Business plan for viet world company in 2011 2013
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (1.84 MB, 69 trang )
HO CHI MINH CITY OPEN UNIVERSITY
SOLVAY BRUSSELS SCHOOL
NGUYEN DIEU PHUONG
BUSINESS PLAN FOR VIET WORLD COMPANY
IN 2011 - 2013
MASTER PROJECT
MASTER IN BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION
(PART-TIME)
Tutor’s Name: HOANG THI PHUONG THAO
Ho Chi Minh City
(2010)
STUDENT DECLARATION
I certified that the attached project is my own work. Materials withdraw from
different sources have been acknowledged according to unit-specific requirements for
referencing purspose.
NGUYEN DIEU PHUONG
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I would like to express my sincere thanks to professors of Solvay Business School –
University of Brussels for the profound knowledge that they managed to impart to me, for
the time they had to spend to answer my questions. My thanks are reserved for my
husband, Mr. Nguyen Van Thien for his advice on conducting choosing the topic and his
idea contributing. I would also like to extend my gratitude to Mr.Vijay S Satwani who
helped me to complete the questionnaires and all distributors in Dubai who spent their time
completing the questionnaires.
My deepest gratefulness goes to Prof. Hoang Thi Phuong Thao, lecturer of the University
of Economics and also my tutor, who enthusiastically helped me from project outline until
to project finishing.
Las but not least, I would also like to thank Mr. Serge Bywaski and Ms. Bui Phan Bao
Tran, our helpful co-ordinators, who have been with us throughout the course, for their
enthusiastic connection between the class and Solvay professors.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
EXERCUTIVE SUMMARY
I.
II.
III.
IV.
V.
INTRODUCTION
1.1. Background
1
1.2. Research objectives
2
1.3. Research methodology
2
1.4. Scope of research
3
1.5. Structure of project
3
LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Market analysis theory
6
2.2 Marketing mix
8
2.3 SWOT analysis
10
BUSINESS DESCRIPTION
3.1. Textile industry overview
12
3.2. Company description
14
3.2.1. Company history and Current status
14
3.2.2. Company organization
16
3.2.3. Products
19
MARKET ANALYSIS
4.1. Market Overview
22
4.2. Distribution Patterns
23
4.3. Main Competitors
25
4.4. Viet World’s SWOT Analysis
27
STRATEGY AND IMPLEMENTATION
5.1 Business Strategy
29
5.1.1 Business Objectives
30
5.1.2 Market Segment and Targeting
30
5.1.3 Market Positioning
31
5.1.4 Marketing mix strategy
32
VI.
5.2. Sales forecast
34
5.3. Action Programs
35
5.4. Company Organization Improvement
39
FINANCIAL PLAN
6.1. Operating forecast
41
6.2. Projected Profit and Loss
42
6.3. Projected Balance Sheet
43
6.4. Projected Cash Flow
43
CONCLUSION
44
REFERENCES
45
APPENDIX
46
ABRIVIATIONS
GCC countries: Gulf Cooperation Council countries
UAE: United Arabica Emirates
VITAS: Vietnam Textile and Apparel Association
VINATEX: Vietnam Textile and Garment Group
GDP: Gross Domestics Product
SWOT: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threads
MOQ: Minimum Order Quantity
LCL: Less Container Load
FCL: Full Container Load
CIF: Cost, Insurance and Freight
LC: Letter of Credit
TT: Telegraphic Transfer
D/P: Documents against Payment
IATF - International Autumn Trade Fair
LIST OF TABLE AND FIGURE
TABLES
Table 3.2.1 - Exporting sales of Viet World Company in 2005 - 2010
Table 5.2. - Export sales forcast for three years 2011-2013
Appendix 3- GDP of Middle East Countries
Appendix 4 - Schedule of Action Plan 2011
Appendix 5 - Export monthly sales forcast in 2011
Appendix 6 - Projected Income statement in 2011
Appendix 7 - Projected Balance sheet at 31 Dec, 2011
Appendix 8 - Projected Cash Flow Statement in 2011
FIGURES
Figure 1 – Project Structure
Figure 2 – Viet World Company Organization
Figure 3 – Fabric Manufacturing Process
Figure 4 – Viet World’s image to distribution channel
Figure 5 – Basic of pricing
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Vietnam's textile industry has increased significantly in the last ten years as it was growing
year by year with very high percentage. According to Vietnam Business & Economy News
– For year 2010, despite the fluctuations on global and domestic markets, the Vietnamese
textile industry continues to grow fast which helps Vietnam remain in top 10 world
garment export countries. Export revenue of the Vietnamese textile in 2010 can surge to
US$11 billion, an increase of 23-24 percent over same period last year and 5 percent above
this year’s set plan. This was an extremely hard target to achieve, according to experts.
