giáo trình bài giảng về polystyrene
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (527.6 KB, 17 trang )
POLYSTYRENE
Polystyrene được biết đến năm 1845 khi đốt nóng styren
trong ống thuỷ tinh ở nhiệt độ 200
o
C, tổng hợp được nhờ
nhiệt phân các hydro cacbon thì loại nhựa này mới được
tổng hợp.
Styrene, một sản phẩm phụ dầu khí, là nguyên liệu
chính từ đó polystyrene được tổng hợp. Styrene, lần đầu
tiên được sản xuất thương mại trong năm 1930, đã đóng
một vai trò quan trọng trong Thế chiến II trong việc sản
xuất cao su tổng hợp.
Sử dụng trong sản xuất các sản phẩm như phụ tùng ô
tô, linh kiện điện tử, thuyền, phương tiện giải trí, và
cao su tổng hợp.
2
3
Expanded polystyrene packaging
A polystyrene yogurt container
Bottom of a vacuum-formed cup;
note how fine details such as the
glass and fork food contact
materials symbol and the resin
identification code symbol are
easily molded
4
CD case made from general purpose
polystyrene (GPPS) and high impact
polystyrene (HIPS)
Disposable polystyrene razor
The resin identification code
symbol for polystyrene
TÍNH CHẤT VẬT LÝ
- Nhựa cứng trong suốt, không có mùi vị, cháy cho ngọn lửa
không ổn định.
- Nhựa dễ tạo màu, hình thức đẹp, dễ gia công bằng phương
pháp ép và ép phun (nhiệt độ gia công vào khoảng 180 -
200
o
C).
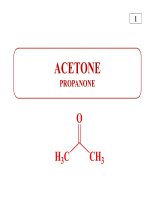
- Hòa tan trong hydrocacbon thơm, dẫn xuất halogen, ester,
ketone.
- Không hòa tan trong hydrocacbon mạch thẳng, rượu thấp
(rượu có độ rượu thấp), ether, phenol, acid acetic và nước.
- Bền trong dung dịch kiềm, acid sulfuric, phosphoric và boric
với bất kỳ nồng độ nào. Bền với acid chlorhydride 10 - 36%,
acid acetic 1-29%, acid formic 1-90% và các acid hữu cơ
khác. Ngoài ra PS còn bền với xăng, dầu thảo mộc và các
dung dịch muối.
- Phân hủy dưới tác dụng của acid nitric đậm đặc và các chất
oxy hóa khác.
5
6
Tỷ trọng
/
0.90458
Độ nhớt cP 0.75
Nhiệt độ sôi C 145.2
Nhiệt độ nóng chảy ºC -30.6
Nhiệt độ bùng cháy ºC 31.0
Nhiệt độ bắt lửa ºC 34.0
Nhiệt độ bay hơi ºC 86.9
Nhiệt cháy cal/g 10.04
Nhiệt trùng hợp cal/g 168
Giới hạn nổ trong không khí %vol. 1.1 – 6.1
Độ co sau khi trùng hợp %vol. 17.0
TÍNH CHẤT CƠ HỌC
• Phụ thuộc vào mức độ trùng hợp.
• PS có trọng lượng phân tử thấp, rất giòn và có độ
bền kéo thấp. Trọng lượng phân tử tăng lên thì độ
bền cơ và nhiệt tăng, độ giòn giảm đi. Nếu vượt quá
mức độ trùng hợp nhất định thì tính chất cơ học lại
giảm.
• Giới hạn bền kéo sẽ giảm nếu nhiệt độ tăng lên. Độ
giãn dài tương đối sẽ bắt đầu tăng khi đạt tới nhiệt độ
80
o
C. Vượt quá nhiệt độ đó PS sẽ trở nên mềm và
dính như cao su.
Do đó PS chỉ được dùng ở nhiệt độ thấp hơn
C.
7
TÍNH CHẤT CƠ HỌC
8
Tỷ trọng 1,05 - 1,06 g/cm
3
Khi kéo 35-59 N/mm
2
Khi nén 56-133 N/mm
2
Khi uốn 80-112 N/mm
2
Module đàn hồi kéo (2,8 - 3,5).10
3
N/mm
2
Độ dai va đập 12-20 kJ/m
2
Độ cứng Brinel 140 - 160 HB
Nhiệt độ làm việc lâu dài 70 - 75
o
C
TỔNG HỢP POLYSTYRENE
This reaction is carried out in an inert organic solvent
environment, which provides the reaction medium for this
cationic polymerization reaction.
