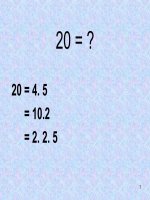Bài giảng Phân tích dịch màng bụng, màng phổi màng tim
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (1.82 MB, 15 trang )
PHAN TICH DICH MANG BUNG,
MANG PHOI & MANG TIM
TS. Nguyễn Hữu Tùng
|. Serous Fluid (Dich mang)
1. Definition
o
o
gq
ce
pericardium
Cavity: Pericardial, pleural, peritoneal
Serous membrane:
Perietal membrane
- Visceral membrane
Parietal pleural
Pleural cavity
with serous fluid
o
Serous fluid
Visceral pleural
Diaphragm
Front
Right
Peritoneum
Left
spine
Back
Retroperitoneum
|. Serous Fluid
2. Formation
Parietal
Visceral
pleura
Chest
\
wall
o
Serous
fluids
ultrafiltrates
no
are
of
additional
formed
plasma,
,
as
with
material
\
pleura
Pleural
\
space
yf
|
|
Lung
Systemic
_
contributed by the mesothelial
cells that line the membranes.
o
Production and reabsorption
are subject to hydrostatic and
colloidal pressures from the
capillaries
that
serve
the
cavities
and
the
capillary
permeability
———
b
pressure }
|
—
pressure
+30
Intrapleural
pressure
_
—-11
-
Intrapleural
pressure
+З>
+10-—©
Lymphatic system
‘Table 13-1
on ae
Pleural Effusion?
| Pathologic Causes
of Effusions
1. Increased capillary hydrostatic pressure
Congestive heart failure
Salt and fluid retention
2. Decreased oncotic pressure
Nephrotic syndrome
Hepatic cirrhosis
Malnutrition
Protein-losing enteropathy
3. Increased capillary permeability
Microbial infections
Membrane inflammations
Malignancy
4. Lymphatic obstruction
Malignant tumors, lymphomas
Infection and inflammation
Thoracic duct injury
3. Specimen Collection and Handling
o
Method: Needle aspiration
o Volume
o
Sample care and Caution
4. Transudate and Exudate
sr); (2&-9e
ŒZ
Laboratory Differentiation of Transudates
and Exudates
Appearance
Transudate
Exudate
Clear
Cloudy
Fluid:serum protein ratio
<0.5
>0.5
Fluid:serum LD ratio
<06
>0.6
WEC count
<1000/uL.
> 1000/pL
Spontancous clotting
No
Possible
Pleural fluid cholesterol
<45-60 mg/dL
>45-60 mg/dL
Pleural fluid:serum cholesterol ratio
<0.3
>0.3
Pleural fluid:bilirubin ratio
<06
>0.6
>1.1
<1.1
Serum-ascites albumin gradient
5. General Laboratory procedures
Serous fluid examination:
Transudate and Exudate
Cell count
Chemistry
¢ Microbiology
Cytology
ll. Pleural Fluid
1.
Pleural Fluid
2.
Pleural Effusion
3.
Examination of Pleural fluid
3. Examination of Pleural fluid
3.1. Appearance
.
_ Table 13-3
~
SU
Correlation of Pleural Fluid Appearance and
DR
Appearance
Disease
Clear, pale yellow
Normal
Turbid, white
Microbial infection
Bloody
Hemothorax
Hemorthagic effusion, pulmonary embolis, tuberculosis,
(tuberculosis)
malignancy
Brown
Rupture of amoebic
liver abscess
Black
Aspergillous
Viscous
Malignant mesothelioma (increased hyaluronic acid)
3. Examination of Pleural fluid
3.2. Hematology test
t3
(2/22
ve
Mesothelial cells
Plasma cells
Malignant cells
Significance of Cells
Seen in Pleural Fluid
Normal and reactive forms have no
Tuberculosis
Primary adenocarcinoma
and smallcell carcinoma
3. Examination of Pleural fluid
3.3. Chemistry test
Â
Glucose
ô
pH
Â
Adenosine deaminase
Â
Amylase
Â
Triglyceride
_ Table 1327.
Significance of Chemical
Testing of Pleural Fluid
Test
Significance
Glucose
Decreased in rheumatoid inflammation
Decreased in purulent infection
Lactate
Elevated in bacterial infection
Triglyceride
Elevated in chylous effusions
pH
Decreased in pneumonia not responding to antibiotics
Markedly decreased with esophageal
rupture
ADA
Elevated in tuberculosis and malignancy
Amylase
Elevated in pancreatitis, esophageal
rupture, and malignancy
3. Examination of Pleural fluid
3.4. Microbiologic and Serologic Tests
PLEURAL FLUID TESTING ALGORITHM
Fluid protein and LD
‘
Fluid: serum protein >0.5
Fluid: serum LD >0.6
Appearance
Fluid LD > 2/3 upper normal serum value
Milky
Any positive
Ị
Ỉ
Yos
Hematocrit | | Triglycerides
Transudate
Glucose
ADA
WBC/Diff
Amylase
pH
TT}
|
ADA >40U/L
WBC/Diff
Amylase
ll. Pericardial Fluid