Textiles will become the country’s largest export sector of Vietnam.
The industry helps generate jobs with good income for many workers. The increase in the
number of orders and quantity of raw materials as well as the raise in workers’ salaries
helped boost the productivity. According to experts, importers want to place orders for
textile products of Vietnam because they trust the quality and price of products, the
reliability of the delivery offered by Vietnamese producers. This is why, many of them
have switched from China to Vietnam. Vietnam has exported textile and garment products
to many countries as United Stated, Japan, Europe, Korea, Singapore, Malaysia, Middle
East…
Dubai is a business hub of Middle East and a huge of many kinds of goods are imported to
Dubai before delivered to other countries in Middle East, Africa, Europe…The $4 billion
plus Dubai textile mart, which sits at the center of a 1.4 billion booming consumer market.
Viet World producing - trading – services Company limited is a private textile company
which is specialized in various types of fabrics as Jacquard, Dobby… The Company has
the independent import and export right. Almost of fabric products of the company are
exported to Middle East, Singapore, Thailand... According to figures of General Statistic
Office of Vietnam based on the first eleven months of 2010, Middle East has a low
percentage of export revenue of the Vietnamese textile. But this market is the main market
of Viet World Company in last few years. For this market, Viet World has exported fabrics
to Dubai and from this business hub goods will be delivered to other countries of Middle
East such as Iran, Kuwait, Egypt and also Africa.
When doing business in Dubai, Viet World Company has found an opportunity for two
kinds of fabric products that the company can develop its business in this market. These
are black and white fabric for traditional clothes of Islam men and women of Middle East
countries. Because developed countries don’t focus to low and medium cost of these
products anymore as they keep the premium segmentation. Viet World has decided to plan
for exporting these products to Dubai and they started to sell some black fabric products to
Dubai in September 2010. Beside of develop new products, Viet World also focus to
improve quality of their products. Although Viet World is established in 2005, the
company didn’t have any Business plan. So, I would like to concentrate to Dubai market
for how to develop Viet World business with launching their new products to this market.
Data, information will collected from website of Government of Dubai, Dubai Economic
Council, website of Government Statistic of Vietnam, data of Viet Word’s documentations.
Beside of it, the primary research was done through sending questionnaire to fifteen key
distributors in Dubai and interview two of them by phone. I also carry out in-depth
interview three key persons of Viet World Company, Chief of Executive, Sales Manager
and Chief of Accounting and Human Department. This primary research has objective to
analysis Dubai textile market in details which concerned to black and white fabric products
for making traditional clothes of Islam women and men. From the results I got I would like
to propose a Business plan for Viet World Company in 2011-2013.
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background:
Viet World producing - trading – services company limited is a company engaged in trading,
which specialized in fabrics producing for oversea and domestic market. The Company has the
independent import and export right. Almost of fabric products of the company are exported to
Middle East, Singapore, Thailand... Thanks to high quality and competitive price of products
as well as thoughtful services, the company has prestigious and good corporations with
customers at abroad.
Among the oversea markets above, Middle East is the core market of Viet World Company as
the sales come from this market obtained more than 90 percent of export sales in last few
years. Dubai is a business hub of Middle East and a huge of many kinds of goods are imported
to Dubai before delivered to other countries in Middle East, Africa, Europe…The $4 billion
plus Dubai textile mart, which sits at the center of a 1.4 billion booming consumer market
extending from the CIS (Commonwealth of Independent States) to Africa and the Indian
subcontinent, has emerged as one of the most modern and profitable trading points in this
region's commercial map.
