Quản trị quan hệ khách hàng của các khách sạn 3 – 5 sao trên địa bàn hà nội TT TIENG ANH
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (270.78 KB, 27 trang )
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING
THUONGMAI UNIVERSITY
-------------------------
BUI THI QUYNH TRANG
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT OF 3 -5
STARS HOTELS IN HANOI
Major
: Business Trade
Code
: 934.01.21
SUMMARY OF ECONOMIC DOCTORAL THESIS
Hanoi, 2021
The work was completed at: Thuongmai University
Science instructor:
1
2
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Nguyen Viet Thai
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Cao Tuan Khanh
Review 1:
Review 2:
Review 3:
Dissertation will be protected before the dissertation review board meeting at
……………………………………………………………………………………
The dissertation can be found at:
National Library
Thuongmai University Library
LIST OF PUBLISHED SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH WORKS
OF THE AUTHOR RELATED TO THE RESEACH TOPIC
1. Nguyen Viet Thai, Bui Thi Quynh Trang (2018), “The application of IDIC
Model in customer relationship management at Tourism accommodation
Establishment of 3 stars or higher in Viet Nam”, Trade magazine Volum6,
number1 April 2018
2. Bui Thi Quynh Trang (2018), “Improving competitiveness for Vietnamese
tourist accommodation establishments”, National Scientific Conference, VCCI
December 2018
3. Bui Thi Quynh Trang (2020), “The influence of human resources on customer
relationship management at hotels in Hanoi”, National Scientific Conference
Improving the quality of tourism human resources in the context of industrial
revolution 4.0
4. Bui Thi Quynh Trang (2020), “Study the impact of customer Experience to
loyalty at hotels in Vietnam”, Trade magazine ,Volum 8, number 2 June 2020.
5. Bui Thi Quynh Trang (2020), “Building a model of the influence of technology
on the implementation of customer relationship management in hotels”,
National Scientific Conference Development of Vietnam's e-commerce in the
digital era.
6. Bui Thi Quynh Trang (2020), “Applying IPA method to evaluate customer
relationship management activities at hotels”, International conference of
young scientists in economics and business, ICYREB 2020
4
INTRODUCTION
1. Necessity
of research
Theoretically, since the 90s of the last century, the theory of CRM has
begun to form and become a scientific field of interest to many managers. With
Rabah et al. (2011) pointed out that 43% of definitions define CRM as a business
strategy, 17% as a process and 22% identify it as an application of technology. Up
to now, the concept of CRM still exists many different views and there is no
concept that is completely accepted.
To identify the components of CRM, theories used in the research include:
Resource Based View (RBV) (Halawi et al., 2005; Coltman, 2007); relationship
marketing theory (RM) (Berry, 1995; Shrivastava and Kale, 2003; Ata and Toker,
2012) and change management theory (CM) (Chen and Popovich, 2003; Kim et
al., 2004; Mendoza et al., 2007; Mohammad Almotairi, 2008). Factors affecting
CRM implementation have been considered by the researchers in relation to the
components of CRM. However, the number of studies integrating these theories
is very limited, especially in the context of the hospitality industry. Some
researchers Amoako et al. (2012); Davids (1999); Zikmund et al. (2003) have
shown that CRM is also capable of creating customer loyalty, but only a few
studies have investigated the relationship between CRM implementation and
loyalty. As for the CRM process, the studies are also diverse and there are many
different points of view.
In practical terms, under the strong influence of technology and outstanding
development, the application of information technology (IT) in management and
business has become popular and CRM is one of them. Nastaran Mohammadhossein
and Nor Hidayati (2012); Zakaria Jayam J Radha (2013), the successful of implement
CRM reduces costs, including administrative costs and customer related costs.
Because the cost of acquiring new customers is 5-6 times higher than retaining
existing customers. According to Krasnikov et al. (2009), a successful CRM
implementation on average will reduce costs by 5.4% and increase profits by 27.5%.
In addition, Chen and Popovich (2013) suggest that solving quickly, reducing the time
to respond to customer needs is considered as a criterion to evaluate the success of
CRM implementation. However, research practice also shows that about 65% of
businesses fail to implement CRM (Chen and Popovich, 2003).
In Vietnam, the hotel business is always a potential market. Hanoi, Nha
Trang, Ho Chi Minh City and Da Nang are destinations with a large supply of 3-5
stars hotels in the country. However, from the beginning of 2020 until now, the
Covid-19 pandemic has caused the hotel industry in the world in general and in
Vietnam in particular to face many difficulties.
5
From theoretical and practical awareness, with all the reasons have presented
above, research student chose the topic: "Customer relationship management of 3
-5 stars hotels in Hanoi" to research for the economics doctor thesis.
2. Research objectives
The thesis is conducted with the aim of proposing some solutions to perfect
CRM of 3-5 star hotels in Hanoi.
Based on the research objectives, the thesis identifies specific objectives including:
-
Identify the CRM theoretical basis related to the CRM process and identify the
factors influencing successful CRM implementation.
-
Describe and analyze the CRM process of some typical 3-5 stars hotels in Hanoi.
-
Test the impact of factors affecting successful CRM implementation and prove
the positive relationship between successful CRM.implementation and customer
loyalty of hotels.
-
Discuss and propose some solutions and recommendations to improve CRM of 35 stars hotels in Hanoi.
Research object and scope
Research object: Customer relationship management activities of 3-5 star hotels
in Hanoi.
- Research scope:
About the research space: Management activities and CRM processes are
using at 3-5 stars hotels in Hanoi.
Research period: secondary data on 3 - 5 stars hotels in Hanoi was collected
in the period 2016 - 2020, primary data was collected from December 2019 to
July 2020; proposed solutions for the coming years.
