to name something: a person, an animal, a place, a thing, or an idea.
For example, all of the following are nouns.
Leah, Ignacio, Lan, Marek
Japan, Venezuela, Atlanta, Kroger, the Gap
pencil, store, music, air
biology, theory of Relativity, Pythagorean theory
Nouns are classified in several ways…
1. Nouns can be singular or plural.
Singular nouns name only one person, place, thing or idea.
One apple, a pencil, the book
Plural nouns name two or more persons, places, things or ideas. Most singular nouns (Not ALL) are made plural
by adding –s. For example, (pencil is a singular noun. The word pencils is a plural noun.)
Exception #1: If a noun ends with the –s, sh, ch, or x like the words, kiss, church, ash or box, then they are made
plural by adding –es (kisses, churches, ashes, and boxes).
Exception #2:There are also irregular nouns that do not follow any rules. For example, the plural form of the word
child is children.
Exercise 2: Complete the sentences with the plural forms of the verbs in brackets:
1. __________________ (baby) are cute, aren´t they?
2. In Autumn __________________(leaf) fall from __________________(tree)
3. She loves __________________(puppy)
4. I have got a pair of __________________(jeans)
5. Superman and Spiderman are my __________________(hero)
6. Let´s put these toys inside these __________________(box)
Exercise 3: Read the sentences. Rewrite them from singular to plural.
1. That watch is in his pocket.____________________________________________________________________
2. This radio is on the desk._____________________________________________________________________
3. You are my sister. _________________________________________________________________________
4. That isn´t a table, it is a chair. _________________________________________________________________
5. The child is five . _________________________________________________________________________
6. The bus isn´t late. _________________________________________________________________________
7. That peach is delicious. ______________________________________________________________________
2. Nouns can be Proper Nouns or Common Nouns
a) Proper nouns refer to specific people, places, things and ideas. A person's name (Leah Graham) is a proper
noun, for example. Other examples are names of places (Atlanta, Georgia) and names of things (the Navy).
They are always capitalized!
Edited and Complied by EQuest Academy
23
People’s names and titles- King Henry, Mrs. Smith
Names for deity, religions, religious followers, and sacred books- God, Allah, Buddha, Islam,
Catholicism, Christians
Races, nationalities, tribes, and languages- African American, Polish-American, Black,
Chinese, Russian
Specific Places like countries, cities, bodies of water, streets, buildings, and parks
Specific organizations- Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), ….
Days of the week, months, and holidays,
Brand names of products
Historical periods, well-known events, and documents- Middle ages, Boston Tea Party,
Magna Carta
Titles of publications and written documents
b) Common nouns are all other nouns. For example: cat, pencil, paper, etc. They are not capitalized unless they
are the first word in the sentence.
3. Nouns can also be collective.
Collective nouns are nouns that are grammatically considered singular, but include more than one person, place,
thing, or idea in its meaning. Words like team, group, jury, committee, audience, crowd, class, troop, family, team,
couple, band, herd, quartet, and society.
Generally, collective nouns are treated as singular because they emphasize the group as one unit. The committee is
going to make a decision.
4. Nouns can also be either count or non-count.
Countable and uncountable nouns
You use nouns to name things.
We need potatoes, oil, apples, tea and
sugar.
Countable nouns
You can count these.
There are singular and plural forms
one cat , two cats
one student, ten students
There is too much furniture in here.
Let’s move the table into the next
room.
Uncountable nouns
You can’t count these.
There is only one form.
rice, milk, water, sugar, furniture, weather,
information
You use single and plural verbs.
You always use a singular verb.
The lesson starts at 9.30.
The lessons start at 9.30.
There is no furniture in there.
You can use a or an in front of them.
an envelope, a letter
You cannot use a or an in front of them.
Edited and Complied by EQuest Academy
24
You can use not many and a few in front of them.
You can use not much and a little in front of them.
There are a few people waiting for the bus.
There aren’t many people here today.
There is a little sugar left.
There is not much flour left.
Exercise 4:
A) Say whether the following are countable (C) or uncountable (U) or both (B).
1.
