Nucleic acids DNA & RNA
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (72.99 KB, 11 trang )
Nucleic Acids
Nucleic Acids
DNA & RNA
DNA & RNA
What are they ?
What are they ?
The 4
The 4
th
th
type of
type of
macromolecules
macromolecules
The chemical link between
The chemical link between
generations
generations
The source of
The source of
genetic
genetic
information in chromosomes
information in chromosomes
What do they do ?
What do they do ?
Dictate
Dictate
amino-acid
amino-acid
sequence in proteins
sequence in proteins
Give information to
Give information to
chromosomes, which is then
chromosomes, which is then
passed from parent to
passed from parent to
offspring
offspring
What are they made of ?
What are they made of ?
Simple units called
Simple units called
nucleotides
nucleotides
,
,
connected in long chains
connected in long chains
Nucleotides
Nucleotides
have 3 parts:
have 3 parts:
1- 5-Carbon sugar (pentose)
1- 5-Carbon sugar (pentose)
2- Nitrogen containing base
2- Nitrogen containing base
(made of C, H and N)
(made of C, H and N)
3- A phosphate group ( P )
3- A phosphate group ( P )
The P groups make the links that unite
The P groups make the links that unite
the sugars (hence a “
the sugars (hence a “
sugar-phosphate
sugar-phosphate
backbone”
backbone”
Two types of Nucleotides
Two types of Nucleotides
(depending on the sugar they
(depending on the sugar they
contain)
contain)
1-
1-
Ribonucleic acids (RNA)
Ribonucleic acids (RNA)
The pentose sugar is
The pentose sugar is
Ribose
Ribose
(has a
(has a
hydroxyl group in the 3
hydroxyl group in the 3
rd
rd
carbon
carbon
OH
OH
)
)
2-
2-
Deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA)
Deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA)
The pentose sugar is
The pentose sugar is
Deoxyribose
Deoxyribose
(has just an
(has just an
hydrogen
hydrogen
in the same
in the same
place
place
H)
H)
D
D
eoxy = “minus
eoxy = “minus
oxygen”
oxygen”
DNA
DNA
Nucleotides
Nucleotides
Composition (3 parts):
Composition (3 parts):
1-
1-
D
D
eoxyribose sugar (
eoxyribose sugar (
no O
no O
in 3
in 3
rd
rd
carbon)
carbon)
2- Phosphate group
2- Phosphate group
3-
3-
One of 4 types of bases
One of 4 types of bases
(all containing
(all containing
nitrogen):
nitrogen):
- Adenine
- Adenine
-
-
Thymine (Only in DNA)
Thymine (Only in DNA)
- Cytosine
- Cytosine
- Guanine
- Guanine
RNA
RNA
Nucleotides
Nucleotides
Composition ( 3 parts):
Composition ( 3 parts):
1-
1-
R
R
ibose sugar (
ibose sugar (
with O
with O
in 3
in 3
rd
rd
carbon)
carbon)
2- Phosphate group
2- Phosphate group
3-
3-
One of 4 types of bases
One of 4 types of bases
(all
(all
containing nitrogen):
containing nitrogen):
- Adenine
- Adenine
-
-
Uracyl (only in RNA)
Uracyl (only in RNA)
- Cytosine
- Cytosine
- Guanine
- Guanine
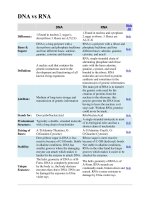
DNA
DNA
vs
vs
RNA
RNA
DNA
DNA
1-
1-
D
D
eoxyribose sugar
eoxyribose sugar
2- Bases: Adenine,
2- Bases: Adenine,
Thymine
Thymine
, Cytosine,
, Cytosine,
Guanine
Guanine
3-
3-
Double
Double
-stranded helix arrangement
-stranded helix arrangement
RNA
RNA
1-
1-
R
R
ibose sugar
ibose sugar
2- Bases: Adenine,
2- Bases: Adenine,
Uracyl
Uracyl
, Cytosine,
, Cytosine,
Guanine
Guanine
4-
4-
Single
Single
stranded
stranded
The Double Helix (DNA)
The Double Helix (DNA)
Structural model:
Structural model:
Model proposed by Watson & Crick, 1953
Model proposed by Watson & Crick, 1953
Two sugar-phosphate strands, next to each
Two sugar-phosphate strands, next to each
other, but running in opposite directions.
other, but running in opposite directions.
Specific Hydrogen bonds
Specific Hydrogen bonds
occur among bases
occur among bases
from one chain to the other:
from one chain to the other:
A T
A T
,
,
C G
C G
Due to this specificity, a certain base on one
Due to this specificity, a certain base on one
strand indicates a certain base in the other
strand indicates a certain base in the other
.
.
The 2 strands intertwine, forming a double-
The 2 strands intertwine, forming a double-
helix that winds around a central axis
helix that winds around a central axis
How DNA Works
How DNA Works
1-
1-
DNA stores genetic information in
DNA stores genetic information in
segments called
segments called
genes
genes
2- The DNA code is in
2- The DNA code is in
Tri
Tri
plet Codons
plet Codons
(short sequences of
(short sequences of
3
3
nucleotides
nucleotides
each)
each)
3- Certain
3- Certain
codons
codons
are translated by
are translated by
the cell into
the cell into
certain Amino
certain Amino
acids.
acids.
4. Thus, the
4. Thus, the
sequence of nucleotides
sequence of nucleotides
in
in
DNA indicate a
DNA indicate a
sequence of Amino
sequence of Amino
acids
acids
in a
in a
protein
protein
.
.