Accounting Principles ACCOUNTING FOR MERCHANDISING OPERATIONS
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (186.29 KB, 45 trang )
CHAPTER 5 - ANSWER:
ACCOUNTING FOR MERCHANDISING
OPERATIONS
TRUE - FALSE STATEMENT
No
1
True/ False
Statements
Retailers and wholesalers are both considered merchandising enterprises.
2
3
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
4
TRUE
5
FALSE
6
TRUE
The operating cycle involves the purchase and sale of merchandise
inventory as well as the subsequent collection of cash from credit sales.
9
TRUE
An advantage of using the periodic inventory system is that it requires less
record keeping than the perpetual inventory system
10
11
12
13
TRUE
14
TRUE
Cost of Goods Sold is considered an expense of a merchandising firm.
Operating expenses are subtracted from revenue for a service enterprise and
from gross profit for a merchandising enterprise.
15
TRUE
16
TRUE
17
TRUE
18
TRUE
19
FALSE
20
FALSE
21
TRUE
22
TRUE
23
24
FALSE
FALSE
Under a perpetual inventory system, the cost of goods sold is determined
each time a sale occurs.
7
8
Net sales minus cost of goods sold is called gross profit
Under the perpetual inventory system, purchases of merchandise for sale
are recorded in the Inventory account.
Freight costs incurred by the seller on outgoing merchandise are an
operating expense to the seller.
The terms 2/10, net/30 mean that a 2 % discount is allowed on payments
made within the 10 days discount period.
A buyer who acquires merchandise under credit terms of 1/10, n/30 has 10
days after the invoice date to take advantage of the cash discount.
Discounts taken by the buyer for early payment of an invoice are
called purchases discounts by the buyer.
If merchandise costing $5,000, with terms 2/10, n/30, is paid within 10
days, the amount of the purchase discount is $100.
When an invoice is paid within the discount period, the amount of the
discount decreases Inventory
25
FALSE
26
TRUE
27
28
29
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
30
TRUE
31
TRUE
32
TRUE
33
FALSE
34
TRUE
35
36
37
38
39
40
TRUE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
41
TRUE
42
TRUE
43
44
45
FALSE
FALSE
TRUE
46
TRUE
47
TRUE
48
TRUE
49
50
51
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
Sales Returns and Allowances is a contra-revenue account.
Sales Discounts is a contra asset account.
The revenue recognition principle applies to merchandisers by recognizing
sales revenues when they are earned
Sales Discounts is a contra revenue account to Sales Revenue.
The normal balance of Sales Returns and Allowances is a debit.
When the terms of sale include a sales discount, it usually is advisable for
the buyer to pay within the discount period.
Sales Discounts and Sales Returns and Allowances both have normal debit
balances.
Merchandise is sold for $5,000 with terms 1/10, n/30. If $1,000 of the
merchandise is returned prior to payment and the invoice is paid within the
discount period, the amount of the sales discount is $40.
The terms 2/10, net/30 mean that a 2 % discount is allowed on payments
made within the 10 days discount period.
The multiple-step income statement is considered more useful than the
single-step income statement because it highlights the components of net
income.
General and administrative expenses are a category of operating expense.
Advertising expense appears as a selling expense in the income statement.
A merchandising company’s net income is determined by subtracting
operating expenses from gross profit.
Sales revenues, cost of goods sold, and gross profit are amounts on a
merchandising company's income statement not commonly found on the
income statement of a service company.
Gross profit represents the merchandising profit of a company.
If net sales are $750,000 and cost of goods sold is $600,000, the gross
profit rate is 20%
With the periodic inventory system, goods available for sale must be
calculated before cost of goods sold
Under the periodic system, the purchases account is used to accumulate all
purchases of merchandise for resale.
Gross profit is computed by subtracting cost of goods sold from net sales.
52
TRUE
Under the periodic inventory system, acquisitions of merchandise are not
recorded in the Inventory account.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
53.
Merchandising companies that sell to retailers are known as
a. brokers.
b. corporations.
c. wholesalers.
d. service firms.
54.
Which of the following would not be considered a merchandising operation?
a. Retailer
b. Wholesaler
c. Service firm
d. Merchandising company
55.
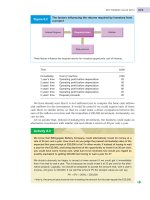
Which of the following activities is not a component of the operating cycle?
a. Sale of merchandise
b. Payment of employees’ salaries
c. Collection of cash from merchandise sales
d. Purchase of merchandise
56.
Which of the following companies would be most likely to use a perpetual
inventory system?
a. Grain company.
b. Beauty salon.
c. Clothing store.
d. Fur dealer.
57.
Gross profit equals the difference between
a. net income and operating expenses.
b. net sales revenues and cost of goods sold.
c. net sales revenues and operating expenses.
d. net sales revenues and cost of goods sold plus operating expenses.
58.
Each of the following companies is a merchandising company except a
a. wholesale parts company.
b. candy store.
c. moving company.
d. furniture store.