Research content: The thesis focuses on two research topics including:
(1) Research to describe the CRM process of typical 3-5 stars hotels in Hanoi
(Due to not being able to evaluate all hotels in the area, research student chose 3 5 stars hotels typical to focus on clearly analyzing the CRM process).
(2) Studying the factors affecting successful CRM implementation and testing the
relationship between successful CRM implementation and customer loyalty;
4. Research Methods
Stemming from the objectives, objects and research scope of the thesis, the
research student used a combination of two methods of qualitative research and
quantitative research (for details, see Chapter 2).
5. Contributions of thesis
Theoretical contributions
3.
-
6
-
-
-
-
-
The thesis has integrated research on theories of RBV, RM and CM to identify the
main components of CRM. From there, the CRM process in the hotel can be
determined based on the principles and functions of management in the business
and must show the focus on the main components of CRM that are: People,
processes and technology.
The thesis identifies a research model of factors affecting successful CRM
implementation and loyalty. These influencing factors have been identified in
relation to the CRM process and key components of the CRM relevant to the
hospitality industry context.
Through qualitative research method, the thesis has added 3 new observed
variables including: Top of management remove barriers in CRM implementation
(CK4), hotels have a measurement system and Employee Rewards (VH6),
Technology Updates System (HT6) and examines the impact relationship
between successful CRM implementation and loyalty.
Practical contributions
Through the results of analysis and evaluation of the CRM process and the
research to verify the factors affecting successful CRM implementation, test the
relationship between successful CRM implementation and customer loyalty, the
thesis has pointed out that all 6 factors: Commitment of top management, CRM
strategy, business processes, corporate culture, technology infrastructure, and
databases all positively affect successful CRM implementation. In which, the
corporate culture factor that has the strongest influence and the weakest influence
on successful CRM implementation is the database factor. The thesis also
confirms the positive relationship between successful CRM implementation and
customer loyalty.
From the research results, the thesis has proposed 03 groups of solutions to
improve CRM activities of 3 - 5 stars hotels in Hanoi: Solutions about people in
the process of implementation, business processes Business and technology help
hotels implement CRM successfully.
6. Thesis struture
In addition to the introduction, conclusion, references, appendices, the
thesis is structured into 4 chapters:
Chapter 1: Overview of research situation and theoretical basis of customer
relationship management of hotels
Chapter 2: Research Methods
Chapter 3: Analysis of the current situation of customer relationship
management of 3-5 stars hotels in Hanoi
Chapter 4: Proposing some solutions and recommendations to improve
customer relationship management of 3 -5 stars hotels in Hanoi
7
CHAPTER 1. OVERVIEW OF THE RESEARCH SITUATION AND
THEORETICAL BASIS ON CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP
MANAGEMENT OF HOTELS
1.1. Research overview
1.1.1. Customer relationship studies
In the world, there have been many different approaches to customer
relationship (QHKH). According to Shawn Grimsley and Steven Scalia (2003),
"Customer relationship is the process and way in which a business establishes
and develops in order to maintain relationships with its customers". Researches
on scientific planning focus on the existence of the scientific planning
relationship, the development process of scientific planning, Arndt (1979), Fall et
al. (2006), Heide (1994), Johanson and Mattsson (1987).
In Vietnam, studies on typical customer planning have the following
authors: Hoang Le Chi (2013), Quality of the relationship between service
providers and customers: A case study of customers in the telecommunications
service industry. Communication, Doctoral thesis, University of Economics Ho
Chi Minh City; Do Giang Nam (2015), Research on the relationship between
banks and businesses for customer relationship management at Vietnamese
commercial banks, Doctor thesis, National Economics University.
1.1.1. Research on customer relationship management
First, with defining CRM concepts and models. Researchers have given a
lot of different views about CRM. Zablah and Johnston (2004) classified the
concepts of CRM into five groups: process, strategy, philosophy, capabilities, and
technology tools. With Rabah et al. (2011), an analysis of CRM definitions
showed that 43% of definitions identify CRM as a business strategy, 17% as a
process and 22% identify it as a technology application process.
Second, about the composition of the CRM. CRM has been studied and
synthesized from different theoretical perspectives and has received considerable
attention from researchers. Theories used to identify CRM components include:
Resource-based theory (RBV) (Halawi et al., 2005; Coltman, 2007; Wang and Feng,
2012) and relationship marketing theory (Halawi et al., 2005; Coltman, 2007; Wang and
Feng, 2012) RM) (Berry, 1995; Shrivastava and Kale, 2003; Plakoyiannaki and Saren,
2006; Ata and Toker, 2012) and change management theory (CM) (Chen & Popovich,
2003; Kim et al., 2004) ; Mendoza et al., 2007; Mohammad Almotairi, 2008).
Third, discuss the CRM process. Process can be defined as the way in
which things are done in a business (Buttle, 2004; Lo, Stalcup et al., 2009), CRM
8
process is understood as the activities carried out by the business involves
customer relationship management and these activities are grouped according to a
relationship vertical perspective (Moutot & G. Bascoul, 2008).
Fourth, CRM measurement criteria. CRM is a widely studied field, most of
the studies focus on CRM implementation (Mendoza et al., 2007; Osarenkhoe
and Bennani, 2007; Reinartz et al., 2004; Rodgers and Howlett, 2000).
However, successful CRM implementation is not the end goal of the business.
According to Faed (2010), the purpose of CRM is to maintain and retain customers
and increase consumer loyalty. Kim et al. (2003) proposed a specific BSC of CRM
outcomes, capturing the various benefits of CRM. The four perspectives of the BSC
specific to CRM are: the Customer Value perspective (measures the financial benefits
obtained from the customer), the Customer Satisfaction perspective (measures the
level of satisfaction achieved by the customer). products and services), the Customer
Engagement perspective (measures operational excellence of internal processes and
omnichannel management) and the Customer Knowledge perspective (measures
analytical quality) customer knowledge and data).
