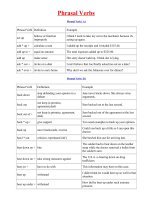
SKKN cách sử dụng lượng từ trong tiếng anh dành cho học sinh THCS
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (179.74 KB, 26 trang )
ỦY BAN NHÂN DÂN THÀNH PHỐ VĨNH YÊN
HỒ SƠ ĐỀ NGHỊ
CÔNG NHẬN SÁNG KIẾN CẤP THÀNH PHỐ
Tác giả sáng kiến: Dương Thị Thu Trang
Chức vụ:Giáo viên
Đơn vị: TRƯỜNG THCS KHAI QUANG – VĨNH YÊN
Hồ sơ gồm:
1. Đơn đề nghị công nhận sáng kiến cấp thành phố
2. Báo cáo kết quả nghiên cứu, ứng dụng sáng kiến
0
Vĩnh Yên, năm 2016
1
CỘNG HÒA XÃ HỘI CHỦ NGHĨA VIỆT NAM
Độc lập - Tự do - Hạnh phúc
---------------ĐƠN YÊU CẦU
CÔNG NHẬN SÁNG KIẾN CẤP THÀNH PHỐ
Kính gửi: Hội đồng Sáng kiến thành phố Vĩnh Yên
(Cơ quan thường trực: Phòng Kinh tế thành phố Vĩnh Yên)
Tên tôi là: Dương Thị Thu Trang
Chức vụ: Giáo viên
Đơn vị/địa phương: Trường THCS Khai Quang - Vĩnh Yên - Vĩnh Phúc
Điện thoại: 0985019904
Đề nghị Hội đồng sáng kiến thành phố Vĩnh Yên công nhận sáng kiến cấp thành
phố như sau:
1. Tên sáng kiến: “Cách sử dụng Lượng từ trong tiếng Anh dành cho học
sinh THCS”
2. Lĩnh vực áp dụng sáng kiến: Giảng dạy môn tiếng Anh tại trường THCS
3. Ngày sáng kiến được áp dụng lần đầu hoặc áp dụng thử: Áp dụng lần đầu
05/09/2015.
4. Nội dung cơ bản của sáng kiến:
Đưa ra một số giải pháp giảng dạy về Lượng từ:
4. 1. Tổng hợp cách sử dụng một số lượng từ thông dụng thông qua các bảng tóm tắt,
có ví dụ minh họa cụ thể với các phần sau:
a. Expressions of quantity.
b. Using“of” in expressions of Quantity.
c. Singular expressions of Quantity: one, each, every.
d. Subject verb Agreement: Using Expresions of Quantity.
e- Using A FEW and FEW; A LITTLE and LITTLE.
f. Using ‘ALL’
4. 2 Chuẩn bị bài dạy thật tốt với nội dung lý thuyết và chọn các dạng bài tập sát
với nội dung lý thuyết đã dạy.
4.3 Áp dụng phương pháp mới, ứng dụng công nghệ thông tin và lựa chọn
phương pháp- kĩ thuật dạy học phù hợp cho từng đối tượng học sinh.
4.4 Phân loại học sinh để đưa ra dạng bài phù hợp, giúp các em tiến bộ dần dần.
2
4. 5 Trong quá trình giảng dạy, giáo viên cần bình tĩnh, không nên nóng vội để
giảng ngay một cấu trúc mà học sinh chưa trả lời được. Cần gợi mở, nêu vấn đề
để các em tự rút ra cấu trúc và áp dụng có hiệu quả.
4. 6 Cho học sinh học bằng sơ đồ tư duy để các em dễ hiểu kiến thức, giúp các
em hình thành thói quen kỹ năng hệ thống một vấn đề. Từ đó các em sẽ làm bài
tập Tiếng Anh một cách dễ dàng hơn.
5. Điều kiện áp dụng:
- Giáo viên nắm vững, sâu về nội dung kiến thức sẽ dạy và có kỹ thuật phương
pháp dạy học phù hợp với đặc thù bộ môn; yêu nghề và mến trẻ.
- Học sinh có ý thức tự giác trong học tập và sự đam mê yêu thích môn học.
6. Khả năng áp dụng: có tính khả thi, áp dụng rộng rãi trong dạy học.
7. Hiệu quả đạt được:
- Giáo có được các giải pháp nâng cao hiệu quả giảng dạy tốt áp dụng phù hợp
cho các đối tượng học sinh khác nhau.
- Học sinh có nhiều hứng thú hơn trong giờ học ngữ pháp.
- Học sinh mạnh dạn làm việc theo cặp, nhóm.
- Khả năng viết và nói tiếng Anh của học sinh có được cải thiện.
- Học sinh đạt kết quả cao hơn khi làm những bài kiểm tra có Lượng từ.
- Tăng khả năng sáng tạo và năng động của học sinh.
- Học sinh biết nhận dạng bài tập, biết phân tích để tìm được đáp án chính xác.
- Thông qua việc làm bài tập tốt, học sinh biêt ứng dụng nó trong các tình huống
khác nhau phục vụ cho giao tiếp.