59.
Net income will result if gross profit exceeds
a. cost of goods sold.
b. operating expenses.
c. purchases.
d. cost of goods sold plus operating expenses.
60.
A merchandiser will earn an operating income of exactly $0 when
a. net sales equals cost of goods sold.
b. cost of goods sold equals gross margin.
c. operating expenses equal net sales.
d. gross profit equals operating expenses.
61.
A merchandiser that sells directly to consumers is a
a. retailer.
b. wholesaler.
c. broker.
d. service enterprise.
62.
Two categories of expenses in merchandising companies are
a. cost of goods sold and financing expenses.
b. operating expenses and financing expenses.
c. cost of goods sold and operating expenses.
d. sales and cost of goods sold.
63.
The primary source of revenue for a wholesaler is
a. investment income.
b. service revenue.
c. the sale of merchandise.
d. the sale of plant assets the company owns.
64.
Generally, the revenue account for a merchandising enterprise is called
a. Sales Revenue or Sales.
b. Investment Income.
c. Gross Profit.
d. Net Sales.
65.
Under a perpetual inventory system
a. accounting records continuously disclose the amount of inventory.
b. increases in inventory resulting from purchases are debited to purchases.
c. there is no need for a year-end physical count.
d. the account purchase returns and allowances is credited when goods are
returned to vendors.
66.
The operating cycle of a merchandising company is
a. always one year in length.
b. ordinarily longer than that of a service company.
c. about the same as that of a service company.
d. ordinarily shorter than that of a service company.
67.
Sales revenue less cost of goods sold is called
a. gross profit.
b. net profit.
c. net income.
d. marginal income.
68.
After gross profit is calculated, operating expenses are deducted to determine
a. gross margin.
b. net income.
c. gross profit on sales.
d. net margin.
69.
Which of the following expressions is incorrect?
a. Gross profit - operating expenses = net income
b. Sales - cost of goods sold - operating expenses = net income
c. Net income + operating expenses = gross profit
d. Operating expenses - cost of goods sold = gross profit
70.
Detailed records of goods held for resale are not maintained under a
a. perpetual inventory system.
b. periodic inventory system.
c. double entry accounting system.
d. single entry accounting system.
71.
A perpetual inventory system would most likely be used by a(n)
a. automobile dealership.
b. hardware store.
c. drugstore.
d. convenience store.
72.
Which of the following is a true statement about inventory systems?
a. Periodic inventory systems require more detailed inventory records.
b. Perpetual inventory systems require more detailed inventory records.
c. A periodic system requires cost of goods sold be determined after each
sale.
d. A perpetual system determines cost of goods sold only at the end of the
accounting period.
73.
The figure for which of the following items is determined at a different time
under the perpetual inventory method than under the periodic method?
a. Sales Revenue
b. Cost of Goods Sold
c. Purchases
d. Accounts Receivable
74.
In a perpetual inventory system, cost of goods sold is recorded
a. on a daily basis.
b. on a monthly basis.
c. on an annual basis.
d. each time a sale occurs.
75.
The primary difference between a periodic and perpetual inventory system is
that a periodic system
a. keeps a record showing the inventory on hand at all time.
b. provides better control over inventories.
c. records the cost of the sale on the date the sale is made.
d. determines the inventory on hand only at the end of the accounting period.
76.
When using the periodic system the physical inventory count is used to
determine
a. only the sales value of goods in the ending inventory.
b. both the cost of the goods in ending inventory and the sales value of goods
sold during the period.
c. both the cost of the goods sold and the cost of ending inventory.
d. only the cost of merchandise sold during the period.
77.
Inventory becomes part of cost of goods sold when a company
a. pays for the inventory.
b. purchases the inventory.
c. sells the inventory.
d. receives payment from the customer.
78.
Under the perpetual inventory system, which of the following accounts would
not be used?
a. Sales Revenue
b. Purchases
c. Cost of Goods Sold
d. Inventory
79.
If a company determines cost of goods sold each time a sale occurs, it
a. must have a computer accounting system.
b. uses a combination of the perpetual and periodic inventory systems.
c. uses a periodic inventory system.
d. uses a perpetual inventory system.
80.
The periodic inventory system is used most commonly by companies that sell
a. low-priced, high-volume merchandise.
b. high-priced, high-volume merchandise.
c. high-priced, low-volume merchandise.
d. high-priced, low and high-volume merchandise.
81.
What is a difference between merchandising companies and service
enterprises?
a. Merchandising companies must prepare multiple-step income statements
and service enterprises must prepare single-step income statements.
b. Merchandising companies generally have a longer operating cycle than
service enterprises.
c. Cost of goods sold is an expense for service enterprises but not for
merchandising companies.
d. All are differences.
82.
