Giáo trình phân tích ứng dụng cấu tạo và công dụng của máy in theo setup catridge p9 docx
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (398.1 KB, 5 trang )
LAN Response
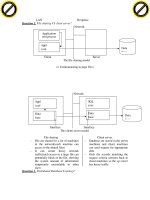
Question 2. File sharing VS client server?
Network
Client Server
The file sharing model
<< Continuousting to page 28>>
Network
Interface Interface
The client/ server model
File sharing
-
File are shared for a lot of machines
in the network(each machine can
access to the shared files)
- It can create heavy network
traffic(each access to a large file can
potentially block of the file, showing
the system amount of information
temporarily unavailable to other
user)
Client server
- Database are stored in the server
machines and client machines
can send request for appropriate
data
- Only the records matching the
request criteria raresent back to
client machines so the sys never
has heavy traffic
Question 3. Distributed Database Topology?
Application
tool process
Appl
icati
Data
base
Appl
icati
Data
base
Data
base
Data
base
SQL
exec
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m
- With distributed processing system, user can access data, that is located among a
number of physically separate servers. It provides user with a globol view of the
data.
- With distributed database, the problems with implementing still exists.
- Developing distributed database application requires extensive planning to
anticipate the many complex possibilities.
- For a large number of transactions travelling across the network the capacity of
communication lines and the possible impact a system must be carefully
considered.
Chapter 12: THE TCP/IP PROTOCOL SUITE.
Question 1. The OSI model? <Open System Interconnection>
- OSI model, adopted in 1983 by IOS <International Organization Standardization>,
which is a framework for defining standards for linking hetenogenerous computer
- The communication function are pastitioned into a vertical set of layers. Each
layer performs are lated subset of the functions required to communicate with
other sys
- The OSI layers
Physical: concerned with transmission of unstructured bit
stream over physical medium, deals with the mechinical,
electrical, functional, and procedual characteristrics to
access the physical medium
Data link: provides for the reliable transfer of information
across the physical link, send blocks of data with the
necessary synchronization, error control, and flow control.
Network: provides upper layers with independence from the
data transmission and switching technologies used to
connect systems, responsible for establishing, maintaining
and terminating connections
Transport: provides rediable, transparent transfer of data
between end points, provide end_to_end error recovery and
flow control.
Session: provides the control structure for communicaton
between applications, establishes, manages, and terminates
connections between cooperating applications.
Presentation: provide independence to the application
processes from difference in data representation(syntax)
Application: provide access to the OSI environment for
users and also propvides distributed information services
User oriented Application Users of transport
Presentation service
End to end Session
connection oriented Transport
Network
Point to point Data link Network service
link oriented Physical
Perspectives on the OSI architecture
Question 2. Protocols?
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m
Both OSI and the TCP/IP protocol suite deal with communications among hetrnogenerous
computers
Both are based on the concept of protocol and have many similarities
a. TCP/IP protocol architecture
TCP: Transmission Control Protocol
IP: Internet Protocol
- The TCP/IP protocol architecture is based on a view of communication that
involves three agents: processes, hosts, and networks
- Communication between processes takes place across networks to which the hosts
are attached
- A network need only be concerned with routing data between hosts, as long as the
hosts agree how to direct data to processes
- It is natural to organize protocols into four layer
i. Network access layer: contains those protocols that provide access to a
communication network
ii. Internet layer consists of the procedures required to allow data to traverse multiple
networks between hosts
iii. Host_host layer: containts protocol entities with the ability to deliver data between
two processes on different host computers
iv. Process/ application layer: contains protocols for resource sharing and remote
access
b. Operation of TCP/IP
Application Application
TCP TCP
OS
IP OS
IP
Network access
protocol 1
Network access
protocol 2
Network 1 Network 2
Netwo
Communications using the TCP/ IP protocol architecture
NAP: Network Access Points
- IP is implemented in all of the end systems it keeps track of blocks of data to
ansure that all are dilivered veliably to the appropriate application
- For successful communication, every entity in the over all sys must have a unique
address, two level of addressing are needed
Global Internet Address(for communication)
Ports(for service)
Try your best, you will get the best!
IP
NAP
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m
Contents
BOOK I: Computer system fundamentals.
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER 2
CHAPTER 2 MICROPROCESSOR 3
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m
CHAPTER 3 BATCH/ ONLINE AND REAL TIME PROCESSING SYSTEM 4
CHAPTER 4 PRINTERS AND TERMINALS 5
CHAPTER 5 DATA STORAGE MEDIA 7
CHAPTER 7 COMPUTER FILES 9
CHAPTER 8 DIRECT ACCESS FILE ORGANIZATION AND STRUCTURES 10
CHAPTER 11 INTRODUCTION TO ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE 12
CHAPTER 12 EXPERT SYSTEMS 12
BOOK II: Computer systems architecture.
CHAPTER 1 NUMBER BASES 13
CHAPTER 2 NUMBER BASES 13
CHAPTER 3 TYPES OF INSTRUCTION AND ADDRESSING 16
CHAPTER 4 PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES 18
CHAPTER 6 TRANSLATORS 20
CHAPTER 7 SOFTWARE 21
CHAPTER 8 MEMORY MANAGEMENT 23
CHAPTER 9 NETWORKING 23
CHAPTER 10 DATA COMMUNICATION 26
CHAPTER 11 DISTRIBUTED PROCESSING 27
CHAPTER 12 THE TCP/IP PROTOCOL SUITE 28
Cách xóa Windows Media Player 11
1a. Cho ai cài wmp11 đàng hoàng:
Code:
"C:\Program Files\Windows Media Player\Setup_wm.exe" /Uninstall
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m