Euros ____________
2.
water ____________
3.
bottle of water _____
4.
pollution __________
5.
food ______________
6.
tea _______________
7.
coffee _____________
8.
ice-cream __________
9.
time_______________
10.
box________________
B) Fill in the gaps with “some” or “any”.
1.
Have you got ______________ brothers or sisters?
2.
We don’t need ______________ milk.
3.
There are ______________ pens on the table.
4.
I want ______________ eggs .
5.
Is there ______________ water in the fridge?
6.
Are there ______________ problems.
C) Fill in the gaps with “some” or “many”.
1.
How ______________ money do you have?
2.
I don’t have ______________ close friends.
3.
There isn’t ______________ petrol left in the car.
4.
How ______________ information have you got?
5.
There are ______________ glasses of water on the table.
6.
Don’t give him ______________ money - just a few euros.
D) Fill in the gaps with “a lot of / a few / a little / much”.
1.
I don’t have ______________ experience.
2.
There are ______________ people waiting to buy tickets. About three or four.
3.
Hurry up! I don´t have ______________ time.
4.
There is ______________ money left over, but not much.
5.
I need ______________ students to help me. Two or three will be enough.
6.
We should go now because there is only ______________ traffic at this time of the morning.
7.
I only need ______________ time to finish this. Wait a second.
8.
I invited ______________ friends for dinner but we can still all fit at the table.
Exercise 5: Say if the nouns are countable (C), uncountable (U) o both (B).
a.
b.
c.
d.
beef
coffee
peach
onion
e.
f.
g.
h.
sugar
strawberry
tea
pork
Edited and Complied by EQuest Academy
i.
j.
k.
l.
pear
jam
a cup of tea
a glass of milk
m.
n.
o.
p.
melon
bread
milk
butter
25
5. Nouns can be abstract or concrete
A noun can be abstract or concrete.
Concrete nouns are nouns that you can touch. They are people, places, and some things. Words like person,
court, Georgia, pencil, hand, paper, car, and door are all examples of concrete nouns.
Abstract nouns are nouns that cannot be physically held. For example, things like air, justice, safety,
Democracy, faith, religion, etc.
6. Nouns can be Gerunds
A gerund is the –ing form of the verb and is used as a noun (functioning as a subject, complement of verb be, and
an object of a preposition)
For example:
Running is good for you.
Her favorite sport is swimming.
Thank you for helping me with my homework.
Exercise 6: Rewrite the following sentences using GERUNDS
Ex. It is easy to learn English. Learning English is easy
1. It was great to see my uncle again. _______________________________________________
2. It will be fun to go to the picnic next week. _______________________________________________
3. It takes me 45 min to get to work every day. ______________________________________________
4. It is difficult for me to understand her. ______________________________________________
5. It was horrible to see that happened to him. ______________________________________________
6. It has been great to learn English. ____________________________________________
PARTS OF SPEECH- NOUNS- HOMEWORK:
Exercise 7. Write the words in the correct form:
1. There are three _____ (apple) on the plate.
2. I’d like to taste these _____ (cookie).
3. Would you like these _____ (orange)?
4. This ____ (cheese) is too salty.
5. How much _____ (water) is theHe fougMy father
DoHe’s sitting coI’d like to knowIt rained heavy / heavily
and there were some accidents because of the heavy/
heavily rain.
This ____ (meat) isn’t fresh.
10. There are many _____ (tomato) in this salad.
11. I don’t eat _____ (butter) at all.
12. This _____ (coffee) is awful.
13. How many _____ (banana) would you like?
14. All her _____ (dress) are beautiful.
15. Put some _____ (salt) into your soup.
16. This _____ (sugar) isn’t sweet.
17. There is some _____ (bread) on the table.
Edited and Complied by EQuest Academy
Exercise 8. Correct the mistakes:
1. These carrot are sweet.
2. I don’t like teas at all.
3. I’d like to cut some pear for this salad.
4. There is much waters in this jar.
5. How many sandwich have you bought?
6. You can take four potato from the basket.
7. Do you eat meats?
8. There is much rices in this dish.
9. Where is breads?
10. These berry are very sweet.
11. There are four chair round the table.
12. These vegetable are green.
13. Where are the onion?
14. I bought some cherry in the afternoon.
15. I adore pear.
16. Don’t put more salts in this dish.
17. Cut these cucumber, please.
26
2. VERBS
Verbs generally express action or a state of being. There are several classifications for verbs- action verbs,/linking
verbs, main verbs/auxiliary verbs, transitive/intransitive and phrasal verbs.