Which statement is incorrect?
a. Periodic inventory systems provide better control over inventories than
perpetual inventory systems.
b. Computers and electronic scanners allow more companies to use a
perpetual inventory system.
c. Freight-in is debited to merchandise inventory when a perpetual inventory
system is used.
d. Regardless of the inventory system that is used, companies should take a
physical inventory count.
83.
Under a perpetual inventory system, acquisition of merchandise for resale is
debited to
a. the Inventory account.
b. the Purchases account.
c. the Supplies account.
d. the Cost of Goods Sold account.
84.
The journal entry to record a return of merchandise purchased on account
under a perpetual inventory system would credit
a. Accounts Payable.
b. Purchase Returns and Allowances.
c. Sales Revenue.
d. Inventory.
85.
Which of the following items does not result in an adjustment in the
merchandise inventory account under a perpetual system?
a. A purchase of merchandise.
b. A return of merchandise inventory to the supplier
c. Payment of freight costs for goods shipped to a customer
d. Payment of freight costs for goods received from a supplier
86.
A company using a perpetual inventory system that returns goods previously
purchased on credit would
a. debit Accounts Payable and credit Inventory.
b. debit Sales and credit Accounts Payable.
c. debit Cash and credit Accounts Payable.
d. debit Accounts Payable and credit Purchases.
87.
If a purchaser using a perpetual inventory system pays the transportation costs,
then the
a. Inventory account is increased.
b. Inventory account is not affected.
c. Freight-out account is increased.
d. Delivery Expense account is increased.
88.
Freight costs incurred by a seller on merchandise sold to customers will cause
an increase
a. in the selling expenses of the buyer.
b. in operating expenses for the seller.
c. to the cost of goods sold of the seller.
d. to a contra-revenue account of the seller.
89.
Conway Company purchased merchandise inventory with an invoice price of
$8,000 and credit terms of 2/10, n/30. What is the net cost of the goods if
Conway Company pays within the discount period?
a. $8,000
b. $7,840
c. $7,200
d. $7,360
90.
A buyer borrows money at 12% interest to pay a $6,000 invoice with terms
1/10, n/30 on the 10th day of the discount period. The loan is repaid on the
30th day of the invoice. What is the buyer’s net savings for this total event?
a. $0
b. $20.00
c. $20.40
d. $40.00
91.
In the credit terms of 1/10, n/30, the “1” represents the
a. number of days in the discount period.
b. full amount of the invoice.
c. number of days when the entire amount is due.
d. percent of the cash discount.
92.
Farwell Company purchased merchandise with an invoice price of $2,000 and
credit terms of 2/10, n/30. Assuming a 360 day year, what is the implied
annual interest rate inherent in the credit terms?
a. 4%
b. 24%
c. 36%
d. 72%
93.
Davies Company purchased merchandise inventory with an invoice price of
$7,500 and credit terms of 2/10, n/30. What is the net cost of the goods if
Davies Company pays within the discount period?
a. $7,500
b. $7,380
c. $7,350
d $6,000
94.
A credit sale of $1,600 is made on April 25, terms 2/10, net/30, on which a
return of $100 is granted on April 28. What amount is received as payment in
full on May 4?
a. $1,470
b. $1,568
c. $1,600
d $1,500
95.
Grayson Company purchased merchandise with an invoice price of $2,000 and
credit terms of 1/10, n/30. Assuming a 360 day year, what is the implied
annual interest rate inherent in the credit terms?
a. 1%
b. 6%
c. 12%
d 18%
96.
A credit sale of $900 is made on July 15, terms 2/10, net/30, on which a return
of $50 is granted on July 18. What amount is received as payment in full on
July 24?
a. $900
b. $833
c. $850
d $882
97.
If a company is given credit terms of 2/10, n/30, it should
a. hold off paying the bill until the end of the credit period, while investing
the money at 10% annual interest during this time.
b. pay within the discount period and recognize a savings.
c. pay within the credit period but don't take the trouble to invest the cash
while waiting to pay the bill.
d. recognize that the supplier is desperate for cash and withhold payment
until the end of the credit period while negotiating a lower sales price.
98.
A purchase invoice is a document that
a. provides support for goods purchased for cash.
b. provides evidence of incurred operating expenses.
c. provides evidence of credit purchases.
d. serves only as a customer receipt.
99.
Adams Company is a retailer and uses a perpetual inventory system. Which
statement is correct?
a. Returns of merchandise inventory by Adams Company to a manufacturer
are credited to Inventory.
b. Freight paid to get merchandise inventory to Adams Company’s store is
debited to Freight Expense.
c. A return of merchandise inventory by one of Adams Company’s customers
is credited to Inventory.
d. Discounts taken by Adams Company’s customers are credited to Inventory.
100.
As the president of Harter Company, you notice that no discounts have been
taken when settling accounts payables. What would be an acceptable
explanation?
a. All invoices have credit terms of n/30.
b. There is not sufficient cash to pay within the discount period.
c. Discounts are missed because no one knows how to enter them in the new
accounting software.
d. The full amount of the invoice is being paid within the discount period and
the treasurer is pocketing the discount amount.
