Giáo trình phân tích ứng dụng cấu tạo và công dụng của máy in theo setup catridge p8 pptx
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (202.06 KB, 5 trang )
3. Worst fit policy, an incoming job is placed in the largest possible hole of free
space
Question 4. Types of scheduling?
- Scheduling of job is also an important part of any OS. It involves keeping
track of and deciding which job is to be executed
- Types of scheduling
Deadline scheduling
First in first out scheduling(FIFO)
Round robin scheduling
Shortest job first(STF) scheduling
Shortest remaining time scheduling(SRT)
- More details about types of scheduling
In deadline scheduling certains are scheduled to be
completed by a specifir time or deadline. Deadline
scheduling can be very complex requiring substantial
overhead in resource management
FIFO scheduling: processes are dispatched according to
their arrival time in the ready queue. This type of
Round robin scheduling is similar to FIFO scheduling but
the difference lies in that each job is given a slice of CPU
time
SJF scheduling: shorter jobs are more favoured than longer
one. SJF selects job that ensures the next jobs will complete
& leave the sys as soon as possible
SRT scheduling: the job will the smallest estimated
remaining run time is executed first. In SRT, a running job
may be replaced by a new job with a shorter estimated run
time
Chapter 8: MEMORY MANAGEMENT.
Question 1. Virtual Storage System?
- Instructions and data not currently needed might even be stored on the disk
and thus free up a portion memory
- Virtual storage systems have evolved to meet these needs. Virtual storage
systems allow programs to be as large as necessary, even larger that the
physical storage capacity of the computer
- Translating the user’s view of the program into the physical reality of
computer storage is one of the major task performed by virtual memory OS
like IBM’s MVS and digital VMS
- Virtual storage system included non paged systems
Paged systems
Chapter 9: NETWORKING.
Question 1. Types of network layout?
Network topology is the name given to the various types of network layout
1. Start network(or centralised network)
- This network all communications go through a central node
Node A
Node D
Central(Hub) active
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m
Passtive
Node C
Node B
- The centra of star network is the hub which performs the function of
routing msgs and data within the network
- The hub manages & senvices all incoming and outgoing communication
traffic. It’s also provide info services from a large central data bases
2. Mesh network (or distributed network)
- This network may be fully connected or partially connected
A
E B
D C
- Data can get from one node to another node via different route
- Multi point to point
3. Ring network( or loop network)
A B
D C
- Work stations connect to the ring
- More cabling requiring than BUS
- The connectors used with a lot of problem
- Cable is used UTP, STP
4. Bus network( or multidrop network)
A B
- All workstations are connected the same cable segment
- Commonly used for implomenting ethenet at 10 mbps(Mb/s)
- The cable is terminalled at each end
- Writing is normally store point to point
- A faulty cable or work station will take the entire LAN down
Question 2. Network control?
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m
1. Modems(modulation demodulation)
A telephone line B
Modem modem
Digital signal analog signal
OR
Data transmission Using a Modem
- To communicate between computers via telephone line, there is a need to
convert signals from the computer into a form suitable for transmission
over the telephone line or convert from digital signals into analogue
signals, and convert back from analogue signals to digital signals
- From source: digitals signals are converted into analogue
signals(modulation)
- At the received end analogue signals are converted back into digital
signals (demodulation)
- A device to handle modulation, demodulation process is called Modem
2. Bandwidth and Fibre Opties
The major benefits of fibre opties are:
- Fibre optic cables are much lighter and smaller in size
- Greatly increased speed in data transmission
- Greatly reliability
- Greater secerity as lines can not be tapped
3. Transmission
a. Simplex transmission
This method allows for transmission in one direction only
b. Half duplex transmission
This method means that’s data can be transmitted in both directions, but is only on
direction at a time
c. Full duplex trasmission
This method of transimission allows for transmission in both directions simultaneously
* Two modes of transmission are used when transmitting data over
communication lines. They are
asynchrorous
synchronous
Asynchronous:
- One character at a time is transmitted or received
- Each character is preceded by a start bit and a stop bit
The start bit is used to indicate or character is being sent
The stop bit is used to indicate the end of the character
- Asynchronous transmission is used for low speed devices
Direction of transmission
Com
pute
Com
pute
Mod
Mod
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m
S S S S
T T T T
A 11000001 O 1111111 A 11000010 O
R P R P
T T
Synchronous:
- The speed of transmission is much faster
- Transmission groups of character can be send down the line without the
start and stop bits
Direction of transmission
000111000001011100000011
Question 3. LAN_Local Area Networks?