A. Action verbs and Linking verbs
1. Action verbs show action.
He runs. He plays. They study.
2. Linking Verbs link the subject to an adjective.
Ricky Martin is beautiful.
The linking verb is links the adjective beautiful with the subject Ricky Martin.
Exercise 9: Circle the verb in each sentence. Write A if it is an action verb. Write L if it is a linking verb.
1.
The girl feels nervous.
_____
2.
Today is her wedding day.
_____
3.
She sits in a fancy chair.
_____
4.
Footmen carry the chair on their shoulders. ______
5.
Her parents arranged the marriage.
______
6.
She is only sixteen years old.
______
7.
She sees her husband for the first time. ______
8.
He looks handsome and kind.
______
9.
She appears happy and content.
_______
10.
The family hopes for a happy marriage.
_______
B. Main verbs and Auxiliary verbs
1. Main verbs can stand alone.
For example: I go to school every day.
2. Auxiliary verbs, also called helping verbs, serve as support to the main verb.
The most common auxiliary verbs are:
Have, has, had
Do, does, did
Be, am, is, are, was, were, being, been
For example: I have been to Paris once.
3. Modal verbs: are considered auxiliary verbs
should, could, will, would, might, can, may, must, shall, ought (to)
For example: She can swim fast.
Edited and Complied by EQuest Academy
27
MODAL
VERBS
USE
CAN
possibility, ability and permission in
the present or future.
neg. - logical impossibility
FORMATION ( AFFIRMATIVE,
INTERROGATIVE, NEGATIVE)
I can speak many languages.
Can I go to the party?
She can’t be at home, I saw her 10 minutes
ago.
COULD
ability, possibility and permission in
the past or in polite requests
He could swim when he was only four.
Could you help me, please?
I couldn’t understand him.
BE ABLE TO
ability and opportunity in the past,
present or future (specific occasion)
I am able to get all the work done.
Were you able to stop the car in time?
They won’t be able to stop it.
possible and probable actions in the
future; permissions and possible
conditions
You may telephone from here.
May I take a photo?
He may not go to the party. He’s sick.
possible actions in the future or
improbable events or situations.
I might be working late tomorrow.
He might not be at home.
What might happen?
obligation, necessity, deduction; in
the negative form - prohibition
You must take your medication regularly.
My glasses must be here somewhere.
He mustn’t tell anyone what I said.
obligation
I have to work on Sundays.
Do you have to get your passport?
She doesn’t have to go to the dentist.
facts in the future, predictions,
invitations, characteristic behaviour
I’ll wait for you if you like.
Will you have a cup of tea?
She’s on diet. She won’t eat at all.
past prediction, prediction about a
possible situation; politeness; past of
“will”
How about a cup of tea? That would be nice.
Would you go without me?
I wouldn’t go without you.
offers, suggestions
Shall I close the window?
Shall we dance?
advice; past form of “shall”; logical
consequence
You should accept the job.
Should we tell him the news?
She shouldn’t be so shy.
saying what is the right thing to do
She ought to be working.
You oughtn’t to forget your obligations.
MAY
MIGHT
MUST
HAVE TO
WILL
WOULD
SHALL
SHOULD
OUGHT TO
Edited and Complied by EQuest Academy
28
Exercise 10: Complete the sentences with appropriate modal verbs.
1.
____________ you ____________ to get up early?
2.
They’re having a baby. They ____________ have to buy a bigger house.
3.
I’m sorry I ____________ help you with your homework.
4.
____________ we go out tonight?
5.
Why don’t you apply for that job? You ____________ get it.
6.
I think we ____________ do something to stop pollution.
7.
____________ I borrow this book?
8.
My wife is waiting for me. I ____________ not be late.