101.
When using a perpetual inventory system, why are discounts credited to
Inventory?
a. The discounts are debited to discount expense and thus the credit has to be
made to merchandise inventory.
b. The discounts reduce the cost of the inventory.
c. The discounts are a reduction of business expenses.
d. None of the answers is correct.
102.
Tony’s Market recorded the following events involving a recent purchase of
inventory:
Received goods for $30,000, terms 2/10, n/30.
Returned $600 of the shipment for credit.
Paid $150 freight on the shipment.
Paid the invoice within the discount period.
As a result of these events, the company’s inventory
a. increased by $28,812.
b. increased by $29,550.
c. increased by $28,959.
d. increased by $28,962.
103.
Stan’s Market recorded the following events involving a recent purchase of
inventory:
Received goods for $60,000, terms 2/10, n/30.
Returned $1,200 of the shipment for credit.
Paid $300 freight on the shipment.
Paid the invoice within the discount period.
As a result of these events, the company’s inventory
a. increased by $57,624.
b. increased by $59,100.
c. increased by $57,918.
d. increased by $57,924.
104.
Assets purchased for resale are recorded in which of the following accounts?
a. Supplies
b. Inventory
c. Equipment
d. More than one of the above is correct.
105.
Under the perpetual system, cash freight costs incurred by the buyer for the
transporting of goods is recorded in which account?
a. Freight Expense
b. Freight-in
c. Inventory
d. Freight-out
106.
Which of the following accounts is classified as a contra revenue account?
a. Sales Revenue
b. Cost of Goods Sold
c. Sales Returns and Allowances
d. Purchase Discounts
107.
Sales revenues are usually considered earned when
a. cash is received from credit sales.
b. an order is received.
c. goods have been transferred from the seller to the buyer.
d. adjusting entries are made.
108.
Sales revenue
a. may be recorded before cash is collected.
b. will always equal cash collections in a month.
c. only results from credit sales.
d. is only recorded after cash is collected.
109.
The journal entry to record a credit sale is
a. Cash
Sales Revenue
b. Cash
Service Revenue
c. Accounts Receivable
Sales Returns and Allowances
d. Accounts Receivable
Sales Revenue
110.
Under the perpetual inventory system, in addition to making the entry to
record a sale, a company would
a. debit Inventory and credit Cost of Goods Sold.
b. debit Cost of Goods Sold and credit Purchases.
c. debit Cost of Goods sold and credit Inventory.
d. make no additional entry until the end of the period.
111.
When sales of merchandise are made for cash, the transaction may be recorded
by the following entry
a. debit Sales Revenue, credit Cash
b. debit Cash, credit Sales
c. debit Sales Revenue, credit Cash Discounts
d. debit Sales Revenue, credit Sales Returns and Allowances
112.
The entry to record a sale of $900 with terms of 2/10, n/30 will include a
a. debit to Sales Discounts for $18.
b. debit to Sales Revenue for $882.
c. credit to Accounts Receivable for $900.
d. credit to Sales Revenue for $900.
113.
A sales invoice is prepared when goods
a. are sold for cash.
b. are sold on credit.
c. sold on credit are returned.
d. are sold on credit or for cash.
114.
The Sales Returns and Allowances account is classified as a(n)
a.
b.
c.
d.
asset account.
contra asset account.
expense account.
contra revenue account.
115.
The entry to record the return of goods from a customer would include a
a. debit to Sales Revenue.
b. credit to Sales Revenue.
c. debit to Sales Returns and Allowances.
d. credit to Sales Returns and Allowances.
116.
The entry to record the receipt of payment within the discount period on a sale
of $500 with terms of 2/10, n/30 will include a
a. credit to Sales Discounts for $10.
b. debit to Sales Revenue for $490.
c. credit to Accounts Receivable for $500.
d. credit to Sales Revenue for $500.
117.
The entry to record a sale of $500 with terms of 2/10, n/30 will include a
a. credit to Sales Discounts for $10.
b. debit to Cash for $490.
c. credit to Accounts Receivable for $500.
d. credit to Sales Revenue for $500.
118. The collection of an $800 account within the 2 percent discount period will
result in a
a. debit to Sales Discounts for $16.
b. debit to Accounts Receivable for $784.
c. credit to Cash for $784.
d. credit to Accounts Receivable for $784.
119.
A sales invoice is used as documentation for a journal entry that requires a
a. debit to Cash and a credit to Sales Revenue.
b. debit to Sales Returns and Allowances and a credit to Accounts
Receivable.
c. debit to Accounts Receivable and a credit to Sales Revenue.
d. debit to Cash and a credit to Sales Returns and Allowances.
120.
If a customer agrees to retain merchandise that is defective because the seller
is willing to reduce the selling price, this transaction is known as a sales
a. discount.
b. return.
c. contra asset.
d. allowance.
121.