8. Các thông tin cần được bảo mật: Không.
(Có gửi kèm theo Báo cáo kết quả nghiên cứu, ứng dụng sáng kiến)
Tôi xin cam đoan mọi thông tin nêu trong đơn là trung thực, đúng sự thật,
không xâm phạm quyền sở hữu trí tuệ của người khác và hoàn toàn chịu trách
nhiệm về thông tin đã nêu trong đơn.
..........., ngày .... tháng .... năm 2016
Xác nhận của Thủ trưởng đơn vị
(Ký tên, đóng dấu)
Khai Quang, ngày 03 tháng 03 năm 2016
Người nộp đơn
(Ký tên, ghi rõ họ tên)
Dương Thị Thu Trang
BÁO CÁO KẾT QUẢ
3
NGHIÊN CỨU, ỨNG DỤNG SÁNG KIẾN
1. Lời giới thiệu:
Việt Nam đang trên con đường xây dựng đất nước trở thành một nước
công nghiệp hóa hiện đại hóa, dân giàu nước mạnh, xã hội công bằng, dân
chủ văn minh.Vì vậy, việc giáo dục hoàn thiện nguồn nhân lực đối với nước
ta trong giai đoan hiện nay là vấn đề cấp bách và quan trọng. Do đó, các nhà
trường phổ thông có nhiệm vụ bồi dưỡng tri thức cho học sinh về mọi lĩnh
vực của khoa học công nghệ. Đặc biệt trong đó có bộ môn ngoại ngữ -Tiếng
Anh.Tiếng Anh là một phương tiện để cho các em học sinh tiếp cận với những
thành tựu khoa học kỹ thuật tiên tiến.Tiếng Anh là một công cụ để giao tiếp, hợp
tác và phát triển kinh tế. Vì thế việc học Tiếng Anh sao cho hiệu quả và vận
dụng vào thực tế là rất quan trọng. Từ thực tiễn giảng dạy, tôi nhận thấy rằng,
trong chương trình Tiếng Anh THCS, LƯỢNG TỪ hay còn gọi là ‘từ chỉ
lượng’ là một phần kiến thức quan trọng có trong các kỳ thi . Hơn nữa LƯỢNG
TỪ là một trong những nội dung thường gây khó khăn cho người học Tiếng
Anh. Nội dung này không chỉ phục vụ học Tiếng Anh thông dụng mà còn được
sử dụng thường xuyên trong các đề thi cấp THCS và THPT cũng như Đại học.
Lượng từ đã được đưa vào ngay từ chương trình Tiếng Anh lớp 6.
Muốn làm tốt được các bài tập về từ chỉ lượng thì mỗi người học sinh cần
nắm rõ cách sử dụng về lượng từ và có phương pháp hệ thống về nó cho dễ hiểu
và dễ nhớ, để vận dụng khi làm bài thi Tiếng Anh. Chính vì thế, việc hiểu rõ
cách sử dụng về Lượng từ là một điều rất cần thiết đối với các em học sinh.
2. Tên sáng kiến: Cách sử dụng Lượng từ trong tiếng Anh dành cho học
sinh THCS
3. Tác giả sáng kiến:
- Họ và tên: Dương Thị thu Trang
- Địa chỉ tác giả sáng kiến: Trường THCS Khai Quang
- Số điện thoại: 0985019904. Email:
4. Chủ đầu tư tạo ra sáng kiến: Dương Thị Thu Trang
5. Lĩnh vực áp dụng sáng kiến: Giảng dạy môn Tiếng Anh bậc THCS
6. Ngày sáng kiến được áp dụng lần đầu hoặc áp dụng thử: Áp dụng lần đầu
05/09/2015.
7. Mô tả bản chất của sáng kiến:
Tóm tắt nội dung, bản chất của SKKN:
7.1 Một số giải pháp giảng dạy về Lượng từ:
1) Đưa ra khái niệm, phân loại và giải thích nội dung về lượng từ
* Thế nào là Lượng từ
4
Lượng từ : là những từ bổ nghĩa cho danh từ. Chúng ta dùng Lượng từ để bổ
sung thêm thông tin cho danh từ; chúng cho ta biết về số lượng của danh từ đó.
I. Từ chỉ lượng lớn và nhỏ. (Large and small quantities)
1. A lot of/ lots of/ many and much (Nhiều)
- a lot of/ lots of + Danh từ số nhiều / Danh từ không đếm được
- many + danh từ số nhiều.
- much + danh từ không đếm được.
VD: - A lot of people / lots of people work in London.
- Plural:
There aren’t many trains on Sunday.
- Uncountable:
You’ll have a lot of
fun at our holiday centre.
lots of
There isn’t much traffic on Sunday.
- A lot of / lots of: dùng trong câu khẳng định.
- Many / much:
dùng trong câu phủ định và câu hỏi.
There aren’t many tourists here.
Are there many tourists here?
How many tourists come here?
- Trước many/ much (but not a lot of) ta có thể dùng very, so, too, as và how.
Very many crimes go unreported.
There’s too much concrete here and not enough grass.
- A lot of thì thân mật hơn much và many.
- Với văn phong thân mật, a lot of có thể được dùng trong câu phủ định và câu
hỏi, cũng như trong câu khẳng định.