Exercise 11: Write a second sentence so that it has a similar meaning to the first. Use the words in brackets.
1.
Perhaps Mary is doing overtime. (may)
________________________________________________________________________
2.
I managed to go to university. (able)
________________________________________________________________________
3.
They should think very well before acting. (ought)
________________________________________________________________________
4.
It’s forbidden to smoke here. (mustn’t)
________________________________________________________________________
5.
It’s impossible for you to see it at this distance. (can’t)
________________________________________________________________________
6.
It is possible that Anne did not see the message. (might)
________________________________________________________________________
7.
I advise you to study more in order to pass the exam. ( should)
________________________________________________________________________
8.
She was able to play the piano when she was only four. (could)
________________________________________________________________________
C. Transitive or Intransitive verbs
1. Transitive Verbs require a direct object in order to make sense.
For Example: Yolanda takes aspirin for her headaches.
Here, takes is a transitive verb since the sentence Yolanda takes has no meaning without its direct object aspirin.
2. Intransitive Verbs do not need direct objects to make them meaningful.
For Example: Julio swims.
The verb swim has meaning for the reader without an object.
Caution: A verb can be either transitive or intransitive depending on its context.
For Example: The cars race.
Here, race is intransitive. It does not need an object.
My father races horses.
Here, races is transitive. It requires the object horses in order to make sense.
Exercise 12:
ENCIRCLE THE VERB USED IN EACH OF THESE SENTENCES AND THEN WRITE ‘transitive’ or
‘intransitive’ IN THE SPACE PROVIDED FOR. MATCH THE SENTENCES TO THE PICTURES.
1.
The magician performed new magic tricks. [ ______________________ ]
2.
The farmer works happily in his farm.
[ ______________________ ]
3.
Chona is carrying a lot of books.
[ ______________________ ]
4.
Henry waited patiently in the park.
[ ______________________ ]
Edited and Complied by EQuest Academy
29
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
The fireman observes proper discipline.
[ ______________________ ]
Isabel missed her flight to California.
[ _____________________ ]
The radio announcer talks clearly.
[ _____________________ ]
The pianist played romantic songs last night. [ _____________________ ]
Lily decorated her scrapbook last Friday. [ _____________________ ]
Chona saw the result of the test in the bulletin board.[ _____________]
Vernie plays happily near the beach.
[ ____________________ ]
Her mom likes black forest cake.
[ ____________________ ]
D. Phrasal verbs
1. Phrasal verbs are made up of a verb and a preposition. The preposition gives the verb a different meaning than
it would have by itself. For example, the verb look has a different meaning from the phrasal verb look up (in
the dictionary).
Some more examples:
call up, find out, hand in, make up, put off, turn on, write up
Exercise 13: Rewrite each sentence replacing the underlined words by a Phrasal Verb:
get on get over head for join in live up to
run out of put forward put up
put up with stand for
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
There isn´t any juice left.___________________________________________________
What´s the meaning of UE? ________________________________________________
The window in my bedroom needs to be fixed._________________________________
My brother was seriously ill, but he has recovered now.__________________________
The show wasn´t as good as we expected._________________________________ ____
What exactly are they suggesting?_____________________________ ______________
When the party began everyone took part. ____________________________________
The plane is going in the direction of Lisbon. ___________________________________
We can´t tolerate such heat.___________________________________ _____________
Exercise 14: Complete each sentence with a suitable form of the Phrasal Verbs in the box..
check out go on call back have on look for
settle down slow down look forward to
write down check in
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
The sun isn´t always shinning, but life must ________________.
I ________________ a blue skirt and a green shirt yesterday.
Guests must ________________ by 6.00 p.m.
I´m ________________ seeing Mary and John again, aren´t you?
All passengers tried to ________________ at the same time.
My mother isn´t here. Can you ______________ later?
I´m going to travel before ________________ and starting a new job.
The plant growth ________________ by the lack of rain.
Before I began writing my book, I ____________ my ideas.
Where have you been? I`ve been_____________ you everywhere.
Edited and Complied by EQuest Academy
30
Exercise 15- Complete each sentences with a suitable form of the
Phrasal verbs in the box.
check out
settle down
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
go on
look for
call back
slow down
have on
look forward to
I know things seem bad, but life must _____________.