Fifth, about research methods and approaches. In the studies, researchers
have approached from both perspectives of business administration (Reinart, et
al., 2004; Bull, C. 2003; Francis Buttle, 2009; Payne, 2005); and economic
management (Farris, 2010; Soudgar, 2011).
In Vietnam, research on CRM is also interested by many researchers in
terms of both theoretical and practical issues such as: Truong Dinh Chien (2013);
Vu Huy Thong, Nguyen Thi Thoa (2012); Phan Thi Thu Hoai, (2013)...
1.1.2. Studies on customer relationship management in hotels
When conducting research on CRM in hotels, researchers have built a
model of factors affecting CRM implementation such as the model of CRM
integration in hotel operations by Marianna Sigana, (2005); (Ada S. Lo et al.,
2010) with a CRM model in hotels in Hong Kong.
To measure CRM outcomes, in general, assessments of CRM outcomes are
mainly based on the effects of CRM implementation outcomes (Akroush et al.,
2011; Josiassen et al., 2014; Sin et al., 2011). et al, 2005; Wu and Chen, 2012; Wu
and Lu, 2012; Yim et al., 2004). Some researchers have noted that CRM is also
capable of generating customer loyalty (Amoako et al., 2012; Davids, 1999;
Zikmund et al., 2003). Although researchers often point out that CRM creates
loyalty, very few studies have focused on the impact of CRM on loyalty.
1.4. Gaps of research
Firstly, the number of studies integrating theories of RBV, RM, and CM in
CRM research is very limited, especially in the context of the hotel industry and
with each individual theoretical approach, the CRM main parts are defined
differently.
Second, there are many perspectives on the CRM process. The wide
difference in CRM approach makes it difficult for managers to implement the
9
CRM process in practice. Currently, there is no specific CRM implementation
process, suitable for the context of the hotel industry.
Third, the factors influencing successful CRM implementation in
enterprises have been examined in relation to CRM components and synthesized
from different theoretical perspectives and have received considerable attention.
With each theoretical point of view, the factors affecting CRM implementation
are identified differently and have not been linked with the main components of
CRM.
Fourth, Some researchers have shown that CRM is also capable of creating
customer loyalty (Amoako et al., 2012; Davids, 1999; Zikmund et al., 2003).
However, only a handful of studies have investigated the impact relationship of
successful CRM implementation on loyalty.
Fifth, the number of studies on hotel CRM is limited, and there is no
research on CRM of 3-5 stars hotels in Hanoi.
The research questions that need to be addressed in the thesis are:
(1) How is the CRM process of 3-5 stars hotels in Hanoi being
implemented?
(2) What factors affect the successful CRM implementation of 3-5 stars
hotels in Hanoi?
(3) How does successful CRM implementation affect customer loyalty of 35 stars hotels in Hanoi?
(4) What solutions should be considered to improve CRM of 3-5 stars hotels
in Hanoi?
1.2. Theoretical foundations of hotel customer relationship management
1.2.1. Research theories related to customer relationship management
1.2.1.1. Resource-based management theory (RBV)
RBV theory is used in CRM studies because according to Coltman (2010),
RBV provides a multidimensional view of CRM, it tries to link available
resources and capabilities to improve the efficiency of the business. . Various
resource-based applications have made it the dominant theoretical view in CRM.
RBV theory is often used to explain the factors affecting the use of resources by
enterprises to enhance competitive advantage and improve business performance
of enterprises.
1.2.1.2. Theory of relationship marketing (RM)
RM is recognized as the foundation of CRM (Battor, 2010; Reinartz et al.,
2004). CRM was conceived as a process for identifying customers, managing
customer insights, and developing customer relationships (Srivastava et al.,
1999). Because of the common ground between RM and CRM, they have been
referred to interchangeably in the literature (Parvatiyar & Sheth, 2000). RM is the
attitude of the organization, while CRM is the tool used to implement that
attitude. As a result, CRM has become a separate area of marketing.
1.2.1.3. Theory of change management (CM)
10
The thesis approaches CRM theory because when implementing a CRM
project, it affects all activities, functional parts of the business and the business
needs to change to match and achieve the project's goals. Armenakis and Harris
(2002), CRM implementation is based on three phases of change: readiness for
change, change implementation, and change retention. In addition, Chen and
Popovich (2003); Kim et al (2004); Mendoza et al. (2007) consider CRM as how
an organization manages its relationship with its customers, and based on CM
theory to successfully implement CRM.
Within the scope of the research, the thesis will carry out an integrated
study of 3 theories RBV, RM and CM to identify the main components of CRM
including: human resources, technology and business processes. On that basis,
the thesis will identify factors affecting successful CRM implementation and
CRM process in relation to the main components of CRM.
1.2.2. Overview of customer relationship management at hotels
1.2.2.1. Hotel customer relationship management
Customer relationship management concept
In this thesis, CRM is understood as follows: “CRM is a business strategy
that integrates processes, people and technology to understand an enterprise's
customers, enhance the value of its stakeholders, and bring benefits to customers.
profits for the business and gain customer loyalty”.
The concept of customer relationship management at the hotel
Based on the concept of CRM identified above, combined with the
characteristics of CRM in the hotel, within the scope of the thesis research, CRM
in the hotel can be understood as follows: “CRM is a strategy business strategy
that integrates processes, people, and technology to understand hotel customers,
drive hotel profitability, and gain customer loyalty.”