Def: A LAN is a communication network in that connects office
equipment to provide a variety of data communication service which
features high transmission rates and low error rates
Characteristics:
- Utilisation of some type of switching topology
- Locality restricted to a few miles or in the same bulding
- Proprietorship by a single organisation
Features:
- LAN is after used in offices & it connects of fire equipment to provide a
variety of data communication. Service with light transmission rate and
low errors rate
- The majorities of LANs are connected by coxial cable, and the
protocol(rule for communication) is very simple
Three other important aspects of LANs:
- Acess method (protocol)
Central control
CSMA_CD
Empty slot access
Token access/token passing
LAN transmission modes:
There are 2 main types of LAN transmission modes
a. Baseband transmission: is essentially & binary method, each bit being
represented by one of two states of an electric pulse passing through the
network.
Baseband is nevertheless suitable for most LANs, and is the mode
employed by Ethernet and Cambridge Ring network
b. Broadband transmission: the data is modulates into a carrier wave.
Broadband transmission has a much greater band width than baseband, it
can transmit sth like ten times as much in a given time
LAN is one of the distributed processing designs
- LAN are considered loosely coupled system processors are located in
separate machines and communicate at relatively low speeds
- LAN is the means by which distribution takes places, regardless of what
are distributed
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m
Chapter 10: DATA COMMUNICATIONS.
Question 1. Write a short note of?
1. Communication is an extensive subject in its own right, encompassing not only
data transmission but also sound and video transmission via telephone lines, radio
links and satellite links.
2. Multiplexing is a means of combining together data from several sources so that it
can be transmitted along one comminication line
3. Front – end processing: A front – end processor is usually a minicomputer or a
microcomputer interposed between the main computer and the multiplexor
Its purpose is to relieve the host computer from the bunden of communications
housekeeping
4. Concentrators are device used to gather the bit from each terminal or group of
terminal and hold them on buffer store unit until there are sufficient to justify
forward transmission
5. Protocol is an “agreement” where by devices can communicate is a fully
understand manner
6. Multidrop line<multipoint line> has several terminals on concentrator attached to
it
7. Distributed data processing sys is one of which interconnected points at which
processing power and storage capacity are availble
Question 2. Fibre Optics?
Fibre optics is that data and other information is transmitted in the form of light
through very fine glass fibres
Ads:
- High bandwidth eg data transmission capacity
- Low cross – talk eg interference between adjacent fibres
- Low attenuation eg loss of signal strength
- Freedom from interference from external electrical and electromagnetic
equipment
- High reliability
- Safe because no heat, sparks or electrical voltages are created
- Economic because glass is loss expensive than copper
Chapter 11: DISTRIBUTED PROCESSING.
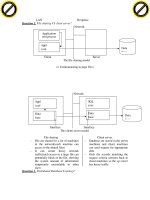
Question 1. Client/ Server Model?
- It’s common way to employ distributed processing that is client/server
architecture which splits into components
- Server store & main palates the actual data & provide secenity, losting function
transaction logging recovery capabilities
- Client/ server model seems like PC lan each server support more users
- Data request in form of SQL(structure quenf language) command travel across the
network from client to server
Client Server
Database
Request
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m
Click to buy NOW!
P
D
F
-
X
C
h
a
n
g
e
V
i
e
w
e
r
w
w
w
.
d
o
c
u
-
t
r
a
c
k
.
c
o
m