I _____________ a pair of jeans and a green t-shirt yesterday.
Guests must _____________ by 12:00 p.m.
I’m _____________ seeing John and Janet again, aren’t you?
All passengers tried to _____________ at the same time.
I’m afraid Mr Thompson isn’t here. Can you _____________ later?
I’m going to travel to America before _____________ and starting a family.
The tree growth _____________ by the lack of rain.
Before I began writing, I _____________ my ideas.
Where have you been? We’ve been _____________ for you everywhere.
Edited and Complied by EQuest Academy
31
3. ADJECTIVES
Adjectives are of different kinds. They
can be:
Numbers / Quantities or Ages
There are twenty students in the class.
Colors
Tim is wearing a blue shirt.
Sizes
There are many huge temples in China.
Shapes
Use a square cake tin for the recipe.
Opinions
Sally is a cute girl.
Origins
I like to eat Italian food.
An adjective is a word that describes
or modifies a noun.
It’s a small house.
An adjective comes before the noun it
describes.
This is a yellow ball.
We can put an adjective after any
tense of verb be.
This dress is pretty.
Adjectives can be used alone after
verbs such as look, sound, smell, feel,
taste etc.
This food smells horrible.
I feel tired.
1. Comparison of Adjectives: Adjectives can be used to make comparisons.
There are three degrees of adjectives: positive, comparative and superlative.
Comparative adjectives are used to compare two things together. They are followed by “than”.
Superlative adjectives are used to compare three or more nouns. We often add “the” before them.
Rule
Add –er or –est to the end
of short adjectives.
Add only –r or –st to the
short adjectives that end
with –e.
Double the last letter if the
short adjective ends with a
vowel and a consonant.
Change the –y to –i if the
short adjective ends with a
–y
preceded
by
a
consonant.
Positive
smart
wise
big
busy
Use more or most before
beautiful
long adjectives.
good
Some
adjectives
have
bad
irregular form in the
little
comparative and in the
much/many
superlative forms.
far
Edited and Complied by EQuest Academy
Comparative
smarter
Tim is smarter than Bob.
wiser
Dan is wiser than his brother.
Superlative
smartest
Jim is the smartest in class.
wisest
Dan is the wisest of all his
brothers.
bigger
biggest
My piece of cake is bigger than I took the biggest piece of cake.
yours.
busier
busiest
It is known that women are Tim is the busiest man I have ever
busier than men.
known.
more beautiful
most beautiful
Roses are more beautiful than Roses are the most beautiful
daisies.
flowers.
better
best
worse
worst
less
least
more
most
farther / further
farthest / furthest
32
Exercise 16: Write the correct form of the adjective.
1. Although the Sheraton is ______________ (cheap), it is ______________ (far) from the beach, so it’s
______________(convenient) to stay in Plaza Hotel.
2. My present boss is ______________(easy) to work with than my previous one.
3. Our new house is ______________(expensive), but it is ______________ (comfortable) and ______________
(modern).
4. It’s ______________(fast) to go by train than by car.
5. This year it has been ______________(cold) and ______________(wet) than last year.
6. The beaches in Algarve are ______________(crowded) than the ones in the Alentejo.
7. This hotel is ______________(old) that that one, but it is ______________(charming).
8. Marriage vows state that you should stay with your spouse for ______________ (good) or for
______________.
9. It is obviously ______________(dangerous) to walk around in Central Park during the day than it is at night.
10. Your little brother may be ______________(young) than you, but he is much ______________clever)!
11. Egypt is ______________(hot) and ______________(dry) than Switzerland.
12. Switzerland is ______________(small) but it is ______________(rich) and ______________(develop).
13. Egypt has a ______________ (interesting) culture even though it is a ______________(poor) country.
14. Egypt is ______________(fertile) than Switzerland because of the Sahara Desert.
2. Adjectives ending with “ing” vs “ed”
Look at this example:
Martin is very interested in
making experiments.
We use adjectives in the “-ed” form to
describe how somebody feels about
something.