When goods are returned that relate to a prior cash sale
a. the Sales Returns and Allowances account should not be used.
b. the Cash account will be credited.
c. Sales Returns and Allowances will be credited.
d. Accounts Receivable will be credited.
122.
The Sales Returns and Allowances account does not provide information to
management about
a. possible inferior merchandise.
b. the percentage of credit sales versus cash sales.
c. inefficiencies in filling orders.
d. errors in filling customers.
123.
A Sales Returns and Allowances account is not debited if a customer
a. returns defective merchandise.
b. receives a credit for merchandise of inferior quality.
c. utilizes a prompt payment incentive.
d. returns goods that are not in accordance with specifications.
124.
As an incentive for customers to pay their accounts promptly, a business may
offer its customers
a. a sales discount.
b. free delivery.
c. a sales allowance.
d. a sales return.
125.
The credit terms offered to a customer by a business firm were 2/10, n/30,
which means
a. the customer must pay the bill within 10 days.
b. the customer can deduct a 2% discount if the bill is paid between the 10th
and 30th day from the invoice date.
c. the customer can deduct a 2% discount if the bill is paid within 10 days of
the invoice date.
d. two sales returns can be made within 10 days of the invoice date and no
returns thereafter.
126.
A sales discount does not
a. provide the purchaser with a cash saving.
b. reduce the amount of cash received from a credit sale.
c. increase a contra revenue account.
d. increase an operating expense account.
127.
Anderson Inc. sells $600 of merchandise on account to Baltic Company with
credit terms of 2/10, n/30. If Baltic Company remits a check taking advantage
of the discount offered, what is the amount of Baltic Company's check?
a. $588
b. $600
c. $540
d. $560
128.
Aber Company sells merchandise on account for $1,500 to Borth Company
with credit terms of 2/10, n/30. Borth Company returns $250 of merchandise
that was damaged, along with a check to settle the account within the discount
period. What is the amount of the check?
a.
b.
c.
d.
$1,220
$1,230
$1,225
$1,125
129.
Casin Company sells $800 of merchandise on account to Delta Exploration
with credit terms of 2/10, n/30. If Delta Exploration remits a check taking
advantage of the discount offered, what is the amount of Delta Exploration's
check?
a. $560
b. $784
c. $720
d. $640
130.
Which sales accounts normally have a debit balance?
a. Sales discounts
b. Sales returns and allowances.
c. both (a) and (b).
d. Neither (a) and (b).
131.
Fehr Company sells merchandise on account for $2,500 to Kelly Company
with credit terms of 2/10, n/30. Kelly Company returns $500 of merchandise
that was damaged, along with a check to settle the account within the discount
period. What is the amount of the check?
a. $2,450
b. $2,460
c. $2,000
d. $1,960
132.
Piper Company sells merchandise on account for $1,800 to Morton Company
with credit terms of 2/10, n/30. Morton Company returns $600 of merchandise
that was damaged, along with a check to settle the account within the discount
period. What entry does Piper Company make upon receipt of the check?
a. Cash
1,200
Accounts Receivable
1,200
b. Cash
Sales Returns and Allowances
Accounts Receivable .
1,176
624
c. Cash
Sales Returns and Allowances
Sales Discounts
Accounts Receivable
1,176
600
24
1,800
d. Cash
1,764
Sales Discounts
36
Sales Returns and Allowances
Accounts Receivable
1,800
600
1,200
133.
The collection of a $900 account beyond the 2 percent discount period will
result in a
a. debit to cash for $882.
b. debit to Accounts Receivable for $900.
c. debit to Cash for $900.
d. debit to Sales Discounts for $18.
134.
The collection of a $500 account beyond the 2 percent discount period will
result in a
a. debit to Cash for $490.
b. credit to Accounts Receivable for $500.
c. credit to Cash for $500.
d. debit to Sales Discounts for $10.
135.
Which of the following would not be classified as a contra account?
a. Sales Revenue
b. Sales Returns and Allowances
c. Accumulated Depreciation
d. Sales Discounts
136.
Which of the following accounts has a normal credit balance?
a. Sales Returns and Allowances
b. Sales Discounts
c. Sales Revenue
d. Cost of Goods Sold
137.
With respect to the income statement
a. contra revenue accounts do not appear on the income statement.
b. sales discounts increase the amount of sales.
c. contra revenue accounts increase the amount of operating expenses.
d. sales discounts are included in the calculation of gross profit.
138.
When a seller records a return of goods, the account that is credited is
a. Sales Revenue.
b. Sales Returns and Allowances.
c. Merchandise Inventory.
d. Accounts Receivable.
139.
The respective normal account balances of Sales, Sales Returns and
Allowances, and Sales Discounts are
a. credit, credit, credit.
b. debit, credit, debit.
c. credit, debit, debit.
d. credit, debit, credit.
140.