Benefits of customer relationship management in hotels
- Cost savings:
- Categorize customers:
- Enhance benefits for customers:
- Customer retention and customer loyalty:
- Tools to support employees to work effectively:
1.2.2.2. Hotel business
Hotel concept
Within the scope of the thesis, the author chooses to approach the concept of
hotel according to the Vietnam Tourism Law 2017: “A hotel is a tourist
accommodation establishment that ensures quality in terms of facilities, equipment
and services. necessary services to serve tourists”.
Hotel business concept
11
“Hotel business is a business activity on the basis of providing accommodation,
catering and additional services under certain conditions of facilities and service
levels in order to meet the needs of tourist for making profit”.
Characteristics of hotel business
- Customer characteristics:
- Product characteristics:
1.2.2.3. Relationship Management Customer Relationships and Loyalty
Oliver (1999, p. 34) defined loyalty as “a deeply held commitment to
rebuy or re-patronise a preferred product/service consistently in the future, thereby
causing repetitive same-brand or same brand-set purchasing, despite situational
influences and marketing efforts having the potential to cause switching behaviour”.
According to the research by Bhattacharya (2011), the implementation of CRM in
an enterprise done to reduce costs and increase the operational efficiency of the
business will lead to beneficial outcomes for the business, customers and increasing
customer base, satisfaction and loyalty.
1.2.3. Process of hotel customer relationship management
Within the scope of the thesis, the CRM process will be established based
on the process of implementation stages to ensure compliance with the principles
and functions of management in the enterprise.
Make CRM plan of hotels
Implement CRM of hotels
Estimate CRM of hotels
Hình 1.2. CRM process of hotels
Source: Author's compilation
1.2.4. Factors affecting the implementation of customer relationship
management of hotels
1.2.4.1. Factors measuring the results of implementing customer relationship
management of hotels
- Cost reduction (Nastaran Mohammadhossein & Nor Hidayati, 2012;
ZakariaJayam J Radha, 2013).
- Increase customer satisfaction (Persson, 2004; Stephen F. King & Thomas F.
Burges, 2008; Bhattacharya, 2011)
- Increase profits from customers (Persson, 2004; Armand Faganel, 2009), Jana
Urdzikova et al., 2012)
- Interact more effectively (Hsin Chang, 2007; Jana Urdzikova et al., 2012)
12
However, successful CRM implementation is not the end goal of the
business. Some researchers have noted that CRM is also capable of generating
customer loyalty (Davids, 1999; Amoako et al., 2012). Inheriting the criteria
identified from the researchers, the thesis uses three criteria to measure loyalty
including:
- Repeat purchase (RP)
- Word of mouth (WOM)
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
1.2.4.2. Determining the factors affecting the implementation of customer
relationship management of hotels
The selection of suitable influencing factors for the research scope of the
thesis will be made based on four bases as follows:
(1) The influencing factors must be generally accepted in the research
literature;
(2) The influencing factors are related to the cause of failure in CRM;
(3) The selected influencing factors must participate in the CRM process
and have a connection with the CRM components identified based on the
integration of 3 theories RBV, RM and CM;
(4) The influencing factors must be relevant to the context of Vietnam's
hospitality industry;
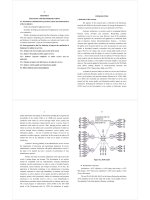
Top of management
commitment
H1
CRM strategy
H2
Business process
H3
Corporate culture
H4
Technology
infrastructure
H5
Databases
H6
Successful CRM
implementation
H7
Loyalty
Hình 1.1. Model of factors affecting successful CRM implementation
Based on the research model, the proposed research hypotheses include:
13
H1: Top of management commitment has a positive influence on successful CRM
implementation
H2: CRM strategy has a positive influence on successful CRM implementation
H3: Business processes have a positive influence on successful CRM
implementation
H4: Corporate culture has a positive influence on successful CRM
implementation
H5: Technology infrastructure has a positive influence on successful CRM
implementation
H6: Database has a positive influence on successful CRM implementation
H7: Successful CRM implementation has a positive effect on customer loyalty
The integrated framework is intended to ensure that each influencing factor
is actually relevant to the CRM and provides a clear framework for managers at
different levels to apply, maintain and control the factors. This involves the
operation and implementation of stages in the CRM process. The integrated
framework is shown as follows:
Make CRM plan
of hotels
Top of management
commitment
CRM strategy
Implement CRM
of hotels
Human
Process
Technology
Factors influencing CRM implementation: Top of
management commitment, CRM strategy, business processes,
corporate culture, technology infrastructure and databases.
Estimate CRM
of hotels
Financial results
Marketing results
CRM process integration framework, factors influencing successful CRM
implementation and key components of hotel CRM
Source: Author's compilation
14
CHAPTER 2. RESEARCH METHODS
2.1. Research process design
Define research problem
Define research goals
Determining the theoretical research model
Choosing a research method
Quantitative research
Qualitative research
Preliminary survey
(n=198 )
Interview typical 3-5 stars hotel managers
Interview experts (n=15)
Adjust and add new observed factors and variables
Analysis CRM process of typical 3-5 stars hotels
Preliminary questionnaire
Official survey (n=396)
Analysis of Cronbach's Alpha, EFA, correlation, regressio
Comment on research results, suggest and suggest solutions
Sơ đồ 2.1. Quy trình nghiên cứu
2.2. Research Methods
2.2.1. Qualitative research
2.2.1.1 Objectives of qualitative research: To test the suitability of the theoretical model
of factors affecting successful CRM implementation of 3-5 stars hotels in Hanoi.
2.2.1.2. Methods of data collection and processing
- Select the data collection method: Document research, in-depth interview.
- Objective of in-depth interview: To screen and check the suitability of
research model and process analysis CRM
- Subjects of in-depth interview: 15 experts are those who work directly or
do research related to the field of hotel, CRM.