You can read some more examples:
We use adjectives in the “-ing” form to
describe a quality somebody or something
has.
You can read some more examples:
I was very surprised by their announcement.
(I felt surprised when I heard their announc I He
Look at this example:
Lisa said the news was really
interesting and advised me to have
a look at it.
They told me the film had been really boring.
goThe girls (They felt bored because the film was boring)
speHis opponent hit the racket hard/hardly and it broke. He got
The worrying weather forecast made us cancel the trip.
very angry/angrily.
(We were worried about the weather and cancelled the trip)
uietly.
when she saw them all.
rived home.
Exercise
17: Complete the sentences using the words in brackets in the “-ed” or “-ing form”. Match the
ient/ impatiently
his girlfriend didn’t arrive on
sentences
to the when
pictures.
time.
She
is
always
late/
lately.
1. The girl was …………….
and fell asleep at once. (TIRE)
ves
a
lot.
2. It was a…………… film and I got…………from start to finish. (BORE)
een working very hard)
3. Was Laura ……………. when she heard the news? (SURPRISE)
4. I told him a very ……….........……. story and he couldn’t stop laughing. (AMUSE)
5. Have you ever tried bungee jumping? It´s really ……………. (EXCITE)
6. He didn’t know what to do. The situation was ……….......... (CONFUSE)
7. She was really……………. when her boyfriend left her. (WORRY)
8. The boy was……….................... when he broke the window. It was the most……............................... situation
in his whole life. (EMBARRASS)
Edited and Complied by EQuest Academy
33
9. Tina was very…….................……….very when she saw her low grades. (DISAPPOINT?)
10. She’s reading an………….story. She’s really………….in it. (INTEREST)
11. It’s really……............……. when people use their mobile phones in public places. (ANNOY)
He didn’t have to go to school. It was a ……….........……. day. (RELAX)
3. Order of Adjectives:
When they are used together, they are arranged in a certain order.
Determiner
Opinion
The, This
Some
My
Pretty
Tall
Expensive
Size
Big
Thin
Small
Age
Color
Origin
Material
Noun
New
Old
Ancient
Blue
Purple
Black
Puerto
Rican
Chinese
Leather
Wood
Silk
Sofa
Scarf
For Example:
I saw that tall, thin, old, blue silk scarf at the store and I bought it.
Leon drives an expensive old Italian car.
Exercise 18:
A. Choose the correct answer.
1. Jack hid in the ……… box.
a) big brown square
b) brown square big
c) big square brown
B.
Put the adjectives in the correct order.
1. Jake works in a/an (trading,
big,
Canadian,
important)…………………
………………………………
…… company.
3. It’s a jar full of …… coins.
a) many golden round bright
b) many bright round golden
c) bright many golden round
2. Mr. Pitt invited his wife to
a/an
(Italian,
romantic,
modern)
……………………………
………………………
restaurant.
3. Roy finally married his
(Greek, beautiful, young)
………………………………
………………………………
……… girlfriend.
4. Your cousin is a …………… boy.
a) little nice blond
b) nice little blond
c) nice blond little
5. Bob likes going out in (hot,
sunny,
long,
summer)
………………………………
………………………………
……………… days.
5. Mrs. Jones is a/an ………… lady.
a) arrogant old English
b) ola arrogant English
c) English old arrogant
6. This is a/an (antique, red,
unusual)
………………………………
………………………………
………………………………
2. The cook is using … knife.
a) a sharp long metal
b) a long metal sharp
c) a long sharp metal
Edited and Complied by EQuest Academy
34
6. The gardener uses a …… can.
a) big useful orange watering
b) useful big orange watering
c) orange big useful watering
7. … bunnies are playing outside.
a) cute small two white
b) two small cute white
c) two cute small white
8. She is wearing a/an ……… ring.
a) diamond expensive big
b) big expensive diamond
c) expensive big diamond
Edited and Complied by EQuest Academy
………………… car.
7. In such weather, Peter wears
his (comfortable, nylon, rain,
yellow)
…………
………………………………
…… coat.
8. Mike likes solving (long,
math,
difficult)
………………
………………………………
………………………………
……… equations.