The different methods available for styrene polymerization
are:
1. Solution (bulk) polymerization
2. Emulsion polymerization
3. Suspension polymerization
9
HC
CH
2
CH
H
2
C
CH
H
2
C
CH
H
2
C
CH
H
2
C
n
Initiators: The initiators generally used are benzoyl
peroxide and t-butylhydroperoxide.
Catalyst: A catalyst is used to control the reaction rate.
The catalysts are usually peroxides. The most common
ones are benzoyl, diacetyl, lauroyl, caproyl and tert-
butyl peroxides. Their concentration varies from 0.1-0.5%
of the monomer charged. The ratio of monomer to
dispersing medium is between 10 and 40%.
- 90-95
o
C.
10
O
O
O
O
Benzoyl peroxide
H
3
C
C
H
3
C
CH
3
O
OH
tert-Butyl hydroperoxide
Stabilizing agent: To keep the drops at proper size, a
stabilizing agent is added. The stabilizing agents are often
insoluble inorganic such as calcium carbonate, calcium
phosphates or bentonite clay. They are present in small
amount than the suspending agents.
Suspending agent: To aid in the formation of the
proper size drops a suspending agent is added. Some
typical suspending agents are methylcellulose, ethyl
cellulose and polyacrylic acids. Their concentration in the
suspension is between 0.01-0.5% of monomer charged.
11
INEOS Technologies
The INEOS polystyrene (PS) technology is based on a
bulk continuous process giving access to a wide range
of general purpose polystyrene (GPPS) also known as
crystal polystyrene and high-impact polystyrene
(HIPS), which incorporates rubber particles for high
shock absorbance.
12
INEOS Technologies
Rubber dissolving (1) Polybutadiene rubber, in bale form, is chopped
into crumbs. To enhance dissolving, preheated styrene is introduced into
a high-shear in-line mixer. This operation allows high capacity
production of dissolved rubber at a high rubber concentration.
Prepolymerization (4) Prepolymerization is conducted in the fist two
reactors that are CSTR-type with proprietary agitator designs.
Prepolymerization may be thermally or chemically initiated depending
on the desired product. For HIPS, this is a critical phase of the process
since this is where the rubber morphology and physical properties of the
resultant product are controlled.
Polymerization (5) Polymerization is conducted in the last reactor,
which is a plug-flow type of proprietary design allowing high efficiency
heat removal and temperature control on viscous media.
Devolatilization (7) This is a two-step operation under high vacuum, to
remove lights components such as unreacted styrene and diluent, which
is enhanced with the addition of a foaming agent in the second stage. The
stripping effect of the foaming agent reduces the residual monomer
content to as low as 200 ppm.
13
INEOS Technologies
Recycle recovery (8) Unreacted styrene and diluents from the
devolatilization operation are distilled and recycled to the
front end of the process. The distillation of the recycle stream
ensures that only styrene and ethylbenzene are recycled back
to the fist pre-polymerization reactor to ensure that the styrene
purge is minimized and the oligomer concentration in the
reactor system is kept low. Two purges are provided to control
the accumulation of light and heavy components in the PS
unit: a lights purge consisting of styrene and ethylbenzene and
a heavy purge consisting of oligomers and other heavy
organics. These purges are used as fuel for the hot oil heater.
Finishing This section consists of fitering the polymer melt,
extruding it into strands, cutting them into cylindrical pellets
of prescribed size, sorting the resultant pellets from fies and
oversize pellets and conveying the product pellets to a quality
control silo.
14
INEOS Technologies
15
INEOS Technologies
Process features
• Proprietary rubber grinding and dissolving unit
• Catalyzed polymerization:
- Enhanced polymer/rubber grafting
- Reduced oligomers byproducts
• Proven proprietary prepoly reactor design allowing
temperature and morphology control
• Proprietary plug-flow reactor design => outstanding
temperature control, highest conversion rates, rubber
morphology preservation
• High-effiiency devolatilization system
• LP steam generation system
• Ongoing development of new and improved formulations.
16
INEOS Technologies
17