On process doing business in Dubai, Viet World has found an opportunity for two kinds of
fabric products that the company can develop its business in this market. These are black and
white fabric for traditional clothes of Islam men and women of Middle East countries. As the
demands of these products are very huge and the market of them are stable, not changing
much. Other thing, developed countries don’t focus to low and medium cost of these products
anymore as they keep the premium segmentation. Viet World has decided to plan for
exporting these products to Dubai and they started to sell some black fabric products to Dubai
in September 2010.
Although Viet World was established in 2005 and has exported their products to foreign
countries about five years but they didn’t have any Business plan for the company. One of the
2
greatest challenges for most organizations in today’s dynamic and competitive business
environment is to uncover new ways to measure and manage their own performances. So a
Business plan is really necessary for Viet World Co. as they have changing in their strategy,
directions in business in this time. A business plan will define the structure of the company
and the objective of the business activity. It contains a market analysis and details of strategic
marketing, management structure, personnel and finance. When properly conceived, it acts as
a valuable tool.
1.2 Research objectives:
This research has following objectives analysis Dubai textile market in details which
concerned to black and white fabric products for making traditional clothes of Islam women
and men. And from this to suggest a Business plan for Viet World Company in 2011-2013.
The research questions for this project are:
1. How is about market situation of Dubai textile market in general? How is about market size,
market trends of the market?
2. What are characteristics of black and white fabric products for this market?
3. How are the main competitors in this market?
4. How should business plan for Viet World be developed to gain more market share in the
next three years?
1.3 Research methodology:
“Research done with intention of applying the results to solving specific problems currently
being experienced in the business is called applied research” (Robert Y.Cavana 2001, p.12).
For applied research, there are two methods: quantity research and qualitative research.
In this project, qualitative method is applied to examine by interviewing and sending
questionnaire to target group who are wholesalers specialize in doing business for black and
white fabrics in Dubai.
Information will be gathered through:
- Secondary data: be collected from statistic figures of website of Government of Dubai,
Dubai Statistic Center, website of Textile Industry’s Reports of Viet Nam and in the World,
3
newspapers and magazines of Textile industry, website of General Statistic Office of Vietnam.
Information were collected such as economic index for market situation
- Primary data: collect information from a group of fifteen key distributors in Dubai who were
specialized in business for black and white fabrics for traditional clothes of Islam by in-depth
interview and sending questionnaire to them.
In-depth interview and discussion with the Chief of Executive of Viet World Company, Head
of Sale Department and Chief of Finance and Human Resource Department.
1.4 Scope of research:
- This primary research has a scope that collection information of Dubai textile market,
specific for Black and White fabrics for making traditional clothes of Islam people.
Information of Viet World Company were collected by in-depth interview.
This research has been done from September to December 2010.
Samples of research: Fifteen distributors in Dubai and three key persons of Viet World
Company as mentioned in above.
- For fifteen distributors in Dubai: sending questionnaire to them by e-mail in September and
October. They have full filled and replied questionnaire until December. After receiving their
feedback carry out in-depth interview by phone with three key distributors for understanding
more about the market. Every interview was done in 30 – 40 minutes.
- For three key persons of Viet World: In-depth interview and discussion face-to-face in about
one hour for every interview in the Company.
1.5 Structure of project:
The project will include six chapters:
Chapter 1: Introduction. The writer will summarize the problem that Viet World is facing.
This chapter also is included objectives, methodology of research.
Chapter 2: Literature review. This chapter will review literature about market analysis,
SWOT analysis as basic things for the next parts.
Chapter 3: Business description. This chapter will give general information about textile
industry; also introduce Viet World Company business activities.
4
Chapter 4: Market analysis. From the information of market research the writer will do
market analysis, target segment analysis and the company SWOT analysis.
Chapter 5: Business Strategy and Implementation. The writer will suggest the strategy and
action plans for Viet World Company in 2011-2013.
Chapter 6: Financial Plan. This chapter will include some basic information concerned to
finance situation of Viet World.
