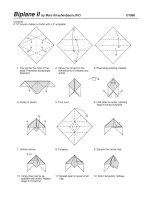
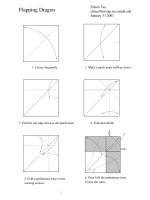
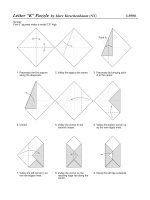
Tài liệu Monopoly docx
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (359.79 KB, 55 trang )
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
Chapter 12
Chapter 12
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
◆
Monopoly is a market structure in
which a single firm makes up the entire
supply side of the market.
◆
Monopoly is the polar opposite of
perfect competition.
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
◆
Monopolies exist because of barriers to
entry into a market that prevent entry by
new firms.
◆
Barriers to entry include legal barriers
such as a patent, and natural barriers
such as the size of the market that can
support only one firm.
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
◆
A competitive firm is too small to affect
the price.
◆
It does not have to take into account the
effect of its output decision on the price it
receives.
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
◆
A competitive firm's marginal revenue is
the market price.
◆
A monopolistic firm’s marginal revenue is not equal to
its price – it takes into account that in order to sell
more it has to decrease the price of its product.
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
◆
Monopolist as the only supplier faces
the entire market demand curve.
◆
Therefore, monopoly demand is
downward sloping, and to increase
output the firm must decrease its price.
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
◆
How much should a monopoly produce
to maximize its profit?
●
and!
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
"
◆
As in perfect competition, profit for the
monopolist is maximized at a point
where MC = MR.
◆
What is different for a monopolist –
marginal revenue does not equal price;
marginal revenue is below price.
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
#
◆
If a monopolist deviates from the output
level at which marginal cost equals
marginal revenue, profits will fall.
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
$
!"
!"
#
#
$%&'%#&()
$%&'%#&()
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
*
*
◆
The marginal revenue curve tells us the
additional revenue the firm will get from
an additional unit of output.
◆
The marginal cost curve is a graph of
the change in firm’s total cost as it
changes output.
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
*
*
◆
To determine the profit-maximizing price
and quantity:
●
% & MC =
MR'(%
●
%)* (
%% )%
!
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
*
*
◆
If MR > MC, the monopolist gains profit
by increasing output.
◆
If MR < MC, the monopolist gains profit
by decreasing output.
◆
If MC = MR, the monopolist is
maximizing profit.
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
*
*
◆
The MR = MC condition determines the
quantity a monopolist produces.
◆
That quantity determines the price the
monopolist will charge.
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
+
+
◆
Profit-maximizing output for the
monopolist, like profit maximizing
output for the competitor in a perfectly
competitive market is where MC = MR.
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
+
+
◆
Because the monopolist’s marginal
revenue is below its price, its
equilibrium output is less than, and
price is higher than that of a perfectly
competitive market.
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
*#
*#
,+-%&'%#&(.
,+-%&'%#&(.
$36
30
24
18
12
6
0
6
12
Price
MC
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
D
MR
Monopolist
price and
output
$!$
!
Perfectly competitive
price and output
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
"
,+
,+
◆
Draw the firm's marginal revenue curve.
◆
Determine the output the monopolist will
produce by the intersection of the MC
and MR curves.
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
#
,+
,+
◆
Determine the price the monopolist will
charge for that output by finding where
the quantity line intersects the demand
curve.
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
$
,+
,+
#
#
,+-%&'&$#&/0
,+-%&'&$#&/0
MR
D
MC
Quantity
Price
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
,+
,+
#
#
,+-%&'&#&/0
,+-%&'&#&/0
MR
D
MC
Quantity
Price
Q
M
P
M
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
,+
,+
◆
Determine the average cost at the
profit-maximizing level of output.
◆
Determine the monopolist's profit (loss)
by subtracting average total cost from
average revenue (P) at that level of
output and multiply by the chosen
output.
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
◆
A monopolist can make a profit, it can
break even, or it can incur a loss.
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
1+
1+
#
#
,+-%&'2#&/%
,+-%&'2#&/%
Price
ATC
MC
Quantity
P
M
0
MR
D
Q
M
Profit
C
M
A
B
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
1+
1+
34#
34#
,+-%&'5#&/&
,+-%&'5#&/&
Price
MC
Quantity
P
M
0
MR
D
Q
M
ATC