15
With the goal of understanding and analyzing the CRM process, the
research student conducted in-depth interviews with 5 managers who are
directors of 5 typical 3 - 5 star hotels selected for research.
- Conduct in-depth interviews: Interviews are conducted directly at the
workplace of experts and managers.
2.2.1.3. Qualitative research results
Through in-depth interviews with 15 experts, 3 additional observations
were added, including: Top of management remove barriers in CRM
implementation; The hotel has a system for measuring and rewarding employees
and a system for updating advances in technology.
2.2.2. Quantitative research
2.2.2.1. Objectives of quantitative research: To test the impact of factors affecting
successful CRM implementation and the influence of successful CRM
implementation on loyalty.
2.2.2.2. Preliminary quantitative research
- Define survey sample:
(1) Identify the survey crowd: The survey subjects in the study are
managers of hotels with titles such as: Director, deputy director, department head,
department head in the hotel.
(2) Define sample framework: Including 30 3-5 stars hotels in Hanoi that
have CRM implementation. In which, there are ten of 5-stars hotels, eight of 4stars hotels and tewlve of 3-stars hotels.
(3) Sample size: According to Nguyen Dinh Tho (2011), preliminary
quantitative research is usually a survey with a convenient sample and small size
(n=100). In the case of factor analysis (EFA), Hair et al. (1998) suggested that the
sample size should be at least 50, preferably 100, and the ratio of the number of
measured variables is 5/1. That is, each measurement variable needs a minimum
of 5 observations. Therefore, the sample size for preliminary quantification was
chosen as n=198 observations.
(4) Sampling method: The research student uses the convenient sampling
method.
- Building the questionnaire: The questionnaire is designed with a structure of 3
parts: part A is the introduction, part B is the content of the survey questions focusing
on factors affecting successful CRM implementation of 3-5 stars hotels in Hanoi.
- Conducting survey: Research student used a mixture of two direct and
indirect survey methods.
- Data processing: Preliminary quantitative research was conducted to
check the validity and reliability of the questionnaire and remove inappropriate
observed variables. Preliminary assessment of the reliability and value of the
scale is done by Cronbach's Alpha reliability coefficient and EFA exploratory
factor analysis through SPSS 20.0 processing software to screen and remove
observed variables. does not meet the standard.
- Preliminary quantitative research results:
16
(1) Assess the reliability of the preliminary set of scales
Based on the results of the reliability assessment of the scales, it was found
that the scales gave Cronbach's Alpha coefficients > 0.6 and the total correlations
of the observed variables were all greater than or equal to 0.3. Therefore, these
observed variables all have the necessary confidence and are not of any kind.
(2) Preliminary EFA discovery factor
The result of this last rotation component matrix shows that the main
component matrix is stable, from the remaining 32 observed variables, they have
been grouped into 7 large factors, respectively:
- Factor 1 (factor 1): includes 6 observed variables, VH4, VH1, VH3, VH2
VH5 and VH6, this factor is named Corporate culture.
- Factor 2 includes 6 observed variables CN1, CN2, CN3, CN4, CN6 and
CN5, this factor is named Technology Infrastructure
- Factor 3 (factor 3) includes 4 observed variables including CK1, CK2,
CK3 and CK4, this factor is named Leadership commitment
- Factor 4 (factor 4) including 4 observed variables CL1, CL2, CL3 and
CL4 is named CRM Strategy
- Factor 5 (factor 5) includes 4 observed variables QT1, QT2, QT3 and
QT4 named Business Process
- Factor 6 (factor 6) includes 4 observed variables CS2, CS1, CS3 and CS4,
this factor is named Database
- Factor 7 (factor 7) includes 4 observed variables TC2, TC3, TC4 and
TC1, this factor is named as successful CRM implementation
Exploratory factor analysis EFA for dependent variable Loyalty
Because only 1 factor can be created, the rotated component matrix does not
appear, the EFA exploratory factor analysis for the loyalty factor is also satisfactory
with the indexes of 3 important variables. LTT monitoring is higher than the required
level of 0.5. This confirms that all three observed variables are grouped into one
factor. This confirms that the EFA method is suitable for the preliminary survey.
The formal research model includes six factors that influence successful
CRM implementation: Top of management commitment, CRM strategy, business
processes, Corporate culture, technology infrastructure and database.
2.2.2.3. Formal quantitative research
- Determining the survey sample: The survey subjects are executives,
directors, deputy directors, department heads, department heads in the hotel.
Overall, the study included 66 of 3-5 stars hotels in Hanoi with CRM
implementation, including 17 of 5-stars hotels, 17 of 4-stars hotels and 32 of 3-stars
hotels.
This research model has 35 observed variables so the minimum sample size
is 35 x 5 = 175, so n = 500 > 175 is appropriate.
- Building the questionnaire: The official questionnaire is also designed
with a structure of 3 parts: part A is the introduction, part B is the content of the
17
survey questions focusing on factors affecting the implement CRM successful of
3-5 stars hotels in Hanoi.
- Conduct surveys: Direct and indirect
- Data processing: At the end of the survey data collection. The collected 396
votes will be cleaned and processed using SPSS version 20.0 data analysis software.
(The official quantitative research results are shown in Chapter 3).
CHAPTER 3. RESULTS OF ANALYSIS THE CUSTOMER
RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT OF 3 -5 STARS HOTELS IN HANOI
3.1. Overview of the 3-5 stars hotel market in Hanoi
3.1.1. Overview of the operation situation of 3 - 5 stars hotels in Hanoi
According to a representative of Savills (a leading corporation providing
real estate services in the world), the hotel market in Hanoi has a promising
growth rate with the advantage of convenient traffic location. benefits, diversified
and abundant resources, high-class service quality... But along with that, the
competition will also become fiercer.