There aren’t
a lot of tourists here.
many tourists here.
Is there a lot of
support for the idea?
much
- Với văn phong trang trọng: Ta có thể dùng many và much trong câu khẳng định
cũng như trong câu phủ định và câu hỏi.
Many tourists come here year after year.
* Chú ý:
- Lots of thì thân mật hơn a lot of.
- Ta có thể dùng quite / rather trước a lot of, với many và much thì không.
5
- A great many: (khá trang trọng)
A great many crimes go unreported.
-Có thể dùng một chủ ngữ với: not many/ not much.
Not many tourists come here.
2. (A) few, (a) little and a bit of.
(a) A few và a little: a small quantity.
- A few / a little mang nghĩa “a positive idea”.
- A few + Danh từ số nhiều.
- A little + danh từ không đếm được.
She has been here only two weeks, but she has already made a few
friends.
(Positive idea: She has made some friends.)
I’m very pleased. I’ve been able to save a little money this month.
(Positive idea: I have saved some money in stead of spending all of it.)
Yes, there are a few night clubs in the city.
I’ve still got
a little
money, fortunately.
a bit of
- A bit of có nghĩa giống với a little nhưng a bit of thân mật hơn.
+ Chú ý:
- Có thể dùng quite trước a few và a bit of.
- Khi kết hợp với only thì mang nghĩa “a negative meaning”.
(b). Few và little:
+ little + danh từ không đếm được - Mang nghĩa “Negative”.
+ few + danh từ số nhiều
I feel sorry for her, she has (very) few friends
(Negative idea: She does not have many friends, she has almost no friend).
I have (very) little money. I don’t even have enough money to buy food
for dinner.
(Negative idea: I do not have much money; I have almost no money).
+ Chú ý:
- Có thể dùng very trước few / little.
3. Mẫu đặc biệt với “many” and “few”
* Trước many và few ta có thể dùng the, these/ those hoặc 1 tính từ sở hữu.
The few hotels in the area are always full.
Can you eat up these few peas?
6
Tim introduced us to one of his many girlfriends.
* Many (nhiều)
Many a ship has come to grief of the coast here.
I’ve driven a long this road many time.
- many time / lots of time ( informal.)
* Many / few là bổ ngữ.
These disadvantages of the scheme are many. (Rather literary).
The scheme has many disadvantages / a lot of disavantages.
(Many + danh từ
more normal).
4. Sự diễn đạt khác cho từ chỉ lượng lớn và nhỏ.
a. Từ chỉ lượng lớn.
- A large number of
- A great deal of
- A large / huge / tremendous amount of + N.
- Numerous
- masses of
- heaps of
+ N (informal).
- loads of
A large number of people couldn’t get ticket.
A dishwasher uses a great deal of electricity.
b. Từ chỉ lượng nhỏ.
got left behind.
Several people
A handful of people
A computer uses only a small / tiny amount of electricity.
II. Whole and part quantities: all, most, both, etc.
1. Patterns.
a. Quantifier + noun.
- every system, both decks, most music.
*Note:
All
Most
Singular
Plural
All systems
Most systems
Uncountable
All music
Most music
7
Both
Both systems
Either
either system
Neither
neither system
Every
every system
Each
each system
Some
some system
some systems
Any
any system
any systems
No
no system
no system
b- Quantifier + determiner + noun: All, both, half.
Some music
any music
no music
All the systems.
Both these decks.
Half my tapes.
c- Quantifier + of + determiner + noun.
- all, both, most, half, none, either, neither, each, any, some, many, much, more
an one, two, three etc.
(but exceptions are every and no)
VD: all of the systems, both of the decks, most of my tapes.
d- Quantifier + of + pronoun: all of them, both of them.
- all, both, most, half, none, either, neither, each, any, some, many, much, more
an one, two, three etc.
e- Quantifier + one.
Either, neither, every, each, any + one.
Of có thể đứng sau one.
Each one of the systems.
Either one of them.
f- Quantifier without a noun.
- Ta có thể dùng tất cả các từ chỉ lượng, ngoại trừ every và no.
Most have to decks.
g- Object pronoun + quantifier.
- Mẫu này được dùng với all và both.
I’ve heard it all before.
We tested them both.
h- Quantifier in mid position.
- Mẫu này ta dùng với all, both và each, giống như một trạng từ.
8
We all agreed.
They were both tested.
2. All / most / half and none.
a. all/ most + Noun
tạo nên một sự tổng quát.
All rabbits love green food.
Most pollution could be avoided.
Những câu này nói về rabbits và pollution nói chung.
- Ta so sánh hai câu sau:
+ Most people want a quiet life.
(people = người nói chung)
+ Most of the people here are strangers to me.
(The people: một nhóm người cụ thể.)
b- All/ most / half / none of + determiner + noun.
- Để nói về diều gì đó cụ thể hơn.
VD: 1.All (of) our rabbits died from some disease.
2. Most of the pubs around here serve food.
3. Copying takes half (of) the normal playing time.
4. None of these jackets fit me any more.
Ở VD1 và 3, ta có thể bỏ đi “of”sau “all”và “half” nhưng khi có 1 đại từ thì luôn
dùng “of”.