Rains Company is a furniture retailer. On January 14, 2012, Rains purchased
merchandise inventory at a cost of $36,000. Credit terms were 2/10, n/30. The
inventory was sold on account for $60,000 on January 21, 2012. Credit terms
were 1/10, n/30. The accounts payable was settled on January 23, 2012 and the
accounts receivables were settled on January 30, 2012. Which statement is
correct?
a. Cash flows were affected on January 14 and January 21.
b. Gross profit percentage is 60%.
c. On January 30, 2012, customers should remit cash in the amount of
$59,400.
d. There is not enough information available to answer this question.
141.
Which statement is incorrect?
a. The sales account is used to record the sales of goods held for resale to
customers.
b. Sales discounts are recorded as debits to the sales account.
c. The sales account is a revenue account.
d. The sales account has a normal credit balance and is closed at the end of
the accounting period.
142.
Indicate which one of the following would not appear on both a single-step
income statement and a multiple-step income statement.
a. Gross profit
b. Operating expenses
c. Sales revenues
d. Cost of goods sold
143.
The form of income statement that derives its name from the fact that the total
of all expenses is deducted from the total of all revenues is called a
a. multiple-step statement.
b. revenue statement.
c. report-form statement.
d. single-step statement.
144.
Gross profit does not appear
a. on a multiple-step income statement.
b. on a single-step income statement.
c. to be relevant in analyzing the operation of a merchandising company.
d. on either a multiple-step or single-step income statement.
145.
Gross profit equals the difference between sales and
a. operating expenses.
b. cost of goods sold.
c. net income.
d. cost of goods sold plus operating expenses.
146.
Positive operating income will result if gross profit exceeds
a. costs of goods sold.
b. selling expenses.
c. cost of goods sold plus operating expenses.
d. operating expenses.
147.
What is the term applied to the excess of sales over the cost of goods sold?
a. Net sales
b. Income from operations
c. Net income
d. Gross profit
148.
Expenses that are associated with sales are classified as
a. general expenses.
b. other expenses.
c. selling expenses.
d. administrative expenses.
149.
Which of the following is not a true statement about a multiple-step income
statement?
a. Operating expenses are often classified as selling and administrative
expenses.
b. There may be a section for non-operating activities.
c. There may be a section for operating assets.
d. There is a section for cost of goods sold.
150.
An advantage of the single-step income statement over the multiple-step form
is
a. the amount of information it provides.
b. its comprehensiveness.
c. its simplicity.
d. its use in computing ratios.
151.
Income from operations appears on
a. both a multiple-step and a single-step income statement.
b. neither a multiple-step nor a single-step income statement.
c. a single-step income statement.
d. a multiple-step income statement.
152.
Income from operations is gross profit less
1. operating expenses and other expenses and losses.
2. operating expenses plus other revenues and gains.
3. operating expenses.
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. both 1 and 2
153.
Multiple-step income statements show
a. gross profit but not income from operations.
b. neither gross profit nor income from operations.
c. both income from operations and gross profit.
d. income from operations but not gross profit.
154.
Interest expense would be classified on a multiple-step income statement
under the heading
a. Other expenses and losses
b. Other revenues and gains
c. Selling expenses
d. Cost of goods sold
155.
Gross profit for a merchandising concern is net sales minus
a. operating expenses.
b. cost of goods sold.
c. sales discounts.
d. cost of goods available for sale.
156.
The sales revenues section of an income statement for a retailer would not
include
a. Sales discounts.
b. Sales.
c. Net sales.
d. Cost of goods sold.
157.
The operating expenses section of an income statement for a merchandising
company would not include
a. Freight-out.
b. Utilities expense.
c. Cost of goods sold.
d. Insurance expense.
158.
Indicate which one of the following would appear on the income statement of
both a merchandising company and a service company.
a. Gross profit
b. Operating expenses
c. Sales revenues
d. Cost of goods sold
159.
Gross profit does not appear
a. on a merchandising company income statement.
b. on a service company income statement.
c. to be relevant in analyzing the operation of a merchandising company.
d. on the income statement if the periodic inventory system is used because it
cannot be calculated.
160.
Financial information is presented below:
Operating Expenses
$ 45,000
Sales Revenue
150,000
Cost of Goods Sold
90,000
Gross profit would be
a. $105,000.
b. $ 45,000.
c. $ 60,000.
d. $ 15,000.
161.
Financial information is presented below:
Operating Expenses
Sales Revenue
Cost of Goods Sold
The gross profit rate would be
a. .60.
b. .10
c. .30.
d. .40.
$ 45,000
150,000
90,000
162.
Financial information is presented below:
Operating Expenses
$ 45,000
Sales Revenue
150,000
Cost of Goods Sold
90,000
The profit margin ratio would be
a. .70.
b. .10.
c. .30.
d. .40.
163.
Financial information is presented below:
Operating Expenses
$ 21,000
Sales Returns and Allowances
7,000
Sales Discounts
3,000
Sales Revenue
150,000
Cost of Goods Sold
105,000
Gross profit would be
a. $42,000.
b. $35,000.
c. $38,000.
d. $45,000.