3.1.1.1. In terms of number and structure of hotels
3.1.1.2. About the form of ownership
3.1.1.3. About price and room capacity
3.1.2. Business results of 3 - 5 stars hotels in Hanoi in the period 2016 - 2020
Table 3.1. of business results of the 3-5 stars hotels market
in Hanoi in the period 2016 - 2019
ST
ĐVT 2016
2020
Targets
2017 2018 2019
T
1 Total number of tourists
Mi.
22,4 23,83 26,30 28,95 8,65
turn
International customers
Mi.
3,81 4,95 5,7 7,025 1,11
turn
Domestic customers
Mi.
18,59 18,88 20,6 21,93 7,54
turn
2 Average length of stay
Day
2,35 2,88 2,995 3,39 NA
Length of stay for international guests Day
3,11 3,64 3,67 3,92 NA
Duration of stay for domestic guests Day
1,6 2,12 2,32 2,86 NA
3 Total revenue
Bil.
68.50 70.95 77.48 103.80 26,6
3
8
0
7
2
4 Average room occupancy
%
60,05 62,28 64,86 67,9 32,7
Source: Author's compilation
NA: Not available
3.2. Status of customer relationship management process of 3 -5 stars hotels in Hanoi
3.2.1. Introduction of the case study sample
Table 3.2. List of hotels selected for a case study
18
Source: Author's compilation
3.2.2. Process of customer relationship management of typical 3-5 stars hotels
in Hanoi
3.2.2.1. CRM planning stage
According to the interview results, when determining the mission and vision
for the business strategy, the 3 - 5 stars hotels were based on specific bases such as:
The core operating purpose of the hotel, the target audience. target customers,
financial resources and market context such as: competitors, advantages of hotels...
- CRM Strategy
Table 3.3: CRM strategy of typical 3-5 stars hotels in Hanoi
Name of hotel
CRM strategy
Hacinco
CRM is just an activity in the business strategy
A25
CRM is just an activity in the business strategy
Candle
Customer-centric marketing strategy
Muong Thanh
Personalized CRM Strategy
JW Marriott Hà Personalized CRM Strategy
Noi
Source: Stage of organization and implementation of the CRM plan
In the organizational structure of typical 3-5 stars hotels in Hanoi, CRM
activities are assigned to different departments
Table 3.4. Steps to implement CRM of typical 3-5 stars hotels
Hacinco
A25
Candle
Muong Thanh JW Marriott Hà
Nội
Collect
Customer
Building and
Update and
Build and
customer
information
managing
analyze
analyze
information
collection
customer
customer
customer
activities
database:
database
portfolio
Identify and
Segmenting
Establish
Interaction
Identify the
establish
customer
relationships
management level of loyalty
interactive
markets and with customers
to maintain
with customers
activities to
establishing
and develop
develop and
relationships
relationships
maintain
with
relationships
customers
with
Maintain and Thực
hiện
Implement
Develop
customers
develop
tương tác nhằm interactions to relationships
relationships duy trì và phát maintain and with customers
with
triển mối quan
develop
customers:
hệ với khách relationships
19
Resolve
complaints
hàng
Assign
responsibility
for ensuring
CRM
implementation
with
customers
Customer
Lifecycle
Management
Cultural
organization to
ensure CRM
implementatio
n
CRM Evaluation Stage
Table 3.5. Evaluation of CRM of typical 3-5 star hotels
in Hanoi area
3-5 stars hotels typical
Evaluation Criteria
Evaluation time
Hacinco
- Business results
Periodically monthly and
- Complaint situation
summarizing and
adjusting after 6 months
A25
- Increase business results
Monthly
- Customer growth
Candle Hanoi
- Measuring satisfaction level
Monthly
- Value of customer's contribution
to the hotel
Mường Thanh
- The increase in the number of weekly
customer databases
- Customer conversion rate
- The
effectiveness of the
implementation of interactive
channels
- Customer
satisfaction
and
economic value contribution
- Weekly revenue
JW Marriott Hanoi
- Customer knowledge
Perform daily. At the end
- Customer satisfaction
of each day, each
- Frequency of repeat purchases by department must make a
customers
report and share it with
- Value of customer contribution
the manager's module at
- Turnover of the day
5pm.
Source: Interview results of manager
3.3. Quantitative research results on factors affecting the implementation of
customer relationship management of 3 - 5 star hotels in Hanoi
3.3.1. Descriptive statistical analysis of the study sample
3.3.2. The results of evaluating the reliability of the scale
3.2.2.1.
20
The processing results show that the Cronbach alpha coefficients of all 6
factors have Crobach alpha coefficients in the range 0.673 to 0.851. On the
other hand, the variable correlation coefficient - the sum of all the scales is
greater than 0.3, so all 35 observed variables of the scales in the research model
to ensure the reliability and meet the requirements. for further in-depth analysis.
3.3.3. The results of exploratory factor analysis EFA
3.3.3.1. EFA analysis results for independent variables/explanatory variables
The first rotation of the principal components matrix shows that the observed
variable HT5 is excluded because this observed variable belongs to 2 components, the
author proceeds to remove the variable HT5 and perform the second EFA.