9. Sally has a (white, cute, fat,
Ragdoll) ……………………
………………………………
…………… cat.
35
4. ADVERBS
Exercise 19: Rewrite the sentences putting the adverb in the correct place.
1. My jumper was expensive. (very)
2. I enjoy it. (a lot)
3. I am writing a letter. (at the moment)
4. My shoes are comfortable. (quite)
5. He plays well (very)
6. Mary does her homework. (every day)
7. He used to teach. (last year)
8. Read this book (now)
9. She got a good result in her English test. ( quite)
10. I went to the cinema with my friends. (last weekend)
Exercise 20: Rewrite the sentences with the adverbs in brackets.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Oliver is late. (sometimes) ______________________________________________
You worry too much. ( often) ___________________________________________
I don't work too hard. (usually) __________________________________________
I’m careful. (normally) __________________________________________________
You can't have good luck (always) _______________________________________
Pessimists expect the worst. (always) _____________________________________
Things don't work out for me. (often) _____________________________________
I do enough work. ( never) ______________________________________________
Edited and Complied by EQuest Academy
36
9. You've got an optimistic view of life. (normally) ___________________________
Exercise 21: Use the adverbs in the box to strengthen the verbs in these sentences:
slowly
gently
angrily
loudly
greedily
sadly
sweetly anxiously accurately quietly
noisily
firmly
badly
happily
carefully tiredly nastily
tightly
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
Sally ran down the road.
The children played in the street.
Jane sang a song for her mother’s birthday.
The little girl picked up the kitten.
He drove round the corner.
The two boys climbed the hill.
Robert threw the ball into the net.
Sue took the child by the hand.
We looked at the clock.
I picked up the vase.
She told me to leave.
The old lady stroked the cat.
Lucy spoke to her sister.
He tucked into a huge hamburger.
Jane opened the door.
He looked over his shoulder to see her leave.
Linda opened the letter.
Sally put the baby on the sofa.
PARTS OF SPEECH- HOMEWORK- ADJECTIVE & ADVERBS
Exercise 22: Write down the correct form of the words in brackets. (adjective or adverb)
Our neighborhood is small & (quiet)………………. Even the people talk (quiet) …………………………….
Jim is a (careless) …………………………… student. He always forgets his homework.
Sam is very (desperate) ……………………………. His friends wanted to comfort him but he looked at them
(sad) …………………………….
4. Salam is an (honest) ………………………… person. She never tells lies.
5. The judge asked the witness and the witness answered (honest) …………………………….
6. The dog barked (angry) ………………………… at the thief who wanted to break (quiet) …………………
into the house.
7. The teacher told her students to check their answers (careful) …………………………… and not to be (hasty)
……………………………….
8. It has been raining (heavy) …………………………… for three hours.
9. The soldiers fought (brave) ………………………… in the battle and they were (luck) ………………………
to won at the end.
10. Ann jumped (happy) ……………………………… when she won the game.
11. We were not in a hurry so we walked (slow) ……………………………… enjoying our walk.
12. Tom is looking (hungry) ………………………………… at my dinner because he hasn’t eaten anything since
morning.
13. My dad is an (excellent) ……………………………… driver. He has never had an accident.
14. The test wasn’t (difficult) …………………………, so we answered the question (easy) …………………….
1.
2.
3.
Edited and Complied by EQuest Academy
37
Exercise 23: The following sentences have mistakes. Spot them and rewrite the sentences in good English.
1. Laura is as beautiful than Sandra.
__________________________________________________________
2. The cinema is more far than the hospital.
__________________________________________________________
3. Natalia is more bad at English than me.
__________________________________________________________
4. Those grapes are more riper than these.
__________________________________________________________
5. Madrid is much crowded than Seville.
__________________________________________________________
6. Your cake is much more better than mine.
__________________________________________________________
7. Lidia’s son is cleverest than my.
__________________________________________________________
8. This metal box is more heavy than the wooden one
__________________________________________________________
9. My car is more slow than my father’s
__________________________________________________________
10. David is fattest than his brother.
__________________________________________________________
Edited and Complied by EQuest Academy
38