Financial information is presented below:
Operating Expenses
$ 21,000
Sales Returns and Allowances
7,000
Sales Discounts
3,000
Sales Revenue
150,000
Cost of Goods Sold
105,000
The gross profit rate would be
a. .30.
b. .25.
c. .75.
d. .27.
164.
165.
Financial information is presented below:
Operating Expenses
$ 21,000
Sales Returns and Allowances
7,000
Sales Discounts
3,000
Sales Revenue
150,000
Cost of Goods Sold
105,000
The profit margin ratio would be
a.
b.
c.
d.
.16.
.14.
.09.
.10.
166.
Financial information is presented below:
Operating Expenses
$ 45,000
Sales Returns and Allowances
13,000
Sales Discounts
6,000
Sales Revenue
160,000
Cost of Goods Sold
77,000
The amount of net sales on the income statement would be
a. $154,000.
b. $141,000.
c. $160,000.
d. $166,000.
167.
Financial information is presented below:
Operating Expenses
$ 45,000
Sales Returns and Allowances
13,000
Sales Discounts
6,000
Sales Revenue
160,000
Cost of Goods Sold
77,000
Gross Profit would be
a. $77,000.
b. $70,000.
c. $64,000.
d. $83,000.
168.
Financial information is presented below:
Operating Expenses
$ 45,000
Sales Returns and Allowances
13,000
Sales Discounts
6,000
Sales Revenue
160,000
Cost of Goods Sold
77,000
The gross profit rate would be
a. .45.
b. .55.
c. .50.
d. .54.
169.
Financial information is presented below:
Operating Expenses
$ 45,000
Sales Returns and Allowances
13,000
Sales Discounts
6,000
Sales Revenue
160,000
Cost of Goods Sold
77,000
The profit margin ratio would be
a. .454.
b. .119.
c. .238.
d. .135.
170.
Financial information is presented below:
Operating Expenses
$ 35,000
Sales Returns and Allowances
12,000
Sales Discounts
3,000
Sales Revenue
140,000
Cost of Goods Sold
80,000
The amount of net sales on the income statement would be
a. $128,000.
b. $125,000.
c. $140,000.
d. $137,000.
171.
Financial information is presented below:
Operating Expenses
$ 35,000
Sales Returns and Allowances
12,000
Sales Discounts
3,000
Sales Revenue
140,000
Cost of Goods Sold
80,000
Gross profit would be
a. $45,000.
b. $48,000.
c. $60,000.
d. $57,000.
172.
Financial information is presented below:
Operating Expenses
$ 35,000
Sales Returns and Allowances
12,000
Sales Discounts
3,000
Sales Revenue
140,000
Cost of Goods Sold
80,000
The gross profit rate would be
a. .64.
b. .43.
c. .36.
d. .32.
173.
Financial information is presented below:
Operating Expenses
$ 35,000
Sales Returns and Allowances
12,000
Sales Discounts
3,000
Sales Revenue
140,000
Cost of Goods Sold
80,000
The profit margin ratio would be
a. .43.
b. .20.
c. .07.
d. .08.
174.
What is an advantage of using the multiple-step income statement?
a. It highlights the components of net income.
b. Gross profit is not a separate item.
c. It is easier to prepare than the single-step income statement.
d. Net income will be higher than net income computed using the single-step
income statement.
175.
For a jewelry retailer, which is an example of Other Revenues and Gains?
a. repair revenue
b. unearned revenue
c. gain on sale of display cases
d. discount received for paying for merchandise inventory within the
discount period
176.
When using a periodic inventory system, which statement concerning the
computation of cost of goods sold is correct?
a. The amount of ending inventory is determined on the last day of the
accounting period.
b. Cost of Goods Available for Sale includes net purchases plus the ending
inventory.
c. Purchases represent cash paid for purchases during the accounting period.
d. Freight in is ignored.
177.
When using the periodic inventory system, which of the following is not a step
in determining cost of goods purchased?
a. Add freight in.
b. Subtract purchase returns and allowances.
c. Subtract cost of ending inventory.
d. All of these are necessary steps.
178.
At the beginning of the year, Uptown Athletic had an inventory of $400,000.
During the year, the company purchased goods costing $1,500,000. If Uptown
Athletic reported ending inventory of $600,000 and sales of $2,000,000, their
cost of goods sold and gross profit rate would be
a. $900,000 and 65%
b. $1,300,000 and 35%
c. $900,000 and 35%
d. $1,300,000 and 65%
179.
At the beginning of the year, Wildcat Athletic had an inventory of $200,000.
During the year, the company purchased goods costing $700,000. If Wildcat
Athletic reported ending inventory of $300,000 and sales of $1,000,000, their
cost of goods sold and gross profit rate would be
a. $400,000 and 60%
b. $600,000 and 40%
c. $400,000 and 40%
d. $600,000 and 60%
180.
During the year, Megan’s Pet Shop’s merchandise inventory decreased by
$20,000. If the company’s cost of goods sold for the year was $300,000,
purchases would have been
a. $320,000.
b. $280,000.
c. $260,000.
d. Unable to determine.
181.
During the year, Sarah’s Pet Shop’s merchandise inventory decreased by
$30,000. If the company’s cost of goods sold for the year was $450,000,
purchases would have been
a. $480,000.
b. $420,000.
c. $480,000.
d. Unable to determine.
182.
The amount of cost of good available for sale during the year depends on the
amounts of
a. beginning merchandise inventory and cost of goods sold.
b. beginning merchandise inventory, net cost of purchases, and ending
merchandise inventory.
c. beginning merchandise inventory, cost of goods sold, and ending
merchandise inventory.
d. beginning merchandise inventory and net costs of purchases.
183.
Which of the following is not considered in computing net cost of purchases?
a. Purchases returns and allowances
b. Purchases
c. Freight paid on purchased goods
d. Freight paid on goods shipped to customers
184.
Assume Grammar Company uses the periodic inventory system and has a
beginning merchandise inventory balance of $5,000, purchases of $75,000,
and sales of $125,000. Grammar closes its records once a year on December
31. In the accounting records, the merchandise inventory account would be
expected to have a balance on December 31 prior to adjusting and closing
entries that was
a. equal to $5,000.
b. more than $5,000.
c. less than $5,000.
d. indeterminate.
185.
All of the following statements are true regarding the periodic inventory
system except:
a. Under the periodic inventory system, the balance of cost of goods sold is
calculated at the end of the period.
b. Under the periodic inventory system, the balance in ending inventory is
calculated at the end of the period.
c. Using the periodic inventory system affects the balance sheet contents
differently than when the perpetual system is used.
d. Under the periodic system, a company uses separate accounts to record
freight costs, returns, and discounts.
186.
Sampson Company's accounting records show the following for the year
ending on December 31, 2012.
Purchase Discounts
$ 5,600
Freight-in
7,800
Purchases
300,010
Beginning Inventory
23,500
Ending Inventory
28,800
Purchase Returns
6,400
Using the periodic system, the cost of goods purchased is
a. $280,210
b. $304,210
c. $308,610
d. $295,810
187.
Sampson Company's accounting records show the following at the year ending
on December 31, 2012.
Purchase Discounts
$ 5,600
Freight-in
7,800
Purchases
300,010
Beginning Inventory
23,500
Ending Inventory
28,800
Purchase Returns
6,400
Using the periodic system, the cost of goods sold is
a. $301,110
b. $298,910
c. $290,510
d. $309,510
188.
Which of the following provides the best rationale regarding analysts' views
about the information value of the gross profit rate versus the gross profit
amount?
a. The gross profit amount is more informative than the gross profit rate
because it is a dollar amount rather than a ratio.
b. The gross profit amount is less informative than the gross profit rate
because the latter presents a meaningful relationship between gross profit
and net sales.
c. The gross profit amount is more informative than the gross profit rate
because the gross profit rate is only used to describe a few industries while
the gross profit amount is universally used.
d. The gross profit amount is more informative than the gross profit rate
because high volume operations are able to calculate the gross profit rate
but not the gross profit amount.
189.
Bolton Company's gross profit rate last year was 32.0% and this year it is
28.4%. Which of the following would not be a possible cause for this decline
in the gross profit rate?
a. Bolton must pay higher prices to suppliers without passing these costs on
to customers.
b. Bolton may have begun selling products with a higher markup.
c. Bolton's average margin between selling price and inventory cost is
decreasing.
d. Bolton may have seen a decline in total gross profit while maintaining net
sales.
190.
Haverty Industries increased its gross profit rate from 18.4% in 2011 to 23.7%
in 2012. Which of the following would be a possible explanation for this
change?
a. Haverty's global sourcing efforts at the beginning of 2012 resulted in a
lower cost of merchandise sold.
b. Haverty's new profit lines with lower margins in 2012 became a larger
component of their sales.
c. Haverty increased its product markdowns in 2012.
d. Haverty's average margin between the selling price and the inventory cost
decreased over this two-year period.
191.
Which of the following statements is true regarding the profit margin ratio?
a. The profit margin ratio can be improved by decreasing the gross profit rate
and/or controlling operating expenses and other costs
b. The profit margin ratio does not vary across industries.
c. Discount stores with high merchandise turnover generally have higher
profit margins.
d. If the profit margin ratio has a higher value, this suggests favorable return
on each dollar of sales.
192.
The gross profit rate is computed by dividing gross profit by
a. sales.
b. cost of goods sold.
c. net sales.
d. operating expenses
193.
A decline in a company’s gross profit could be caused by all of the following
except
a. selling products with a lower markup.
b. clearance of discontinued inventory.
c. paying lower prices to its suppliers.
d. increasing competition resulting in a lower selling price.
194.
If Hostell Company has net sales of $500,000 and cost of goods sold of
$300,000, Hostell’s gross profit rate is