The results of running EFA show that the main component matrix table has
stabilized, from 27 observed variables that have been grouped into 6 main
components as follows:
- Factor 1: includes 6 observed variables VH1, VH5, VH3, VH6, VH2 and
VH4, this factor is named corporate culture and denoted as F1_VH
- Factor 2: includes 4 observed variables CL1, CL4, CL3 and CL2 This
factor is named CRM Strategy and denoted by F2_CL
- Factor 3: includes 5 observed variables including HT2, HT3, HT6, HT4 and
HT1, this factor is named Technology infrastructure and denoted by F3_Technology
infrastructure
- Factor 4: includes 4 observed variables CS2, CS3, CS1 and CS4 named
Database and denoted by F4_CS
- Factor 5: includes 4 observed variables QT1, QT2, QT4 and QT3 named
Business Process and denoted as F5_QT
- Factor 6: includes 4 observed variables, CK2, CK3, CK1 and CK4, this
factor is named Leadership commitment and denoted as F6_CK
These 6 factors have a total explanatory variance of 60.708% > 50% and a
stop Eigenvalue = 1,081 > 1. These numbers indicate that it is appropriate to use
the EFA method, the observations produced 6 main factor. All observed variables
were analyzed using Varimax rotation with cut-off 0.5.
3.3.3.2. EFA analysis results for successful CRM implementation variable
The EFA exploratory factor analysis for customer loyalty factor was also
satisfactory with KMO index = 0.624 > 0.5, with a total explained variance of
53,936% > 50% and a stop point Eigenvalue = 1.618 > 1. These numbers indicate that
it is appropriate to use the EFA method, the observations generated a key factor. All
observed variables were analyzed using Varimax rotation with cut-off 0.5.
3.3.3.3. EFA analysis results for the variable Loyalty
The EFA exploratory factor analysis for the customer loyalty factor was
also satisfactory with the KMO index = 0.612 > 0.5, the total explained variance
was 53,980 % > 50% and the Eigenvalue stop = 1.619 > 1. These numbers
indicate that it is appropriate to use the EFA method, the observations generated a
21
key factor. All observed variables were factored using Varimax rotation with cutoff 0.5. 3.3.4. Correlation analysis results
The absolute r correlation coefficients of the variables in the correlation
coefficient matrix table are in the range [0.22-0.571], proving that the variables are all
correlated with each other. The variables in the model are all correlated and
statistically significant with very small sig values (all sig < 0.05).
3.3.5. Model estimation results of factors affecting successful CRM implementation
3.3.5.1. Estimation results of the weight value of the model
The results from the estimation table of multiple linear regression models
by the Enter method show that all 6 factors have a statistically significant
influence on successful CRM implementation, which are the following factors:
Leadership commitment, strategy CRM strategy, business processes, hotel
culture, IT infrastructure and finally the database element. This means that all 06
factors are statistically significant (with 95% confidence) in the research model.
Thus, all 6 initial hypotheses are accepted.
The regression model to evaluate the impact of factors on the successful
CRM implementation of the hotel is rewritten as follows:
F7_TC = -0.341 + 0.309*F1_VH + 0.257*F2_CL + 0.165*F3_HT +
0.089*F4_CS+ 0.152*F5_QT + 0,158*F6_CK
The results of multiple linear regression model analysis show that there are
6 factors that all have a positive and positive impact on successful CRM
implementation. The degree of influence of each of these factors on successful
CRM implementation of customers. The hotel is not the same, but each different
factor has different intensity of impact.
3.3.5.2. Evaluate the fit of the linear regression model
The analysis results show that R2 = 0.48 and adjusted R2 = 0.465 mean
that nearly 48% of the variation in hotel CRM implementation success is
explained by 6 independent variables included in the model. research.
3.3.5.3. Check for multicollinearity based on variance exaggeration index VIF
Variance inflation factor (VIF) of all 6 independent variables in the model
is much lower than 2 (see Coefficient table)-> This proves that there is no
multicollinearity in the model. model the factors that influence successful CRM
implementation, and the model is built on the template and can be generalized
and used later.
3.2.1.6. Results of model estimation of the influence of successful CRM
implementation on customer loyalty
Successful CRM implementation also has a statistically significant and
positive effect on customer loyalty, the regression weight is 0.598 > 0 and the
significance level is sig = 0.000 < 0.05. The regression coefficient is positive and
significant, which confirms that the initial hypothesis H7 is accepted.
22
Since the model for the influence of successful CRM implementation on loyalty
is a single regression model, there is no phenomenon like multicollinearity (because
there is only one independent variable), so the assumptions about the squared method
smallest (OLS) is satisfied.
3.4. Overall assessment of the current situation of customer relationship
management of 3 -5 star hotels in Hanoi
3.4.1. Successes and causes
3.4.1.1. Success
- Human factors:
Top of management: Most leaders are aware of the importance of CRM
implementation.
CRM strategy: CRM implementation helps hotels approach and communicate
with customers more effectively and systematically. CRM strategic goals are clearly
defined by hotels based on business strategy and customer strategy.
Hotel culture: Every hotel is very successful with building a hotel culture
based on core values and putting their employees in mind.
- Process factors: Business processes are fully designed, optimized by hotels
and adjusted in line with CRM strategies and processes.
- Technology factors: The hotels all use synchronous technology
infrastructure and constantly invest, upgrade and equip at all departments. In
addition, with the development of technology, hotels have learned to leverage the
power of technology to better manage customer relationships. Hardware and
software systems are always innovated and improved to meet most of the
activities in the hotel's departments.
Customer database is regularly updated, classified and stored. This helps
each hotel have a fairly rich amount of customer data.
3.4.1.2. Reasons for success
Firstly, the hotel market already has strong competition. However, in the
context of the severe impact from the covid-19 pandemic, the competition is
more intense when all hotels are targeting the domestic market.
Second, today, hotel management software is designed to ensure that
customer information is always updated and stored in the database management
system in a systematic and specific manner.
Third, the advancement of science and technology, especially the industrial
revolution 4.0, has brought many opportunities for hotels.
Fourth, the management of the hotel is aware that customers are the most
important, the center of business activities
3.4.2. Limitations and reasons
3.4.2.1. Limitations
- Human factors
23
Top of management: Hotel management may encounter non-cooperation
from employees during CRM implementation.