We had some rabbits, but all of them died.
I read the book, but I couldn’t understand half of it.
* Chú ý:
- Ta có thể dùng: half a / an.
We waited half an hour.
Ta có thể dùng số sau “all”.
all fifty systems.
c. All + an object pronoun.
VD: The rabbits died. We lost them all / all of them.
- All có thể ở giữa hoặc sau chủ ngữ.
The systems can all copy a tape from one deck to the other.
The rabbits all died.
- Most không thể dùng ở vị trí này, nhưng ta có thể dùng trạng từ “mostly”.
VD: Package systems mostly / usually have 2 cassette decks.
9
d- None
- None: có nghĩa phủ định.
- None + of + N.
VD: None of the rabbits survived. They all died.
Not: All of the rabbits didn’t survive
- Nhưng khi dùng not all, có nghĩa là less than all.
3. Whole
- Dùng whole như là một tính từ trước 1 danh từ số ít.
VD: This whole idea is crazy.
- Có thể dùng whole như 1 danh từ.
VD: Did you copy the whole of the tape.
4. Both, either và neither.
+ Ta dùng những từ này để nói về 2 thứ.
VD: If you’re ambidextrous, you can write with both hands.
- Both = the one and the other.
- Either = the one or the other.
- Neither = not the one or the other
+ So sánh: both / neither và all / none
Positive
Two
Both prisoners escaped.
Three or more All the prisoners escaped.
Negative
Neither of the prisoners escaped.
None of the prisoners escaped.
- Mẫu câu dùng với “both” thì giống mẫu dùng với “all”.
Both decks / Both the decks / Both of the decks play tapes.
They both play tapes.
+ Either / Neither:
- Dùng either và neither trước 1 danh từ hoặc kết hợp với “of”.
You can use either deck / either of the decks.
Neither of our cars is / are very economical to run.
Neither car is very economical to run.
so sánh:: I don’t like either of those pictures.
I like neither of those pictures.
Neither more emphatic and
rather more formal than not either.
+ Either or both không thể đứng trước một câu phủ định.
VD: Neither of those pictures are any good.
10
Không viết là: Either / both of those pictues aren’t any good.
5. Every and Each.
- Every / each + a singular noun.
- chủ ngữ với every và each thì động từ chia ở hình thức số ít.
There were flags flying from every / each building.
Every / each ticket has a number.
* Some more examples:
Every shop was open (= all the shops).
Each child was given a medal with his or her name engraved on it.
“every” nói đến con số lớn hơn “each”.
- Each ám chỉ hai hay nhiều hơn.
- Every ám chỉ 3 hay nhiều hơn
The owner name’s was painted
on each side.
on both sides.
of the van.
Missiles were being thown from
every direction.
all directions.
* Chú ý:
- Trước every ta có thể dùng almost hoặc nearly.
VD: There were flags flying from almost every building.
- Every single có nghĩa là “every on without exeption.”
VD: Every single child was given a medal.
- Chúng ta thường sử dụng "every" với những điều xảy ra đều đặn. "each" ít
hơn bình thường.
Sandra does aerobics every Thursday.
each Thursday.
The meetings are every four weeks.
d. Chúng ta có thể dùng “each” (không dùng every) trong các mẫu sau đây:
Each of the students has a personal tutor.
Each has a personal tutor.
Before the visitor left, we gave them each a souvenir.
They each received a souvenir.
- Each có thể được dùng như trạng từ sau 1 danh từ.
VD: The tickets are $5 each.
11
e. Ta không thể dùng động từ phủ định với every/ each.
VD: None of the doors were locked.
NOTE: Every / Each door wasn’t locked.
- “Not every” được dùng với nghĩa “less than all”.
VD: Not every door was locked. Some of them were open.
6. Part:
- Part: có thể là một danh từ bình thường với một determiner.
VD: This next part of the film is exciting.
- Ta có thể dùng “part” như là từ chỉ lượng mà không cần mạo từ đi theo.
VD: (A) part of the film was shot in Iceland.
7. A lot of, many, much, a few and a little.
Những từ này diễn tả từ chỉ lượng lớn và nhỏ. Nhưng khi " many, much, a few
and a little " thể hiện một phần của một số lượng, chúng ta sử dụng ‘of’.
Many of these features are just gimmicks.
Much of my time is spent answering enquiries.
A few of the photos didn’t come out properly.
III. Some, any and no.
1. Some/any expressing a quantity.
a/ Some + plural or uncountable noun isnequivelent to a/an + singular noun.
VD: You need a hammer, some nails and some wood.
b/ Some diễn tả từ chỉ lượng tích cực.
- Some nails = a number of nails.
- But any không mang nghĩa tích cực. Ta thường dùng any trong câu phủ định
và câu hỏi.
+ Positive: I’ve got some wood.
+ Negative: I haven’t got any wood.
+ Question: Have you got any/some wood?
+ Any means that the quantity may be zero.
* Chú ý:
Trong câu phủ định đôi khi ta có thể dùng any + danh từ số ít.
VD: A: Pass me the hammer.
B: I can’t see any hammer/ a hammer.
c/ Trong câu phủ định, ta hầu hết dùng any chứ không dùng some, bao gồm cả
câu có chứa từ phủ định như: never và hardy.
I can’t find any nails.
12
I never have any spare time.
We’re won hardly any games this season.
d/ Any thường được dùng trong câu hỏi và nó để dạng câu trả lời mở.
Have you got any nails?
Yes/ No / I don’t know.
- But we use some to give the question a more positive tone, especially when
making an offer or request. It suggests that we expect the answer “yes”.
Did you catch some fish?
(I expect you caught some fish).
Could you lend me some money.
(Please lend me some money).
e/ Trong mệnh đề “If”, chúng ta có thể chọn some hoặc any. Some is more
positive.
VD. If you need some/ any help, do let me know.
- Chúng ta có thể dùng ‘any’ trong mệnh đề chính để diễn tả 1 điều kiện.
VD. Any problems will be dealt with by our agent.
(If there are any problem, they with be dealt with by our agent).
f/ Từ ghép với some hoặc any.
There was someone in the phonebox.
There isn’t anywhere to leave our coat.
Could you do something for me?
Have you got anything/ some thing suitable to wear?
2. No
a.‘No’ là danh từ phủ định.
No + Countable noun.
+ Uncountable no.
There is no alternative.
There are no rivers in Saudi Arabia.
b/ Chúng ta có thể dùng ‘no’ với chủ ngữ, nhưng không thể dùng “any”.
No warning was given.
Not: Any warning was not given.
c/ Chúng ta bắt buộc dùng No với một danh từ.
3. “Some” expressing part of a quantity.
- Some mang nghĩa “some but not all”.
Some fish can change their sex.
13
Some trains have a restaurant car.
So sánh 2 nghĩa của “some”.
Some people enjoy quiz shows = some but not all.
There were some people in the garden.
= some but not very many.
4. Cách dùng đặc biệt của “any”
a. Đôi khi ta dùng “any” với nghĩa “It doesn’t matter which”
You can choose any colour you like.
Play any music. I don’t mind what you play.
b. So sánh “either” và “any”:
Two: There are two colours. You can have either of them. (= one of the two).
There or more: There are several colours. You can have any of them (= one of
the several.)
c. Ta có thể dùng từ ghép với any.
VD.The door isn’t locked. Anyone can just walk in.
5. Cách dùng đặc biệt của ‘some’.
- Some + singular noun có thể có nghĩa là một người không xác định hoặc một
điều không xác định.
Some idiot dropped a milk bottle.
The flight was delayed for some rearon.
(Some idiot means “an unknown idiot”. It si not important who the idiot is)
- Some day/ time: có nghĩa là một thời gian không xác định trong tương lai.
I’ll be famous some day/ one day.
You must come and see me some time.
-‘Some’có thể diễn tả cảm giác mạnh mẽ về một cái gì đó.
VD.That was some parade (wasn’t it?)
Ở đây “some” là đại từ. Nó có nghĩa là cuộc diễu hành thì đặc biệt, có lẽ là
một cuộc diễu hành lớn và ấn tượng.
“Some” before a number means “about”.
Some twenty people attended the meeting.
IV. Các từ chỉ lượng khác.
1. Enough và plenty of.
a. Ta có thể dùng “enough” trước một danh từ số nhiều hoặc một danh từ không
đếm được.
There aren’t enough people to play that game.
14
Have we enough time for a quick coffee?
- Ta có thể sử dụng “enough” với “of”
VD.We’ve written enough of this essay for today.
b. “Plenty of” có nghĩa là “more than enough”
There’ll be plenty of people to lend a hand.
Yes, we’ve got plenty of time.
* Chú ý:
We use “plenty of” to talk about something which is a good thing. For “more
than enough” in a bad sense we use ‘too many/ too much’.
-The store was very crowed. There were too many people to look round
properly.
2. Another và some more.
a. Another and some more diễn tả ‘extra quantity’.
- another + a singular noun.
- some more + a plural or uncountable noun.
singular: Have another sausage. – No, thanks. I’ve had enough.
plural: Have some more beans._ Thank you.
uncountable: Have some more cheese. _Yes, I will. Thank you.
b. Another có thể mang nghĩa ‘an extra one’ hoặc ‘a different one’.
We really need another car. One isn’t enough for us. (= an extra one)
I’m going to sell this car and get another one. (= a different one)
c. Trong một vài ngữ cảnh, ta dùng any hơn dùng some.
There aren’t any more sausages, I’m afraid.
Trước more ta có thể dùng: a lot, lots, many, much, a few, a little and a bit.
3. Other.
a. Other là một tính từ có nghĩa là ‘different’.
You are supposed to go out through the other door.
Có thể dùng other/ others mà không có danh từ đi kèm để ám chỉ ‘things
hoặc ‘people’.
You take one bag and I’ll take the other one.
They ate half the sandwiches. The others / the rest were thrown away.
Some pubs serve food, but others don’t.
**Chú ý.
-The other day/ week nghĩa là ‘recently, not long ago’.
I saw Miranda the other day.
15
b. Ta sử dụng another trước ‘a number + noun’
We were enjoying ourselves so much we decided to stay on for another three
days/ for three more days.( Here we are talking about an extra period, an extra
number of days.)
Ta có thể dùng other (= diferent) sau a number.
There are two other rooms/ two more rooms/ another two room upstais.
V. Quantifiers without a noun.
- Ta có thể dùng a quantifier mà không kèm theo một danh từ, dùng như một
đại từ.
Two have car parks.
Some sell food.
None stay open all night.
- Ta có thể dùng mẫu này với of.
Many of them also have hairdressing salons.
-Ta có thể dùng each mà không có một danh từ đi kèm.( với every thì không)
Each can choose its own half day.
- Ta không thể dùng no mà không có danh từ kèm theo.
There are several routes up the mountain. None of them are easy.
-Ta có thể dùng mẫu này với a lot, plenty ….( khi không có danh từ đi kèm, ta
không dùng of)
A lot serve lunches
If you want to climb a mountain. There are plenty to choose from.
Khi dùng với of thì phải có một danh từ hoặc đại từ theo sau.
A lot (of them/of the stores) serve lunches.
2) Tổng hợp cách sử dụng một số lượng từ thông dụng thông qua các bảng tóm tắt, có
ví dụ minh họa cụ thể với các phần sau:
a. Expressions of quantity.
- Một số lượng từ chỉ được dùng với danh từ đếm được, một số lại chỉ dùng với
danh từ không đếm được và một vài lượng tự lại dùng với cả danh từ đếm được
và không đếm được.
- Chúng ta quan sát bảng sau đây.
Expressions of Quantity
Used with count nouns
Used with noncount
nouns
16
One, each
every
Two
Both
A couple of
Three, etc
A few
Several
Many
A number of
A little
Much
A great deal of
One apple
Each apple
Every apple
Two apples
Both apples
A couple of apples
Three apples
A few apples
Sevral apples
Many apples
A number of apples
Ø
Ø
Ø
Ø
Ø
Ø
Ø
Ø
Ø
Ø
Ø
Ø
Ø
Ø
A little rice
Much rice
A great deal of rice
Not any /no
Some
A lot of
Lots of
Plenty of
Most
all
Not any / no apples
Some apples
A lot of apples
lost of apples
Plenty of apples
Most apples
All apples
Not any / no rice
Some rice
A lot of rice
Lots of rice
Plenty of rice
Most rice
All rice
b.Using “ of “ in expressions of Quantity.
-Sau đây là các lượng từ thông dụng được dùng với “of”
* Most + nonspecific noun.
a, Most books are interesting.
b, Incorrect: Most of books are
interesting.
* Most+of+ specific nouns.
c, Most of those books are mine.
d, Most of my books are English.
e, Most of the books on that table are
mine.
In (a) The speaker is not referring to
specific books The speaker is not
referring “Those books” or “your
books “or “the books written by Mark
Twain”. The noun “books” is
nonspecific.
In(b). The word “of” is not added to
an expresstion of quantity (eg most)
If the noun it modifies is non specific.
- A noun is specific when it is
preceded by:
+This, that, these, those, as in (c) : OR
+ my, John’s, their (any possessive) as
in (d), OR
+ The , as in (e)
17
-When a noun is specific, of is used
with an expression of quantity.
* Expressions of quantity followed by of + a specific noun.
+ all, most, some/any +of + specific plural count noun, as in (f).
+ many, (a) few, several, both, two, one + of + specific plural count noun or
noncount noun, as in (g)
+ much, (a) little + of + specific noncount noun, as in (h).
(f) Count: Most of those chairs are uncomfor table.
Noncount: Most of that furniture is uncomfortable.
(g) Count: Many of those chairs are uncomfortable
(h) Noncount: Much of that furniture is uncomfrtable.
+ Note: “of” is always a part of the following expressions of quantity, whether
the noun is nonspecific or specific: a lot of / lots of, a couple of, plenty of, a
great deal of.
- Nonspecific: I’ve read a lot of books.
- Specific: I’ve read a lot of those books.
c. Singular expressions of Quantity: one, each, every.
a. One student was late to class.
b. Each student has a schedule.
c. Every student has a schedule.
d. One of the students was late to class.
e. Each (one) of the students has a schedule.
f. Every one of the students has a schedule.
One, each and Every được
theo sau bởi danh từ đếm được
số ít.
- One of, each of, every one of
được theo sau bởi danh từ số
nhiều cụ thể.
* Ta so sánh các từ sau:
+ Every one (phát âm 2 từ) là chỉ lượng từ.
Eg: I have read every one of those books.
+ Everyone (phát âm là 1 từ) là 1 đại từ không xác định. Nó có nghĩa tương tự
“everybody”
Eg: Everyone/ Every body has a schedule.
d. Subject verb Agreement: Using Expresions of Quantity.
Sing ular verb
Plural verb
18
(a) Some of the
book is good
(c) A lot of the
equipment is new.
(e) Two – thirds of
the money is
mine.
(b) Some of the
books are good
(d) A lot of my
friends are here.
(f) Two – thirds
of the pennies
are mine.
- The verb is determined by the noun (or
pronoun) that follows “of” in most expressions
of quantity. Notice in.(a) & (b):
- Some of + singular noun + singular verb
- Some of + plural noun + plural verb.
(g) One of my
fiends is here
(h) Each of my
friends is here
(i) Every one of
my friends is here.
(j) None of the
(k) None of the
boys is here.
boys are here.
(Informal)
(e) The number of (m) A number
students in the
of students were
class is fifteen.
late for class
* EXCEPTIONS: One of/ each of and every
one of + singular verb
One of
Each of
+ Plural noun + singular verb.
Every one of
- Subjects with “none of” are considered
singular in very formal English, but plural verbs
are often used in informal speech and writing.
* Compare: In (l) the number is the subject. In
(m) A number of is an expression of quantity
meaning “a lot of”. It is followed by a plural
noun and a plural verb.
e- Using A FEW and FEW; A LITTLE and LITTLE.
A few
A little
Few
(a) She has been here only two
weeks,
but she has already made a few friends.
(Positive idea: She has made some friends.)
(b) I’m very pleased. I’ve been able to save a
little money this month.
(Pasitive idea: I have saved some money
instead of spending all of it.)
A few and a little*
give a positive idea;
they indicate that
something exists, is
present, as in (a) and
(b).
(c) I feel sorry for her. She has (very) few
friends.
(Negative idea: She does not have many
friends; she has almost no friends.)
Few and little
(without a) give a
negative idea; they
indicate that
something is largely
absent.
Very (+ few/ little)
makes the negative
Little
(d) I have (very) little money. I don’t even
enough money to buy food for dinner.
(Negative idea: I do not have much money; I
19
have almost no money.)
f. Using ‘ALL’
(a) CORRECT: All of the students in my
class are here.
(b) CORRECT: All the students in my class
are here.
(c) CORRECT: All students must have an
I.D. card.
(d) INCORRECT: All of students must have
an I.D. card.
(e) I know both (of) those men.
idea stronger, the
number/ amount
smaller.
When a noun is specific (e.g.,
the students), using of after all
is optional.
When a noun is nonspecific, of
does NOT follow all.
Simiarly, using of after both is
optional when the noun is
specific.
3) Chuẩn bị bài dạy thật tốt với nội dung lý thuyết và chọn các dạng bài tập sát
với nội dung lý thuyết đã dạy.
EXAMPLES:
EX1. Using a few/ few; a little/little
Directions: Without substantially changing the meaning of the sentence, replace
the italicized words with a few, (very) few, a little, or (very) little.
1. I think that some lemon juice on fish makes it taste better.
2. Many people are multilingual, but not many people speak more than ten
languages.
3. Some sunshine is better than none.
4. January is a cold and dreary month in the north states. There is not much
sunshine during that month.
5. My parents like to watch TV. Every evening thay watch two or three
programs on TV before they go to bed.
6. I don’t watch TV very much because there are hardly any televison programs
that I enjoy.
7. If a door squeaks several drops of oil in the right places can prevent future
trouble.
8. If your door squeaks, put some oil on the hinges.
9. Mr. Adams doesn’t like to wear rings on his fingers. He wears almost no
jewely.
10. You might reach your goal if you put forth some more effort.
20
11. Even though the mountain is very steep and the climb is hazardous, several
strong-willed people have managed to reach the top.
12. The number of people in the world who are willing to risk their lives
climbing a dangerous mountain is small. Not very many people will actually
face death to climb a mountain.
Key:
1. a little
2. (very) few
3. A little
4. (very) little
5. a few
6. (very) few
7. a few
8. a little
9. (very) little
10. a little
11. a few
12. (very) few
EX2. If the given noun can be used to complete the sentence, write it in its
correct from (singular or plural). If the given noun cannot be used to
complete the sentence, write Ø
1. Helen bought several….
3. Sam bought a lot of …..
lamp
...lamps…...
stamp
………………...
furniture
……Ø……..
rice
………………...
jewely
……Ø..……
stuff
…………………
necklace
..necklaces..
thing
…………………
2. Jack bought too much……
4. Alice bought a couple of……
shoe
……………….
bread
………………….
salt
……………….
loaf of bread …………………
equipment ………………
honey
.………………..
tool
………………
jar of honey ………………..
5. I read a few………..
6. I bought some……………..
novel
…………...…
orange juice
……………
literature
………………
light blub
……………
poem
………………
hardware
……………
poetry
………………
computer stofware ……………
Key:
1. lamps
Ø
Ø
necklaces
4. Ø
loaves of bread
Ø
jars of honey
2. Ø
salt
quipment
Ø
5. novels
Ø
poems
Ø
3. stamps
rice
stuff
things
6. orange juice
light bulbs
hardware
computer software
EX3. Using one, each, every
Directions: Choose the correct word in italics.
21
1. Each student, students in the class is required to take the final examination.
2. Each of the student, students in the class is required to take the final
examination.
3. There is at least one window in every room, rooms in our apartment.
4. Every one of the room, rooms in our apartment has at least one window.
5. My bedroom has only one, very small window, windows.
6. One of the smallest window, windows in our apartment is my bedroom.
7. When john bought some supplies at the hardware store, he thought the total
amount on the bill was incorrect, so he checked each item,items on his bill very
carefully.
8. Each of the item, items on the bill was correct.
9. Sussan has traveled widely, but she has has visited only one Scandinavian
country, countries.
10. Alex took an extended vacation in northem Europe last summer. Swden was
one of the country, countries he visited when he was in Scandinavia.
11. Tom believes that there are no strangers. He views each person, people in the
world as a friend he hasn’t met yet.
12. I answered every question, questions on the examination. I didn’t skip any.
13. Each one of the child, children in the classwas given a piece of paper and a
crayon. Each child, children drew a picture.
14. Hunger is one of the biggest problem, problems in the world today.
15. Each of the applicant, applicants for the scholarship is required to furnish
five references (that is, names of people who are willing to write letters of
recommendation).
KEY
1. Student
2. Students
3. room
4. rooms
5. window
6. windows
7. Item
8. Items
9. Country
10.Countries
11. person
12.Question
13.Children… child
14.Problems
15.applicants
EX4. Subject - verb agrrement
Choose the correct completion for the sentence.
1. The number of students who knew the answer to the last question on the exam
was, were very low.
22
2. Studying a foreign language often leads lead students to leam about the culture
of the countries where it is spoken.
3. The United States of America consists, consist of fifty separate states.
4. Two hours is, are too long to wait, don’tyou think?
5. Isn’t, Aren’t Portuguese spoken in Brazil?
6. A lot of Brazilians speaks and understands, speak and understand Spanish.
7. Why is, are the police standing over there?
8. Why does, do most of the television stations broadcast national news at the same
hour?
9. Some of the most imporatant books for my report is, are not availale in the
school library.
10. There has, have been times when I have seriously considered dropping out of
school.
11. Not one of the men in the original group of U.S. astronauts continues; continue
in the space program today.
12. The news on the radio and TV stations confims, confirm that a serious storm is
approaching our city.
13.Geography is, are fascinating. Mathematics is, are fascinating.
14. Mathematics and geography is, are my favorite subjects.
15. All of the windows in our house was, were broken in the earthquake.
16. By law, every man, woman, and child is, are guaranteed the right to free speech.
17. Some of the movie about the creatures from outer space was, were surprisingly
funny.
18. Some of the movies these days contains, contain too much violence.
19. Is, Are pineapple and sugar the leading crops in Hawaii today?
20. Why is, are there a shortage of certified school teachers at the present time?
KEY.
1. was
2. leads
3. consists
4. is
5. isn’t
6. speak and understand
7. are
8. do
9. are
10.have
11.continues
12.confirms
13.is….is
14.are
15.were
16.is
17.was
18. contain
19.are
20.is
4) Áp dụng phương pháp mới, ứng dụng công nghệ thông tin và lựa chọn
phương pháp- kĩ thuật dạy học phù hợp cho từng đối tượng học sinh.
5) Phân loại học sinh để đưa ra dạng bài phù hợp, giúp các em tiến bộ dần dần.
23
6) Trong quá trình giảng dạy, giáo viên cần bình tĩnh, không nên nóng vội để
giảng ngay một cấu trúc mà học sinh chưa trả lời được. Cần gợi mở, nêu vấn đề
để các em tự rút ra cấu trúc và áp dụng có hiệu quả.
7) Cho học sinh học bằng sơ đồ tư duy để các em dễ hiểu kiến thức, giúp các em
hình thành thói quen kỹ năng hệ thống một vấn đề. Từ đó các em sẽ làm bài tập
Tiếng Anh một cách dễ dàng hơn.
7.2. Hiệu quả của sáng kiến:
Việc vận dụng SKKN này bản thân tôi đã đạt được một số kết quả hết sức
khả quan. Trước hết những kinh nghiệm này phù hợp với chương trình, với
SGK. học sinh hứng thú học tập, chủ động, sáng tạo hơn, không khí học tập sôi
nổi, nhẹ nhàng. Học sinh có cơ hội khẳng định mình, không còn lúng túng, lo
ngại khi vào giờ học ngữ pháp. Và đây cũng chính là những nguyên nhân đi đến
những kết quả tương đối khả quan.
* Kết qủa trước khi áp dụng đề tài:
STT Lớp
Bài kiểm tra đánh giá chất lượng
Sĩ số
Giỏi
Khá
TB
Yếu
Kém
1
6A
41
1
10
24
6
0
2
6B
41
0
5
21
15
0
3
7A
38
3
18
13
4
0
4
7B
37
0
5
20
12
0
* Kết quả sau khi áp dụng đề tài:
STT Lớp
Bài kiểm tra đánh giá chất lượng
Sĩ số
Giỏi
Khá
TB
Yếu
Kém
1
6A
41
5
6
30
0
0
2
6B
41
0
10
31
0
0
3
7A
38
3
25
10
0
0
4
7B
37
0
10
27
0
0
7.3. Về khả năng áp dụng của sáng kiến: có tính khả thi, áp dụng rộng rãi cho
các cấp học đặc biệt là cấp THCS.
8. Những thông tin cần được bảo mật: không
24