5
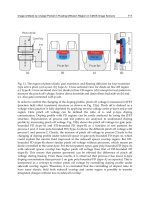
Primary research
(15 questionnaires;
In-depth interviews)
Secondary research
(Statistics figures,
articles...)
Analysis
Textile market
in Dubai
Viet World business
current situation
Competitor analysis
Recommendation Business Plan
for Viet World in three years
(2011-2013)
- Product: Sourcing and Production
- Business strategy
- Price policy
- Distribution patterns
- Promotion programs
- Company organization
- Financial plan
Conclusion
Figure 1: Project structure
Viet World
SWOT analysis
6
CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Market analysis theory
One of the most critical sections of a firm’s business plan is its manager’s market analysis.
Find out just what information managers need to know about their potential customers.
Every business plan should include market analysis. This is one of the first and most important
reasons to do a business plan. And whether everyone is just starting a new business or
reviewing an existing business, they should renew their market analysis at least every year.
Markets change--a business needs to watch for changes in its market.
The market we need to look at is our potential market, not the actual market served, the one
that's limited to our existing customers. Firm’s target market is much wider than just the
people the company already reaches.
For example, the market of a local movie theater or restaurant includes not just the people who
regularly go there but everybody who lives within driving distance. The market for a
landscaping business includes all the homes and commercial properties within a logical reach.
The market for downloadable e-books over the internet includes everyone connected to the
web. The market for personal computers includes homes, schools, businesses, and government
organizations.
It's a firm’s plan--and every plan is different--so managers need to know as much as they can
know about their target market.
2.1.1 Getting the Information
The information sources that will help managers conduct a market analysis are different for
every business plan. For example, a firm might need local information that can be get from its
local chamber of commerce. They might also need to find other government statistics, or other
commercial statistics, so they may be conducting some internet searches to track down the
information.
7
Not all the information managers need is going to be publicly available, and they may have to
settle for educated estimates. Sometimes they'll have to extrapolate information from different
sources to get the information they're seeking. A good market research may be come from
telephone directories, catalogs, industry association statistical compilations, real estate
information and density maps.
2.1.2 Segmentation
Marketers always try to divide their target market into useful slices or segments by geography,
education background, ages, income, lifestyle…. Example: a computer manufacturing
company that targeted such market segments as homes, small offices, businesses, educational
organizations, and government. Dividing the market into these segments helped the company
address the more specific market needs, media, pricing patterns and decision criteria in each of
their different market segments.
Segmentation helps firms target specific people with specific messages and helps them focus
on user needs. Families might need quick, consistent service while students might need latenight service. Families read the newspaper; students read posters on bookstore walls. Knowing
your market segments will help you make smart decisions when it comes to providing the
products and services that will work best for them and for communicating with them.
2.1.3 Market Size and Growth
Firm’s managers need to be able to measure and quantify their market. For example, if local
homeowners are part of their target market, then they should be able to count them. They need
to know whether they have 500 people in your market, or 200,000, or 2 billion. Be able to
show what the total market is for their business.
When it comes to market growth, managers need to think about percentage change as a market
forecast. Is the number of homeowners in the target market increasing or decreasing? By how
much per year? Market forecasts start with the total numbers of possible purchasers in each
market segment, then project percentage change over the next three to five years.
2.1.4 Market Trends
Business man needs to understand what's going on with his market. What trends and fashions
do you see having an influence on firm’s market segments? If he is selling cars, for example,
8
is there a trend that shows people responding to higher gasoline prices or more environmental
concerns? In computers, is there a trend toward more power and lower prices? How does the
increase in TV recorder equipment affect market? The questions that affect target markets will
be different for every business, and these are just examples. What's important is that as a
person creates his or her business plan, he/she become aware of the market trends that affect
his/her specific market.
2.2 Marketing mix
The marketing mix is probably the most famous marketing term. Its elements are the basic,
tactical components of a marketing plan. Also known as the Four P's, the marketing mix
elements are Price, Place, Product and Promotion.
When marketing their products firms need to create a successful mix of:
•
The right product
•
Sold at the right price
•
In the right place
•
Using the most suitable promotion.
To create the right marketing mix, businesses have to meet the following conditions:
2.2.1. Product
•
The product has to have the right features - for example, it must look good and work well.
•
The price must be right. Consumer will need to buy in large numbers to produce a healthy
profit.
•
The goods must be in the right place at the right time. Making sure that the goods arrive
when and where they are wanted is an important operation.
•
The target group needs to be made aware of the existence and availability of the product
through promotion. Successful promotion helps a firm to spread costs over a larger output.
For example, a company like Kellogg's is constantly developing new breakfast cereals - the
product element is the new product itself, getting the price right involves examining customer
perceptions and rival products as well as cost of manufacture, promotion involves engaging in
a range of promotional activities e.g. competitions, product tasting etc, and place involves
using the best possible channels of distribution such as leading supermarket chains. The
9
product is the central point on which marketing energy must focus. Finding out how to make
the product, setting up the production line, providing the finance and manufacturing the
product are not the responsibility of the marketing function. However, it is concerned with
what the product means to the customer. Marketing therefore plays a key role in determining
such aspects as:
•
the appearance of the product - in line with the requirements of the market
•
the function of the product - products must address the needs of customers as identified
through market research.
The product range and how it is used is a function of the marketing mix. The range may be
broadened or a brand may be extended for tactical reasons, such as matching competition or
catering for seasonal fluctuations. Alternatively, a product may be repositioned to make it
more acceptable for a new group of consumers as part of a long-term plan.
2.2.2. Price
Of all the aspects of the marketing mix, price is the one, which creates sales revenue - all the
others are costs. The price of an item is clearly an important determinant of the value of sales
made. In theory, price is really determined by the discovery of what customers perceive is the
value of the item on sale. Researching consumers' opinions about pricing is important as it
indicates how they value what they are looking for as well as what they want to pay. An
organization’s pricing policy will vary according to time and circumstances. Crudely
speaking, the value of water in the Lake District will be considerably different from the value
of water in the desert.
2.2.3. Place
Although figures vary widely from product to product, roughly a fifth of the cost of a product
goes on getting it to the customer. 'Place' is concerned with various methods of transporting
and storing goods, and then making them available for the customer. Getting the right product
to the right place at the right time involves the distribution system. The choice of distribution
method will depend on a variety of circumstances. It will be more convenient for some
manufacturers to sell to wholesalers who then sell to retailers, while others will prefer to sell
directly to retailers or customers.
10
2.2.4. Promotion
Promotion is the business of communicating with customers. It will provide information that
will assist them in making a decision to purchase a product or service. The razzmatazz, pace
and creativity of some promotional activities are almost alien to normal business activities.
The cost associated with promotion or advertising goods and services often represents a
sizeable proportion of the overall cost of producing an item. However, successful promotion
increases sales so that advertising and other costs are spread over a larger output. Though
increased promotional activity is often a sign of a response to a problem such as competitive
activity, it enables an organization to develop and build up a succession of messages and can
be extremely cost-effective.
2.3. SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a tool for auditing an organization and its environment. It is the first stage
of planning and helps marketers to focus on key issues. SWOT stands for Strengths,
Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats. Strengths and weaknesses are internal factors.
Opportunities and threats are external factors.
2.3.1. Strengths
A firm’s strengths are its resources and capabilities that can be used as a basis for developing
competitive advantage. Examples of such strengths included:
•
Your specialist marketing expertise.
•
A new, innovative product or service.
•
Location of company’s business.
•
Quality processes and procedures.
2.3.2. Weaknesses
The absence of certain strengths may be viewed as a weakness. For example, each of the
following may be considered weaknesses:
•
Lack of marketing expertise.
•
Undifferentiated products or services (i.e. in relation to your competitors).
•
Location of company’s business.
•
Poor quality goods or services.
11
•
Damaged reputation.
•
Damaged reputation.
2.3.3. Opportunities
The external environmental analysis may reveal certain new opportunities for profit and
growth. Some examples of such opportunities include:
•
Developing market such as the Internet.