CRM strategy: Under the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic, CRM
strategies in hotels have changed and adjusted in terms of goals and processes.
Hotel culture: in the process of implementing CRM, each employee's
starting point is different, young employees adapt to technology faster, older
employees will be slower to approach and adapt.
- Regarding the process: there may be conflicts and disagreements in
defining tasks and functions, and limiting the rights and obligations of each
department in implementing CRM.
- About technology: 4 and 5 star hotels have exploited digital technology
applications mainly to advertise via social networks such as Facebook, Twitter or
other websites during online check-in and personalize the experience. customers
through mobile applications are less interested.
Regarding the database, the challenge for hotels is to organize the collection,
storage, processing and analysis to get a comprehensive data source.
3.4.2.2. The cause of the restriction
Objective reasons:
The Covid -19 epidemic has had an unprecedented impact in decades, the
world economy has fallen into recession, and major countries and partners of
Vietnam have been seriously affected.
Vietnam had 58 million mobile social network users as of early 2019, this
number increased to 8 million users compared to the same period last year.
Therefore, hotels must use social media channels to attract attention from users.
Most of the hotel's computer system is connected to the Internet, but it also
leads to many serious risks for computers such as malicious code, hackers...
leading to data loss.
Subjective reasons
Firstly, in order to adapt to the complicated developments of the Covid-19
epidemic, the management of hotels had to plan, actively change and adjust
business strategies.
Second, changing habits is hard work. Their usual mentality is to resist the
change of daily routine.
Third, due to the increasing number of customers and increasingly diverse
and strict demands
Fourth, the technology infrastructure in the hotel has not yet met the
requirements
Fifth, the training content does not have specific content related to
changing mindsets based on the hotel's interests above personal interests, training
the spirit of collaboration and sharing to achieve goals. be of common interest.
24
CHAPTER 4. PROPOSED SOME SOLUTIONS AND COMMENDATIONS
TO COMPLETE CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT OF 3 - 5
STAR HOTEL IN HANOI
4.1. Forecasting the development trend of the 3 - 5 star
hotel market in Hanoi
4.1.1. The context of the 3 - 5 star hotel market in Hanoi
About the opportunity
The fourth industrial revolution with new technological achievements
creates opportunities for Vietnam's tourism to develop in a modern direction.
Although the Covid-19 epidemic will leave a lot of damage and far-reaching
impact on the market, the development outlook of the hotel industry will
remain positive in the long term.
Vietnam is known worldwide as one of the countries that successfully
and effectively responded to the pandemic. According to a representative of
Savills Group, along with the vaccination schedule that is taking place on a
large scale in Europe, the US and many countries around the world, the hotel
segment in Asia may recover in a V-shape.
About the challenge
In the coming period, the world situation will continue to be complicated
and unpredictable, while the domestic economy will still face many difficulties
and potential risks, posing many challenges for sustainable development. That
is the complicated development of the Covid-19 pandemic. Hanoi as the
capital, the political center of the country, the pressure on population,
urbanization process, transport infrastructure, environmental sanitation and
social order and safety have placed on the Hanoi is not a small challenge in the
context of increasing tourists to Hanoi.
4.1.2. Orientation to develop business activities of 3 - 5 star hotels in Hanoi
in the period of 2021 – 2025
According to the 5-year tourism development plan for the period of 2021
- 2025, which was developed by the Hanoi Department of Tourism and issued
by the City People's Committee., when the epidemic is initially controlled, all
policies and actions of the tourism industry must focus on recovering the
domestic tourism market, Hanoi green economy sector. Doing well in domestic
tourism, the capital's tourism industry in particular, and Vietnam in general will
also create more imprints for the international tourism market.
25
4.2. Some solutions to improve customer relationship management of 3 -5
star hotels in Hanoi
4.2.1. Human factor solutions in CRM implementation
4.2.1.1. Enhance top of management commitment to supporting, directing, and
operating the hotel's CRM implementation
Firstly, each leader needs to understand the vision and mission of the
hotel to come up with an appropriate business strategy.
Second, top of management needs to be committed to providing the
necessary resources and budget to implement CRM.
Third, top managers need to pay attention to removing barriers and
obstacles while implementing CRM.
4.2.1.2. Complete hotel culture
Firstly, the customer-centric business strategy orientation needs to be
clearly reflected in the hotel culture.
Second, hotels need to promote the building of a hotel culture that
upholds the spirit of cooperation and sharing in the working process of staff.
Third, the hotel needs to invest time in training to improve staff capacity
and qualifications when participating in CRM implementation.
Fourth, hotels should build working environment and effective
evaluation methods.
4.2.1.3. Complete CRM strategy
Firstly, building a CRM strategy must be based on a business strategy
Second, the CRM strategy must clearly and fully demonstrate the goals
Third, ensure the general consensus from senior leaders to employees
4.2.2. Process solutions
First, ensure business processes are consistent throughout the hotel system.
Second, the hotel needs to find a CRM content model suitable for
business characteristics.
Third, adjust the organizational structure of departments in the hotel to
ensure a favorable coordination mechanism in the process of establishing
relationships and providing products and services to customers
Fourth, set up interactive channels in accordance with customer needs.
When applying CRM, hotel staff will have to follow the process of
approaching customer groups through CRM, not with each customer
Fifth, business processes related to customer interactions are analyzed
and evaluated.
4.2.3. Group of solutions on technological factors
4.2.3.1. Investment in technology infrastructure
Firstly, hotels should continue to invest and upgrade the software system
to support customer management.
Second, hotels need to invest in customer information security systems
4.2.3.2. Solutions to improve database quality: