- Trang chủ >>
- Y - Dược >>
- Gây mê hồi sức
HÔ HẤP GIẢI PHẨU SINH LÍ+VIÊM PHỔI
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (777.45 KB, 36 trang )
Hô hấp trẻ em
I.Giải phẫu+sinh lý
•
•
•
•
•
•
Hệ hô hấp:
Lồng ngực
Các cơ hô hấp
Màng phổi
Đường dẫn khí:hh trên:miệng hầu thanh quản
Đường hô hấp dưới:khí quản phế quản tiểu PQ
•
Phát triển trước sinh:
Đến tuần thứ 32->completed
Sau sinh:
-Surfactant=phospholipid+protein
Tiết bởi tb pn type 2
Giảm sức căng bề mặt
-glucocorticoid tăng tổng hợp apoprotein+ lipid=>phòng ngừa HC SHH trẻ đẻ non
•
Mũi:
Nhỏ ngắn
Dễ sung huyết (nm mỏng, nhiều mmạch)
TSS ko thở đc =Miệng=>dễ khó thở khi sung huyết mũi
-3 yto giúp xoang cạnh mũi cn bt:
+lỗ thông xoang
+lớp tb có lông
+t/c chất tiết
•
Miệng hầu:hẹp
-Lympho nm họng chưa ptr=> dễ NTr
-hạch hạnh nhân ptr max 4-10yrs->teo dần đến tuổi dậy thì
•
Thanh quản: càng nhỏ TQ càng hẹp
•
•
•
TSS: hô hấp di động ngực-bụng ngược chiều
Tkinh chưa hchỉnh=> cơn ngừng thở/thở ko đều
Cần làm ấm+ẩm kk,oxy=>tránh làm khô màng nhày
Paediatric Disease
I.Pneumonia
ĐN, PL
•
•
•
•
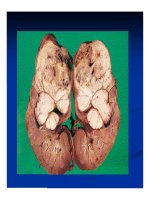
Viêm phổi là Viêm nhu mô phổi= Viêm PQ, VPQP, VP thùy,áp xe phổi
VPQ-Phổi=80% trẻ <3yrs (<12mons)
VP thùy-tiểu thùy: trẻ >3yrs
VP kẽ: mọi lứa tuổi
•
•
VP nhẹ: SHH I, Hc NT nhẹ, không có HC nhiễm độc
VP nặng: SHH 2-3,HC Nt nặng, có HC NĐộc
Nguyên nhân
3 nhóm:
•
80-85% do virus
•
•
Bacteria
Không do vi trùng:hít sặc:TĂ,dvi,dị vật…/dị ứng/thuốc,chất pxa
•
•
•
Dòng vk mũi hầu: gram dương
Bệnh lý răng miệng:Gr (-)
Sau 72h nằm viện: Gr (-)
LS+CLS
-Children with pneumonia may have a range of clinical presentations, depending on
their age and the cause of the pneumonia. Children who have bacterial pneumonia
usually become severely ill and show the following symptoms:
•
•
•
•
•
Fast or difficult breathing (see table below)
Cough
Fever and chills
Loss of appetite
Wheezing.
-Adults with pneumonia also have fever, cough, and fast or difficult breathing.
•
In severe cases of pneumonia, children under five-years-old may struggle to breathe and usually show chest in-drawing, which
you can observe as drawing inwards or retracting of the lower chest (red arrows in the figure below) during inhalation (taking air
into the lungs).
•
Chest in-drawing during inspiration: the lower chest wall moves in sharply as the child breathes in. (Diagram: Dr Radmila
Mileusnic)
If the child is:
The child has fast breathing
if you count:
2 months up to 12 months:
50 breaths per minute or more
12 months up to 5 years:
40 breaths per minute or more.
•
A child with fast breathing, chest in-drawing or stridor should be immediately
referred to hospital.
Severe signs of pneumonia in children and adults
Children
•
•
•
•
•
Age less than 2 months
Presence of general danger signs (unable to drink or eat, lethargic or unconscious)
Chest in-drawing
Stridor (a harsh noise made during inhalation)
Respiratory rate exceeding the limits.
Adults
•
•
•
Age 65 years or older
Respiratory rate equal to or greater than 30 breaths per minute
Presence of confusion.
If a child with pneumonia has fast breathing, but no general danger signs, or chest indrawing, or stridor, classify him/her as having non-severe pneumonia. Adults with
pneumonia who do not have the severe signs given in the box above, are also
classified as having non-severe pneumonia.