•
Mergers, joint ventures or strategic alliances.
•
Moving into new market segments that offer improved profits.
•
A new international market.
•
A market vacated by an ineffective competitor.
2.3.4 Threats
Changes in the external environmental also may present threats to the firm. Some examples of
such threats include:
•
Shifts in consumer tastes away from the firm’s products.
•
Price wars with competitors.
•
A competitor has a new, innovative product or service.
•
Competitors have superior access to channels of distribution.
•
Emergence of substitute products
•
New regulations. Taxation is introduced on your product or service.
However, SWOT analysis can be very subjective. Two people rarely come-up with the same
final version of SWOT.
Chapter Summary
In the Chapter II, the writer has reviewed literature about market analysis such as how to
getting information, segmentation, market size and market trend. The writer also reviewed the
theory of Marketing mix, SWOT analysis. This information is basic things for the next parts.
In the next Chapter, the writer will describe the overview of textile industry, company history
and current status.
12
CHAPTER III
BUSINESS DESCRIPTION
3.1. Textile industry overview
Vietnam's textile industry has increased significantly since normalizing relationships with the
United States in the 1990's. Vietnam was granted most favored nation status (MFN) in
December 2001, which led to a dramatic reduction in import tariffs in the US market.
Vietnam's induction to the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2007 and the Vietnamese
government's strong support of the textile and garment sector have provided strong incentives
to attract foreign investors.
According to Vietnam Business and Economic News on 31 December 2010 - Despite the
fluctuations on global and domestic markets, the Vietnamese textile industry continues to
grow fast which helps Vietnam remain in top 10 world garment export countries. Export
revenue of the Vietnamese textile in 2010 can surge to US$11.2 billion, an increase of 23-24
percent over same period last year and 5 percent above this year’s set plan. This was an
extremely hard target to achieve, according to experts. December will be the sixth successive
month that export revenue from garments exceeds US$1 billion, said Le Van Dao, Deputy
Head of the Vietnam Textile and Apparel Association (Vitas). This means that the net profit
for the whole industry will increase by 18 percent to over US$4.5 billion. Textiles will become
the country’s largest export sector in this 2010.
According to the article by Mr. Tielman Nieuwoudt, on 19 November 2009 - In the textile
industry, companies are increasingly looking for lower cost countries that can provide
outsourcing opportunities. The rising cost of land and labour are diminishing China's labour
cost advantage and Vietnam is increasingly seen as a low cost sourcing alternative to China.
Estimates are that wage levels in Vietnam are about one third of those in China's coastal
region. Companies that are chasing lower labour costs are increasingly moving production to
Vietnam. In a 2008 Booz Allen Hamilton survey 88 percent of companies originally chose
China for its lower labour costs. Of the companies surveyed, 55 percent believe China is
13
losing its competitive edge to countries such as Vietnam. The survey also indicated that 63
percent named Vietnam as their top low cost sourcing alternative to China. However, costs
may be rising and low cost labour is hardly a competitive advantage in the long term. Labour
cost keeps changing and today's low cost location is not necessarily tomorrow's viable
outsourcing location. As labour costs increased, manufacturing was later moved to South
Korea and Taiwan. When labour cost increased in South Korea and Taiwan, it was moved to
China and later also to Vietnam. Justin Wood, a Director of the Economist Intelligence Unit
Corporate Network in Singapore makes the point that in the last 15 years Vietnam has moved
from a low to a middle income country. The move towards a middle income will likely put
additional pressure on Vietnam's low cost labour status.
The manufacturing advantages in Vietnam go beyond labour cost and the country has some
competitive advantages as Vietnam has very good embroidery skills and needle work. A lot of
designers and manufacturers need embroidery skills and Vietnam has kept in touch with its
traditional roots. Vietnam is currently a great location for smaller manufacturers as the market
is more flexible. Vietnam has higher production minimums than many other countries.
According to specialists in textile, lower minimums would allow smaller companies to source
their product in Vietnam.
For many companies outsourcing to Vietnam, intellectual property (IP) remains a concern.
Within the fashion industry, IP is not as enforced as it is within the film and music industries.
Designers can "take inspiration" and it is seen as a major driver for setting trends in the
industry. The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) has called for stricter
intellectual property enforcement within the fashion industry to better protect companies and
promote competitiveness within the textile and clothing industries.
For Vietnam to advance as an outsourcing location, the textile industry supply chain needs to
be considered. Local logistics are influenced by direct and indirect cost. In Vietnam's textile
industry raw materials are often imported, which increases cost compared with those countries
able to source locally. Managing reverse logistics can also be a challenging undertaking in
Vietnam. Procedures, processes and infrastructure are sometimes not in place to manage
repairs, returns and warranties.
14
Even with cheap labour cost, poor infrastructure remains a major barrier for entry. This is
largely due to Vietnam being in the early stages of infrastructure development.Through
assessing the overall supply chain, rather than a singular focus on labour costs, it is easier to
identify where Vietnam's opportunities and challenges lie in the textile industry. While small
scale designers and manufacturers take advantage of a flexible environment, infrastructure and
logistics processes will need further investment to make Vietnam an outsourcing destination.
3.2. Company description
Viet World Co. is a private limited company producing, trading and services of textile
products, specializing in jacquard, plain from polyester and visco, etc. These goods are made
mostly by using advanced technologies transferred from Korea.
Name and Address of the Company:
VIET WORLD COMPANY Ltd.Pte.
18 Tan Chau – Dist.Tan Binh – Ho Chi Minh City – Viet Nam
Tel.: 84 8 3 9717065 – 3 9717046
Fax: 84 8 3 9717066
3.2.1 Company History and Current status
Viet World was found in 2005 by two persons Mr. Nguyen Van Thien and Mr. Chau Van
Tuan. Both of them had knowledge and experiences in textile industry before they started up
their company.
Mr. Thien has worked for textile industry at big textile companies in Vietnam from 1993. He
is specialized in business of textile from fibers to fabrics, not only domestic market but also
for export products to other countries, especially for Middle East countries market. He had
experiences in doing textile business in Dubai and had relationship with some wholesalers of
textile products. He is CEO, the main person who runs business of Viet World Company in
last few years.
Mr. Tuan has specialized in manufacturing of fabrics; he had run his own small factory before
he and Mr. Thien cooperate to establish Viet World Company. He is a technician specialize in
fabric manufacturing.
15
In the start-up years, Viet World Co. has focused on export fabric products to Middle East
market and other countries as Thailand, Singapore. The Company has got orders from
customers and then did contract with many different manufacturers for producing. That means
Viet World had to work with many small or medium factories for sourcing.
The Company’s turnover was growing up very fast in the first three years, turnover of
exporting sales growth every year from eight to fifteen per cent.
However, there were many issues that happened in these years. Viet World can’t control
qualities of their products and sometime it can’t meet requirements of their customers. The
problem is the company doesn’t have sources of high quality fabrics as most of suppliers using
the old-fashioned technology. For getting orders as much as possible, the company has tried to
decrease the price of their products.
Other hand, they were always facing with lacking of capital and they had overcome by
borrowing debt from banks. So the company couldn’t get profit as they expected because their
finance costs was too high when they couldn’t sell their products with better prices. Beside of
these issues, due to lacking of professional management, Viet World also has faced with the
problem of high cost for administrative expenses.
In 2008, the owners of Viet World Company have decided to invest to Viet Thanh
manufacturer, to import Korea textile machines and technology. From this action, Viet World
had Agreement with Viet Thanh manufacturer that Viet Thanh will supply fabrics mainly for
Viet World Company. Viet Thanh will produce fabrics follow to requirements of Viet World’s
orders. By this way, Viet World can solve the problem of sourcing of good quality products in
this period. But Viet Thanh couldn’t supply all quantities as Viet World’s orders as their
limited productivity. And Viet World still had to use other manufacturers in two years of 2008
and 2009. For year 2010, the company focused to improve the quality of their products and
they just sold the fabrics of Viet Thanh manufacturer. The average unit price was increased, so
the turnover of 2010 was maintained while the quantity of sold goods was decreased.